Function of the kl3403 bus terminal, Cos φ, Sin φ – BECKHOFF DK9222-1209-0007 User Manual
Page 2
I/O
Measurement technology
Application Note DK9222-1209-0007
As a rule, the following are starting points that need to be addressed in order to reduce energy costs:
– reduction in electricity costs: total active energy obtained, reactive power costs and also costs for peak loads
– stabilisation of manufacturing processes and avoidance of production losses
– identification of ‘energy hogs’
– lowering of maintenance costs
– extension of the service lives of electronic and electrical equipment
– cost centre allocation
Both the EL3403 EtherCAT Terminal and the KL3403 Bus Terminal provide the hardware for the analysis and localisation of
energy consumption. In addition to the important data from a three-phase supply network, they also record any energy peaks
occurring over a selectable time period and total up the energy consumption internally, so that different modes of operation or
shifted peak usage times can be judged even after just one production cycle. In addition to a general consideration of energy
efficiency, the quantity of energy used for the production of a particular lot size can be determined in order to adapt the price
per unit accordingly or to optimise manufacturing costs.
Function of the KL3403 Bus Terminal
The KL3403 Bus Terminal enables analysis via the fieldbus of the energy consumption of the connected plant or building
segment or, quite specifically, the key energy data of individual consumers. The voltages of the three phases and neutral can be
measured by directly wiring the individual cables to the terminal. In order to measure current, the current of the three phases
L1, L2 and L3 is fed in via simple current transformers. The measured current and voltage values are output as effective values.
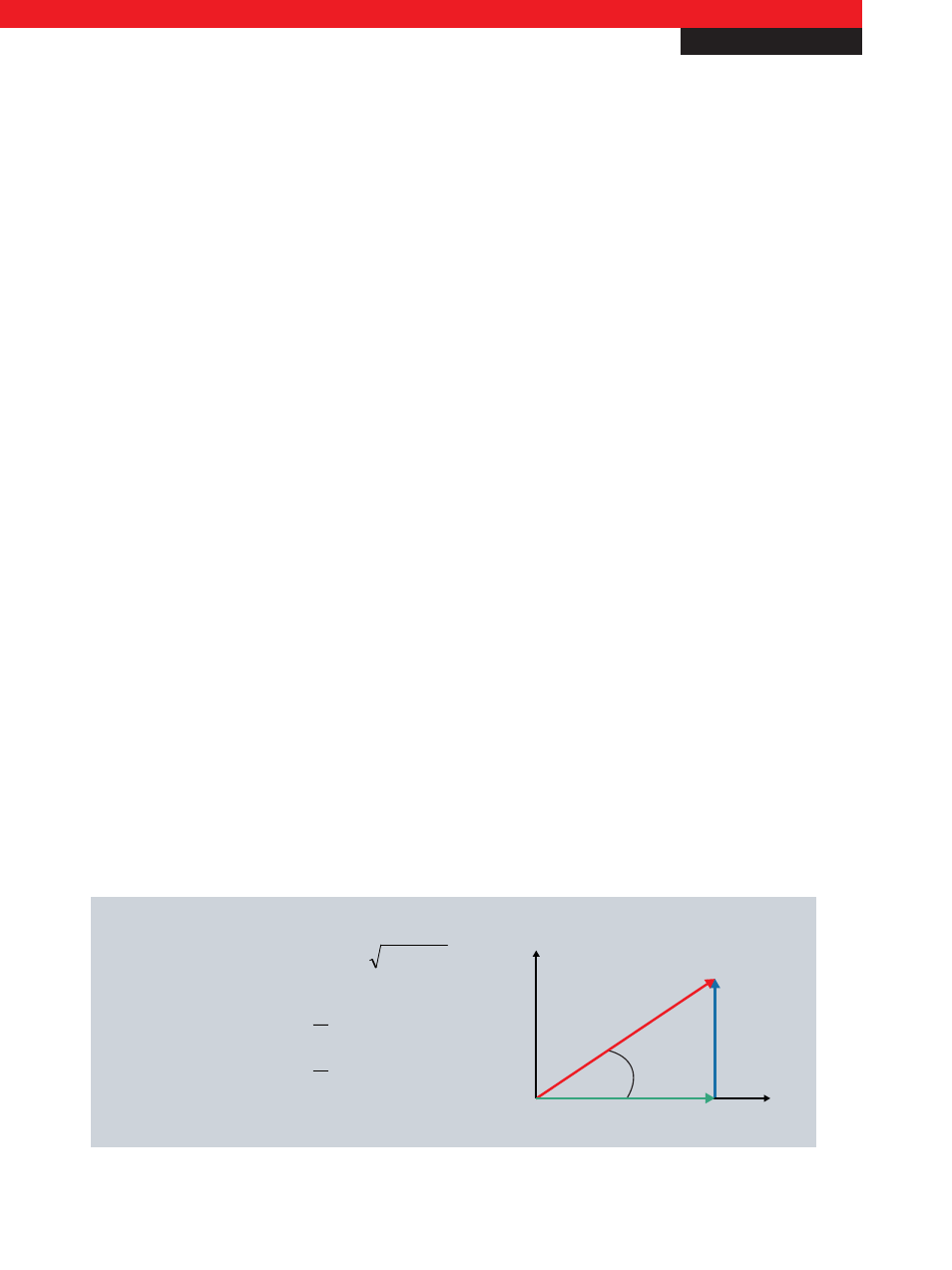
From the effective values for voltage (U) and current (I), the KL3403 calculates the effective power (P), the energy consumption
(W) and the power factor (cos φ) for each phase. The apparent power (S) and the phase shift angle (φ) can be derived from
these values.
Active power
P
Apparent power
S
Reactive power
Q
Active power factor
cos
φ
Reactive power factor
sin
φ
Electric work
W
~ Energy consumption
= U * I * cos
φ
= U
eff
* I
eff
= P
2
+Q
2
= U * I * sin
φ
=
=
= U * I * t
P
S
Q
S
Q
S
P
φ
Fig. 1: Calculation of the important energy consumption variables
New Automation Technology
Beckhoff
2
For application notes see disclaimer on the last page