Remko etf 400, Air dehumidification – REMKO ETF 400 User Manual
Page 4
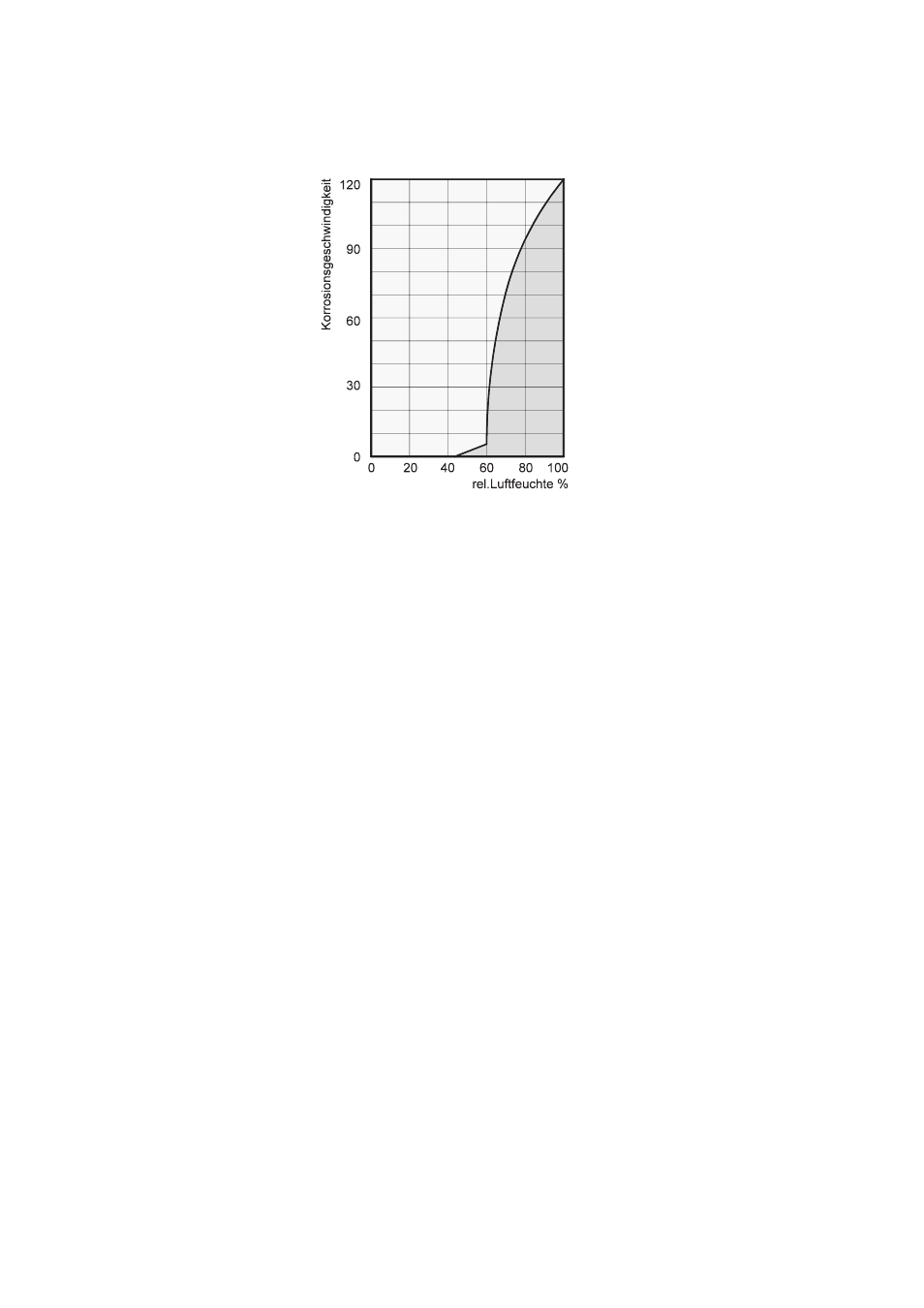
It is evident that the corrosion
rate below 50% relative humidity
(RH) is low, and below 40%
is negligible.
The corrosion rate increases
significantly above 60% RH. This
threshold for damage as the result
of humidity also applies to other
materials, such as powdery
substances, packaging, wood
and electronic units.
Buildings may be dried in a variety
of
1. By heating and
air exchange:
The air in the room is
heated in order for moisture
to be removed and drained
outside. All of the energy that
is involved is lost together with
the moist air that is released.
2. By air dehumidification:
The moist air that is present
within an enclosed space
is continuously dehumidified
according to the condensation
principle.
The correlations occurring when
air is dehumidified are based
on physical laws.
These are depicted here
in graphical form in order
to provide you with a brief
overview of the principles of air
dehumidification.
The use of
REMKO air dehumidifiers
– Even if Windows and doors
are well insulated, water
and moisture are capable
of penetrating even thick
concrete walls.
– The water required
for setting in the production
of concrete, mortar and plaster
etc. may only be diffused after
1-2 months.
– Even moisture trapped
in the masonry after high-
water or a flood is released very
slowly.
– The same is also true of moisture
contained in for example stored
materials.
The moisture (water vapour)
released from parts of a building
or materials is absorbed
by the surrounding air. As a result,
the moisture content increases,
which ultimately gives rise
to corrosion, mould, rot, peeling
of paint and other unwanted
damage.
By way of example, the diagram
shows the corrosion rate of metal
in different levels of humidity.
Air dehumidification
With regard to energy
consumption, air dehumidification
has one distinct advantage:
Energy expenditure is limited
exclusively to the air volumes
present., The mechanical heat that
is released by the dehumidification
process is fed back into the room.
Under normal use, the air
dehumidifier uses approximately
25% of the energy that
is required for the "heating
and ventilating" principle.
Relative humidity
Our ambient air is a gaseous
mixture which always contains
a certain volume of water
in the form of water vapour.
This volume of water is specified
in g per kg of dry air (absolute
moisture content).
1m
3
of air weighs approx. 1.2 kg at
20°C
Depending on the temperature,
each kg of air is only capable
of absorbing a certain volume
of water vapour. Once this
capacity has been reached, the
air is referred to as "saturated"
and has a relative humidity (RH)
of 100%.
Relative humidity is understood
to mean the ratio between
the current volume of water
vapour in the air and the maximum
possible volume of water vapour
at the same temperature.
The ability of the air to absorb
water vapour increases
as the temperature rises.
I.e. the maximum possible
(absolute) water content becomes
greater as the temperature rises.
4
REMKO ETF 400