Client-initiated tunneling mode – H3C Technologies H3C SecPath F5020 User Manual
Page 34
26
4.
The LAC sends the authentication information (username and password) to its RADIUS server
(RADIUS server A) for authentication.
5.
RADIUS server A authenticates the user and returns the result.
6.
If the user passes the authentication and the user is determined to be an L2TP user according to the
username or the ISP domain to which the user belongs, the LAC initiates an L2TP tunneling request
to the LNS (Device B).
7.
If tunnel authentication is needed, the LAC and LNS send CHAP challenge messages to
authenticate each other before successfully establishing an L2TP tunnel.
8.
The LAC and LNS negotiate to establish L2TP sessions.
9.
The LAC sends PPP user information and PPP negotiation parameters to the LNS.
10.
The LNS sends the authentication information to its RADIUS server (RADIUS server B) for
authentication.
11.
RADIUS server B authenticates the user and returns the result.
12.
In the case of successful authentication, the LNS authenticates the PPP user by sending a CHAP
challenge if mandatory CHAP authentication is configured on the LNS. The PPP user replies with a
CHAP response.
13.
The LNS sends the authentication information to RADIUS server B for authentication.
14.
RADIUS server B authenticates the user and returns the result.
15.
If the user passes the authentication, the LNS assigns a private IP address to the remote system
(Host A).
16.
The PPP user can access internal resources of the enterprise.
In steps 12, 15, and 16, the LAC forwards packets for the remote system and LNS. Host A and LAC
exchange PPP frames, and the LAC and LNS exchange L2TP packets.
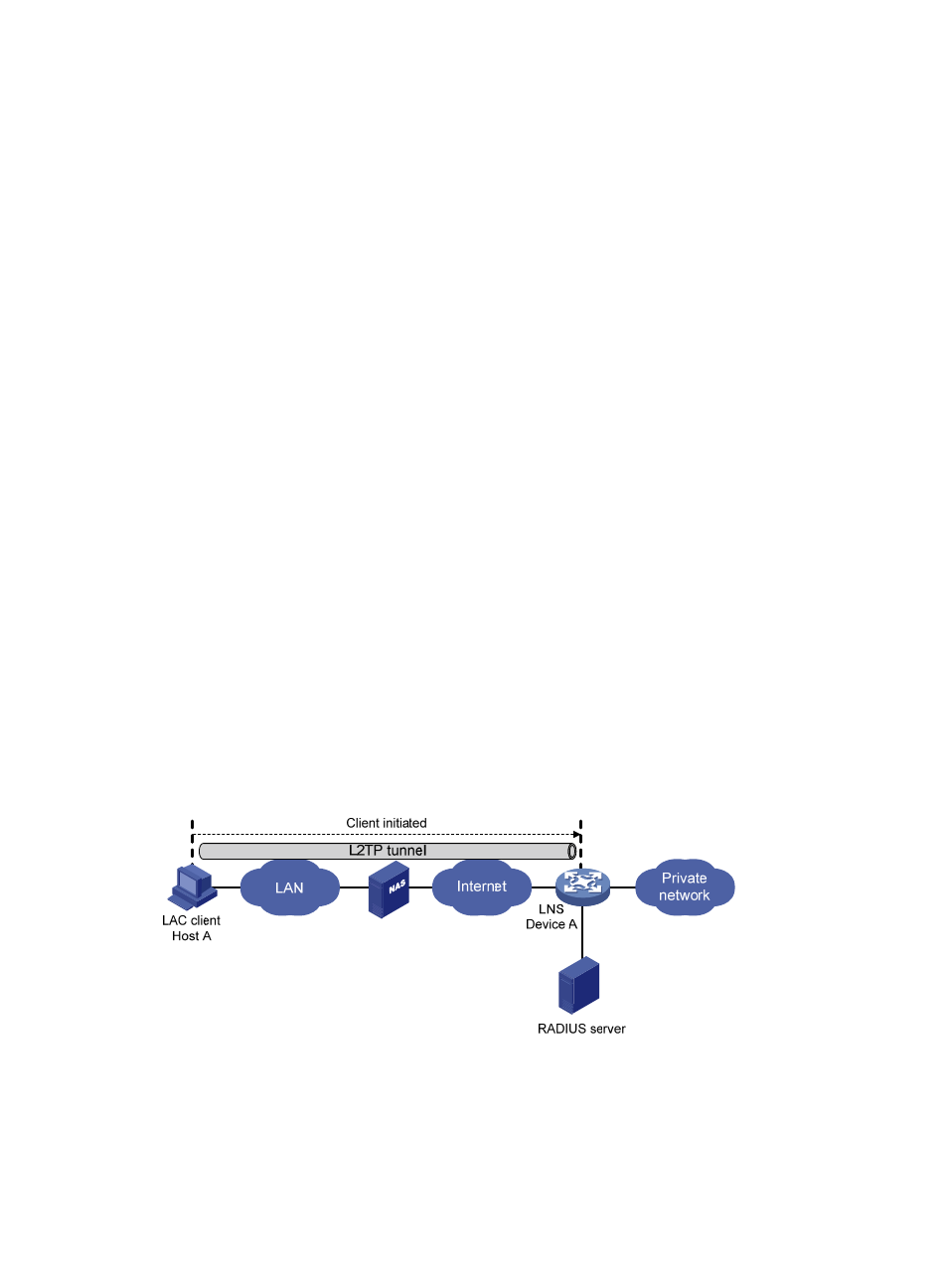
Client-initiated tunneling mode
As shown in
, after being permitted to access the Internet, a remote system running L2TP (LAC
client) directly initiates a tunneling request to the LNS without any dedicated LAC device. The LAC client
has a public IP address to communicate with the LNS through the Internet.
Figure 9 Client-initiated tunneling mode
A client-initiated tunnel has the following characteristics:
•
A client-initiated tunnel has higher security because it is established between a remote system and
the LNS.
•
The remote system must support L2TP and can communicate with the LNS. This causes poor
expandability.