3 voltage dividers – Measurement Computing PC104-DIO48 User Manual
Page 19
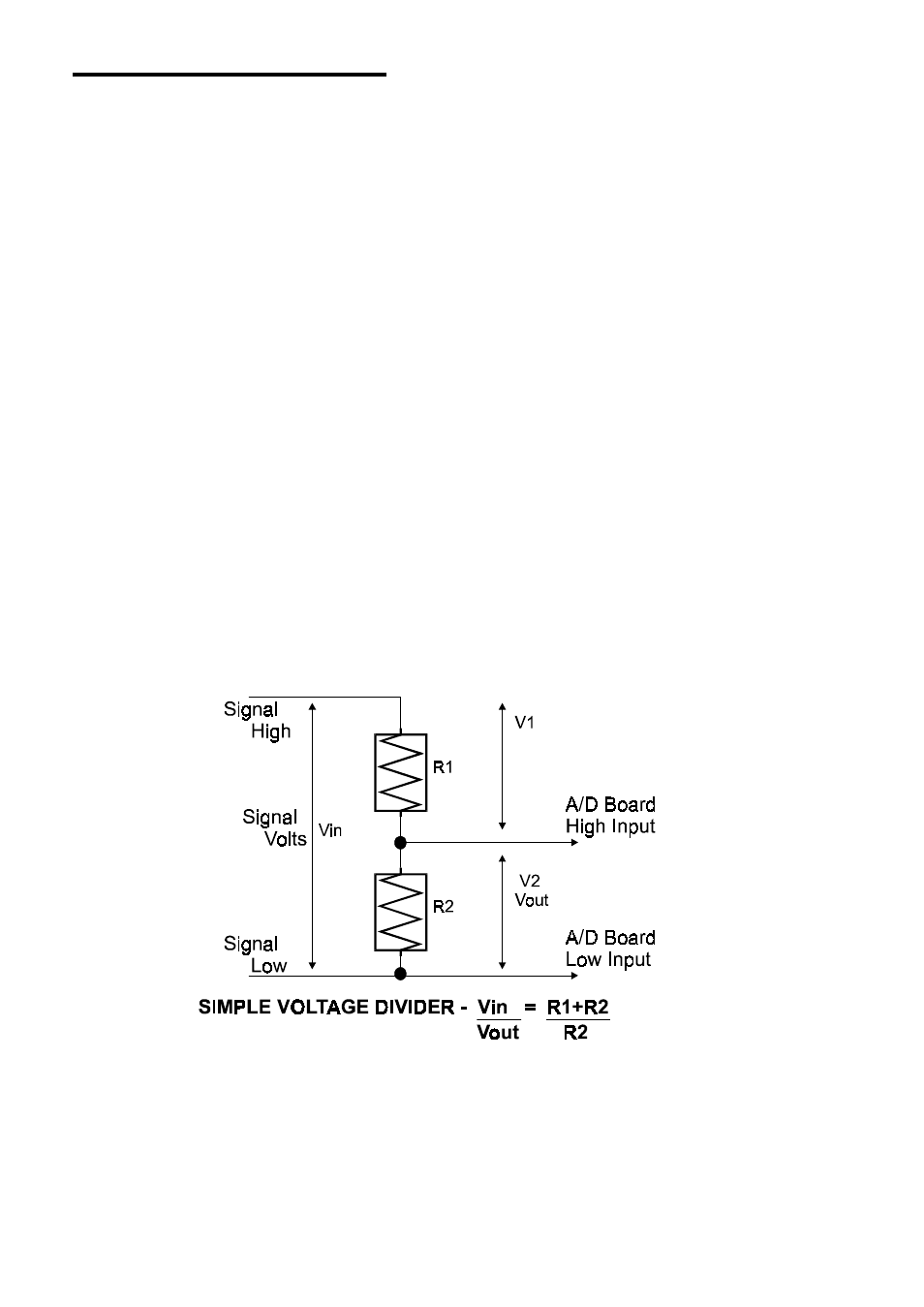
5.3 VOLTAGE DIVIDERS
If you wish to measure a signal which varies over a range greater than
the input range of a digital input, a proper voltage divider will drop the
voltage of the input signal to a safe level.
A voltage divider takes advantage of Ohm's law, which states,
Voltage = Current * Resistance
and Kirkoff's voltage law which states,
The sum of the voltage drops around a circuit will be equal to
the voltage drop for the entire circuit.
Implied in the above is that any variation in the voltage drop for the
circuit as a whole will have a proportional variation in all the voltage
drops in the circuit.
In a voltage divider, the voltage across one of the resistors in a circuit is
proportional to the ratio of that resistor to the total resistance in the
circuit.
Therefore, you setup a voltage divider choosing two resistors with the
proper proportions relative to the full scale of the voltage input and the
maximum signal voltage to the board.
Figure 5-2. Voltage Divider
15