Implementation, Negotiation, Functions – H3C Technologies H3C SR8800 User Manual
Page 30: Configuring ppp
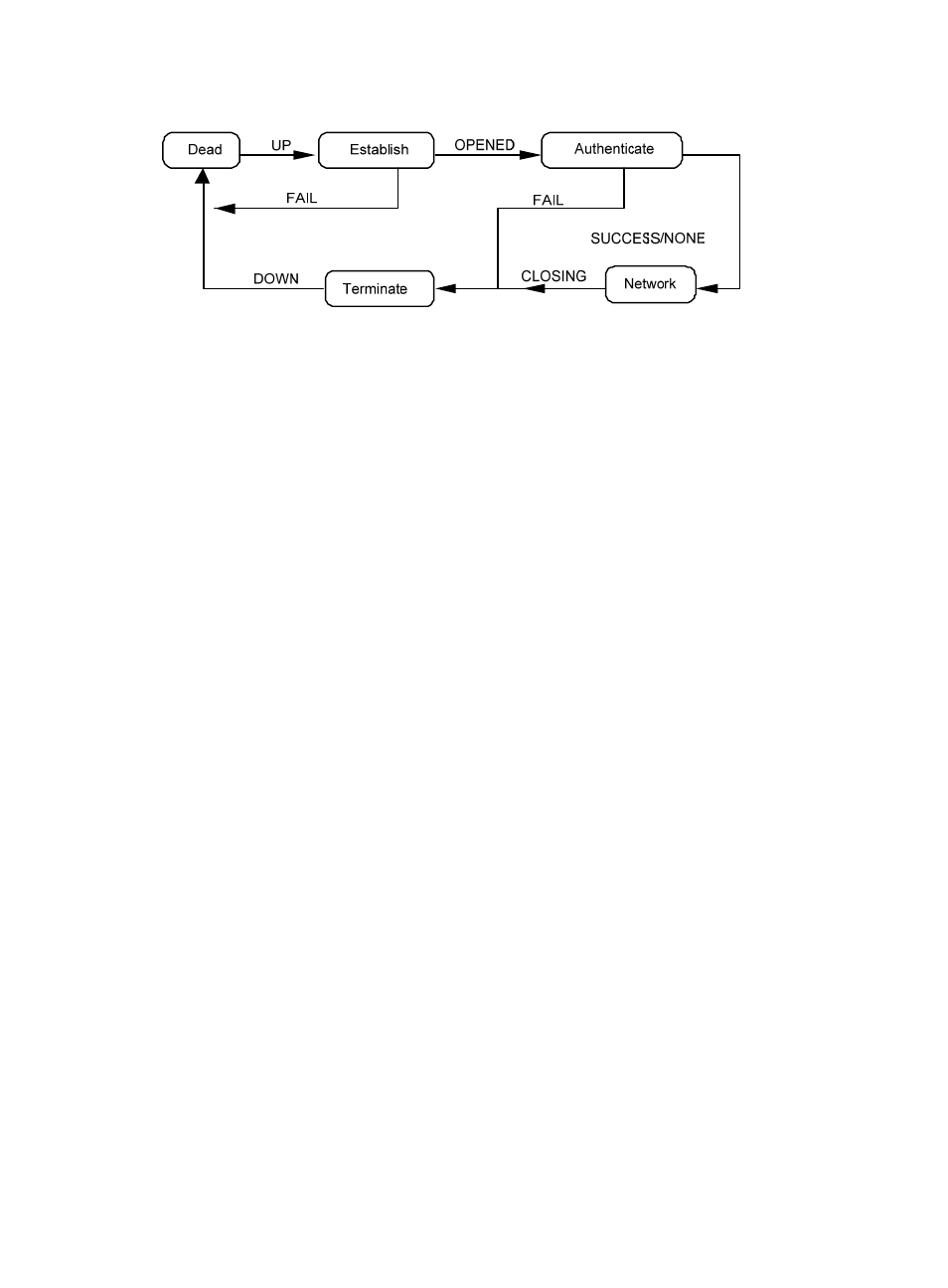
22
Figure 9 PPP operation flow chart
MP
Multilink PPP (MP) provides an approach to increasing bandwidth. It allows multiple PPP links to form an
MP bundle. After receiving a packet that is larger than the minimum packet size for fragmentation, MP
segments the packet into fragments and distributes them over multiple PPP links to the remote end. After
the remote end receives these fragments, it assembles them into a packet and passes the packet to the
network layer.
Implementation
You can implement MP using MP-group interfaces. MP-group interfaces are designed only for MP. On an
MP-group interface, only one bundle is allowed. In addition, MP-group interfaces do not support bundle
creation based on the peer user name.
Negotiation
MP negotiation involves two processes: first LCP negotiation, and then NCP negotiation.
•
LCP negotiation, during which both sides negotiate the common LCP parameters and check whether
their peer interface is working in the MP mode. If not, the LCP negotiation fails. After the LCP
negotiation succeeds, NCP negotiation starts.
•
NCP negotiation, which are performed based on the NCP parameters of the MP-group interface.
NCP parameters on physical interfaces are not effective.
MP link is established after the NCP negotiation succeeds.
Functions
MP functions to:
•
Increase bandwidth
•
Perform load sharing
•
Perform backup
•
Decrease transmission delay through fragmentation
Configuring PPP
Configuring PPP
To configure PPP: