Casio ALGEBRA FX2.0 Advanced Statistics Examples 1 User Manual
Page 23
23
examples
○ ○ ○ ○ ○
Example
A psychologist is studying pattern recognition skills under four
laboratory settings. In each setting, a fourth-grade child is given a
pattern recognition test with ten patterns to identify. In setting A, the
child is given praise for each correct answer and no comment about
wrong answers. In setting B, the child is given criticism for each
wrong answer and no comment about correct answers. In setting C,
the child is given no praise or criticism but the observer expresses
interest in what the child is doing. In setting D, the observer remains
silent in an adjacent room watching the child through a one-way
mirror. A random sample of fourth-grade children was used, and each
child participated in the test only once. The test scores (number
correct) for each group follow. Find F
0.01
, the critical values for an
α
=
0.01 level of significance. Does the test indicate we should accept or
reject the null hypothesis?
Group A = {10, 8, 7, 9, 11}
Group B = { 2, 5, 3, 3, 4}
Group C = { 9, 3, 7, 8, 5, 6}
Group D = { 5, 7, 3, 6, 7}
Procedure
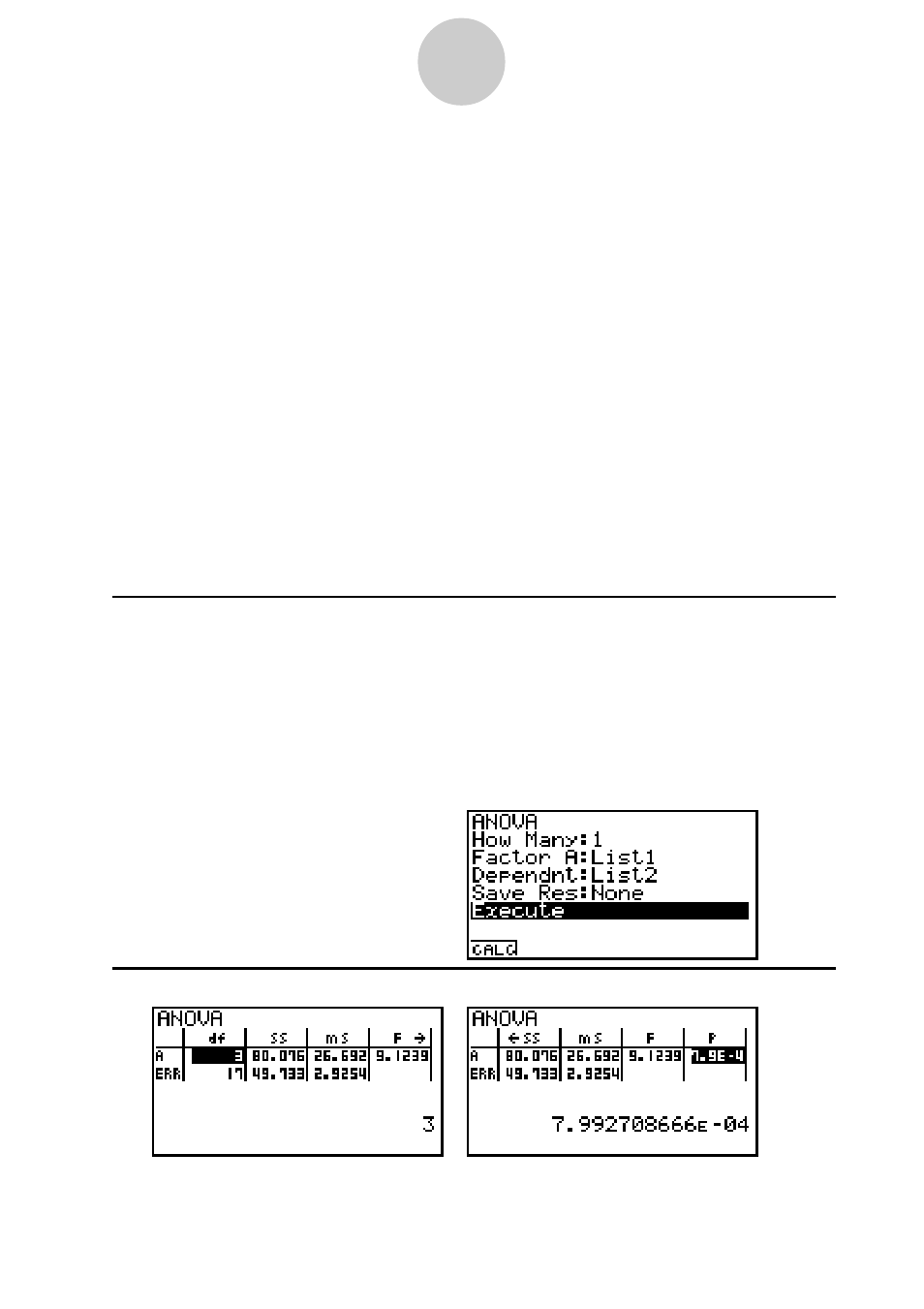
1
m
STAT2
2 b
wbwbwbwbwcwcwcwcwcw
d
wdwdwdwdwdwewewewewew
e
ba
wiwhwjwbbwcwfwdwdwew
j
wdwhwiwfwgwfwhwdwgwhw
3
3
(TEST)
f
(ANOVA)
4
1
(1)
c
1
(LIST)
b
wc
1
(LIST)
c
wc
1
(None)
c
5
1
(CALC)
Result Screen
Since P = 7.992708666e-4 < 0.01 (level of significance), we can reject the null hypothesis
and conclude that the laboratory setting affects the mean score.