Casio ALGEBRA FX2.0 series User Manual
Page 3
1-2
Using the DIFF EQ Mode
6. Specify variables to graph or to store in LIST.
Press 5(SET) and select c(Output) to display the list setting screen.
x
,
y
,
y
(1)
,
y
(2)
, .....,
y
(8)
stand for the independent variable, the dependent variable, the
first order derivative, the second order derivative, ....., and the eighth order derivative,
respectively.
1st, 2nd, 3rd, ...., 9th stand for the initial values in order.
To specify a variable to graph, select it using the cursor keys (
f, c) and press
1(SEL).
To specify a variable to store in LIST, select it using the cursor keys (
f, c) and
press 2(LIST).
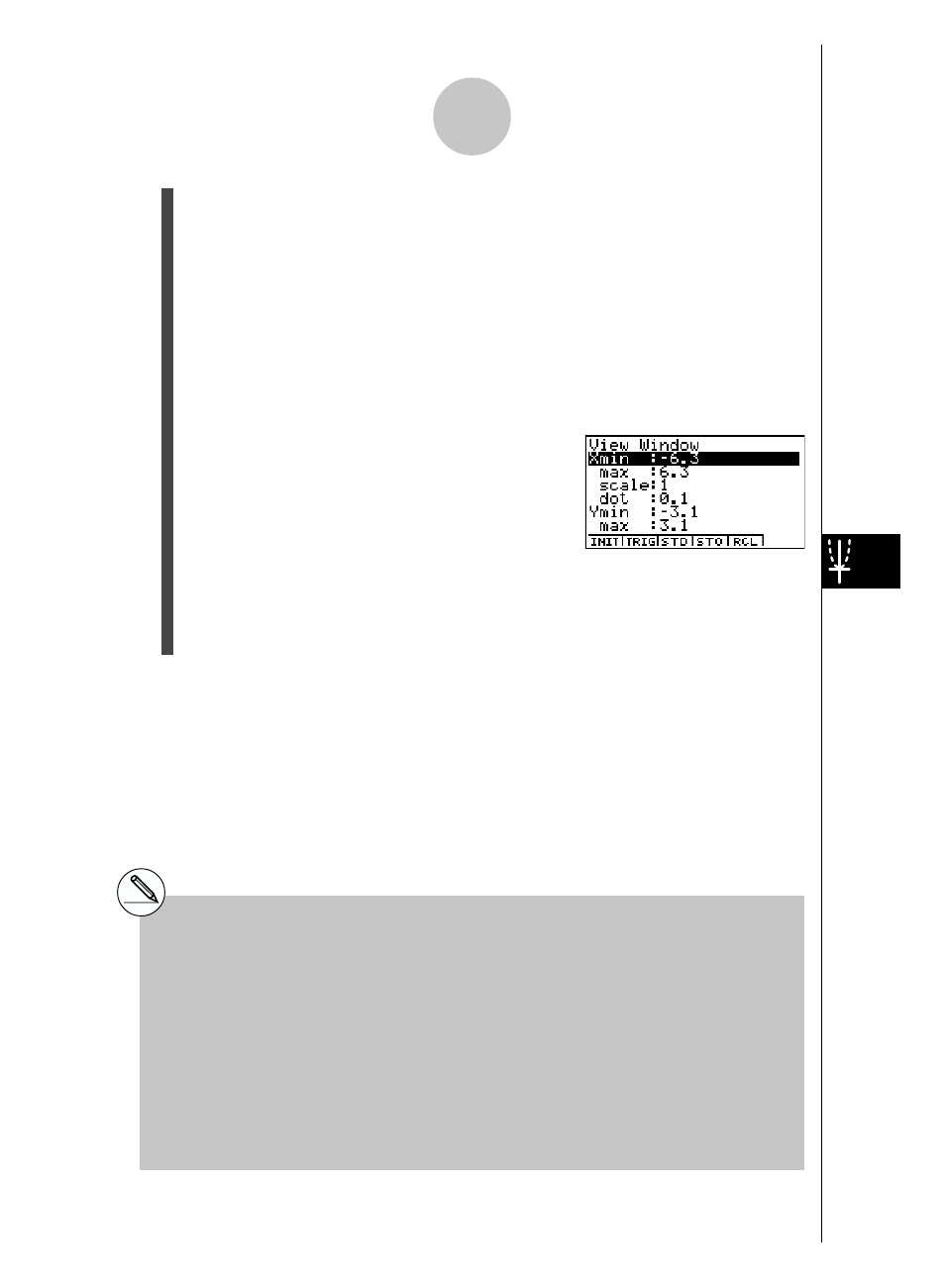
7. Press !K(V-Window) to display the V-Window setting screen. Before you solve a
differential equation, you need to make V-Window settings.
Xmin …
x
-axis minimum value
max …
x
-axis maximum value
scale …
x
-axis value spacing
dot … value corresponding to one
x
-axis dot
Ymin …
y
-axis minimum value
max …
y
-axis maximum value
scale …
y
-axis value spacing
8. Press 6(CALC) to solve the differential equation.
• The calculated result is graphed or stored in the list.
# Only the slope fields are displayed if you do
not input initial values or if you input the wrong
type of initial values.
# An error occurs if you set SF to zero and you
do not input the initial values, or if you input
the initial values inappropriately.
# You are advised to input parentheses and a
multiplication sign between a value and an
expression in order to prevent calculation
errors.
# Do not confuse the - key and the - key.
A syntax error occurs if you use the - key
as the subtraction symbol.
# An error occurs if you input variable
y
in the
function
f
(
x
). Variable
x
is treated as a
variable. Other variables (A through
Ζ
,
r
,
θ
,
excluding X and Y) are treated as constants
and the value currently assigned to that
variable is applied during the calculation.
# An error occurs if you input variable
x
in the
function
g
(
y
). Variable
y
is treated as a
variable. Other variables (A through
Ζ
,
r
,
θ
,
excluding X and Y) are treated as constants
and the value currently assigned to that
variable is applied during the calculation.