Flowserve 1400 Valtek Logix User Manual
Page 16
46-16
Flowserve Corporation, Valtek Control Products, Tel. USA 801 489 8611
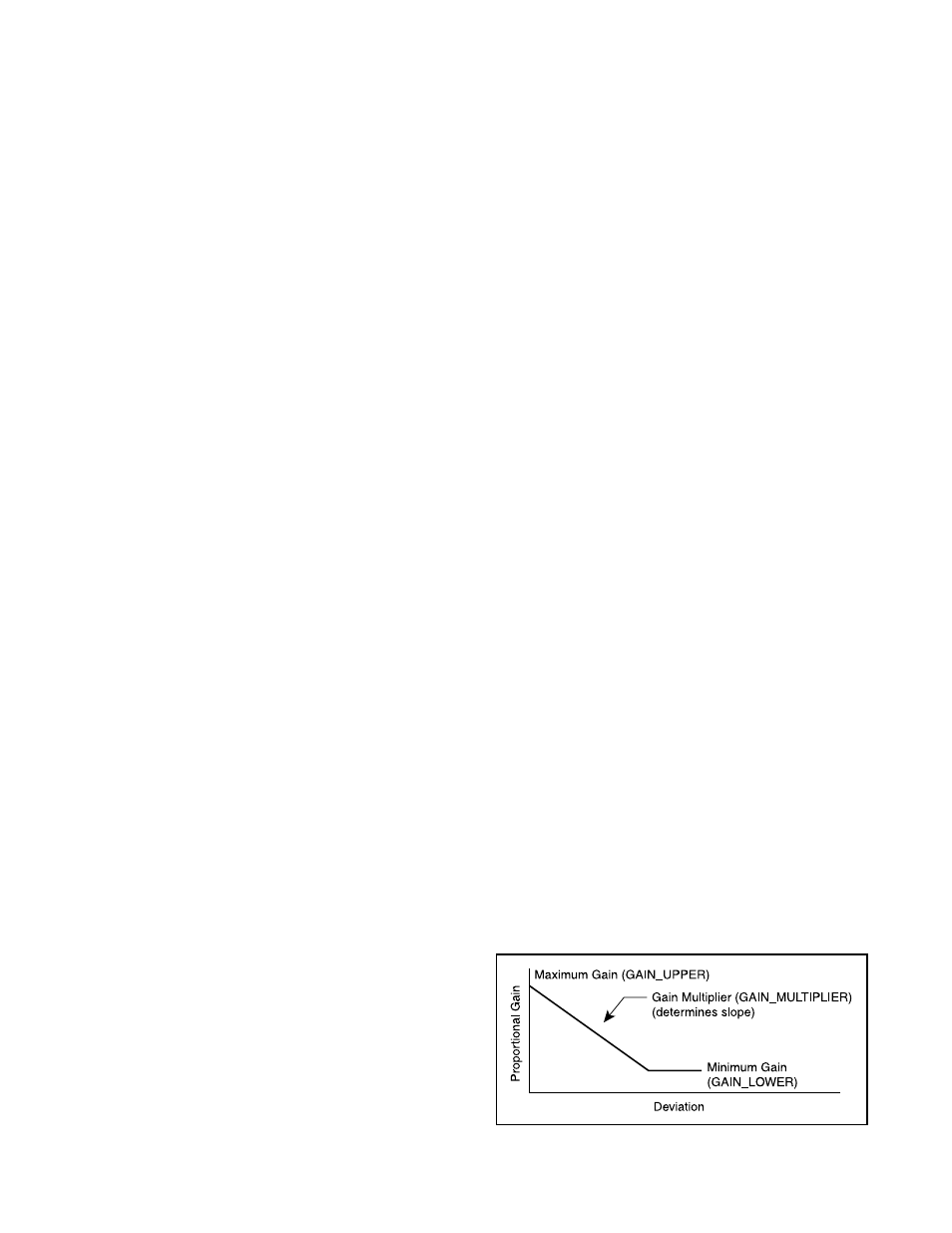
Figure 16: Gain Effect Diagram
Centering the rotary linkage
To determine whether the rotary linkage is centered in the
100 degrees range move the valve to the fully closed
position. The slot in the take-off arm has enough clear-
ance around the roller pin to move the follower arm
slightly. At this position, move the follower arm within the
slot clearance. If the valve does not respond, linkage
adjustment is necessary. Repeat this test at the fully
open position.
To adjust the stem position linkage, use the AD_RAW_FB
variable. With the valve in its mechanical fail position
(i.e. no pressure applied), slightly move the follower arm
while watching the A/D feedback. If the number does not
change, the arm is not centered in the electrical range.
(The number will bounce 1 or 2 counts due to noise at a
fixed position and should not be considered a change, it
should move greater than 10 to 20 counts if the linkage
is centered correctly). Rotate the take-off arm, if neces-
sary, to bring the linkage in range. This procedure is only
necessary on a rotary mounting. For linear mountings,
the red LED will blink if you exceed 65 degrees travel.
Refer to the
Calibration section for further information on
stroke calibration errors.
To view the feedback variable use the FB configurator of
view the AD_RAW_FB in the transducer function block.
NOTE: To update the AD_RAW_FB variable, the ‘Enable
Diagnostic Variable Access’ selection must be enabled in
TEST_MODE of the transducer block.
Calibration
Re-Cal
Re-Cal is a method by which the valve can be stroke
calibrated without using the fieldbus configurator.
NOTE:The transducer function block must be in OOS (out
of service) mode for the Re-Cal button to be operational.
Re-Cal only affects position calibration. Any previous
configuration or stored information is not affected.
Position 0% Calibration Flag in
CALIBRATE_FLAGS
During stroke calibration, the Logix 1400 digital posi-
tioner checks to see if the linkage is placing the stem
position sensor in range. If the valve stroke causes stem
position measurement to go out of range in the closed
position, a
Position 0% Flag will be generated. The valve
stem will stop in the closed position and the red LED will
blink. Linkage must be adjusted to bring the sensor in
range.
Special LED indication: If the linkage is out of
range, the LEDs can be used as an adjustment guide. The
LED will change from a red to yellow when the linkage is
brought into range.
Position 100% Calibration Flag in
CALIBRATE_FLAGS
During stroke calibration, the Logix 1400 digital posi-
tioner checks to see if the linkage is placing the stem
position sensor in range. If the valve stroke causes stem
position measurement to go out of range in the open
position, a
Position 100% Flag will be generated. The
valve stem will stop in the open position and the red LED
will blink. Linkage must be adjusted to bring the sensor
in range.
Special LED indication: If the linkage is out of
range, the LEDs can be used as an adjustment guide. The
LED will change from a red to yellow when the linkage is
brought into range.
Position Span Flag in
CALIBRATE_FLAGS
Position span is a check during stroke calibration to
verify that the valve stem moved. The algorithm waits to
see if no movement is detected when the valve is
automatically stroked open. Anything which could pre-
vent the valve from stroking will generate a
Position Span
error (no supply pressure, malfunctioning spool valve).
Control and Tuning
Setting P + I Parameters
Using the configurator, you can set individual tuning
parameters. A few key points are mentioned below. (See
Figure 17.)
GAIN_UPPER, GAIN_LOWER, and GAIN_MULT: These
three parameters are related by the following formula.
Proportional Gain =
Maximum Gain - Ideviation| x Gain Multiplier
If Proportional Gain < Minimum Gain,
then Proportional Gain = Minimum Gain
This algorithm allows for quicker response to smaller
steps yet stable control for large steps. Setting the gain
multiplier to zero and max gain = min gain results in a
typical fixed proportional gain.
The higher the gain multiplier, the larger the required
deviation before the gain increases. Default values
upon initiating a RESET to factory defaults (under