Fig.17, Fig.18, Fig.16 – Sealey POWERMIG3525 User Manual
Page 6: Powermig controls, Welding principles
6.3.2 The gas cup is a friction fit onto the torch and can be pulled off with a
twisting action in either direction. Unscrew the copper contact tip using
the maintenance spanner provided across the 6mm flats of the contact
tip. It has a conventional right hand thread.
6.3.3 To feed the wire through to the torch it will be necessary to power up
the welder.
6.3.4 The wire is required to feed through the full length of the torch cable
and if possible it should be laid out straight. If this is not possible the
cable should not be coiled at a diameter of less than 1mtr.
6.3.5 Check that the welder POWER switch is in the 'OFF' position, and that
the earth clamp is isolated and away from the torch tip.
6.3.6 Connect the welder to the mains power supply and set the voltage
switch to “1”.
6.3.7 Using the wire feed speed control (welding current), set the knob to
position 5 or 6, (the higher the number the faster the speed). See
figs.17 & 18. Keep the torch cable as straight as possible and press the
torch switch to feed the wire through to the torch.
6.3.8 When the wire has fed through, switch welder off, unplug from mains.
6.3.9 Replace contact tip and gas cup. Cut wire so that it is protruding 1/4”
from the cup.
wARNING! During these operations the wire is live and subject to
mechanical stress; therefore, if adequate precautions are not taken the
wire could cause hazardous electric shock, injury and striking of electric
arcs. Do not direct the torch tip towards parts of the body and keep the
torch away from the gas bottle.
6.4 SETTING WIRE TENSION.
IMPORTANT: You must set the correct tension, too little or too much
tension will cause problematic wire feed and result in poor welding.
6.4 .1. Tension between rollers is checked by slowing down the wire between
your fingers. If the top feed rollers skid the tension is correct. Use as
low a tension as possible, too high a tension will deform wire and result
in a blown fuse on the printed circuit board. Adjust tension by turning the
pressure knob as shown in fig.10.
6.5
CLUTCh ADJUSTMENT
It is essential that the clutch is adjusted correctly. Once the wire is fed
through the torch, switch on the machine and set the wire speed and
voltage switch to maximum. Depress the torch switch and release
quickly. If spool overruns it indicates that the clutch is too loose. Tighten
the reel clutch adjuster (located in the centre of the reel holder (fig.9),
and test the machine as above until the wire stops over running.
WARNING! DO NOT over tighten the clutch as this will cause
wire feed problems.
6.6
WIRE FEED CONTROL
6.6.1 The wire feed speed can be set using the 'Welding Current' control
situated on the front panel of each welder. (See figs.17 & 18). Use this
rotary control to set the basic wire feed speed required by the welding
parameters of the weld to be executed.
fig.16
Original Language Version
© Jack Sealey Limited
7. POWERMIG CONTROLS
fig.17
7.1
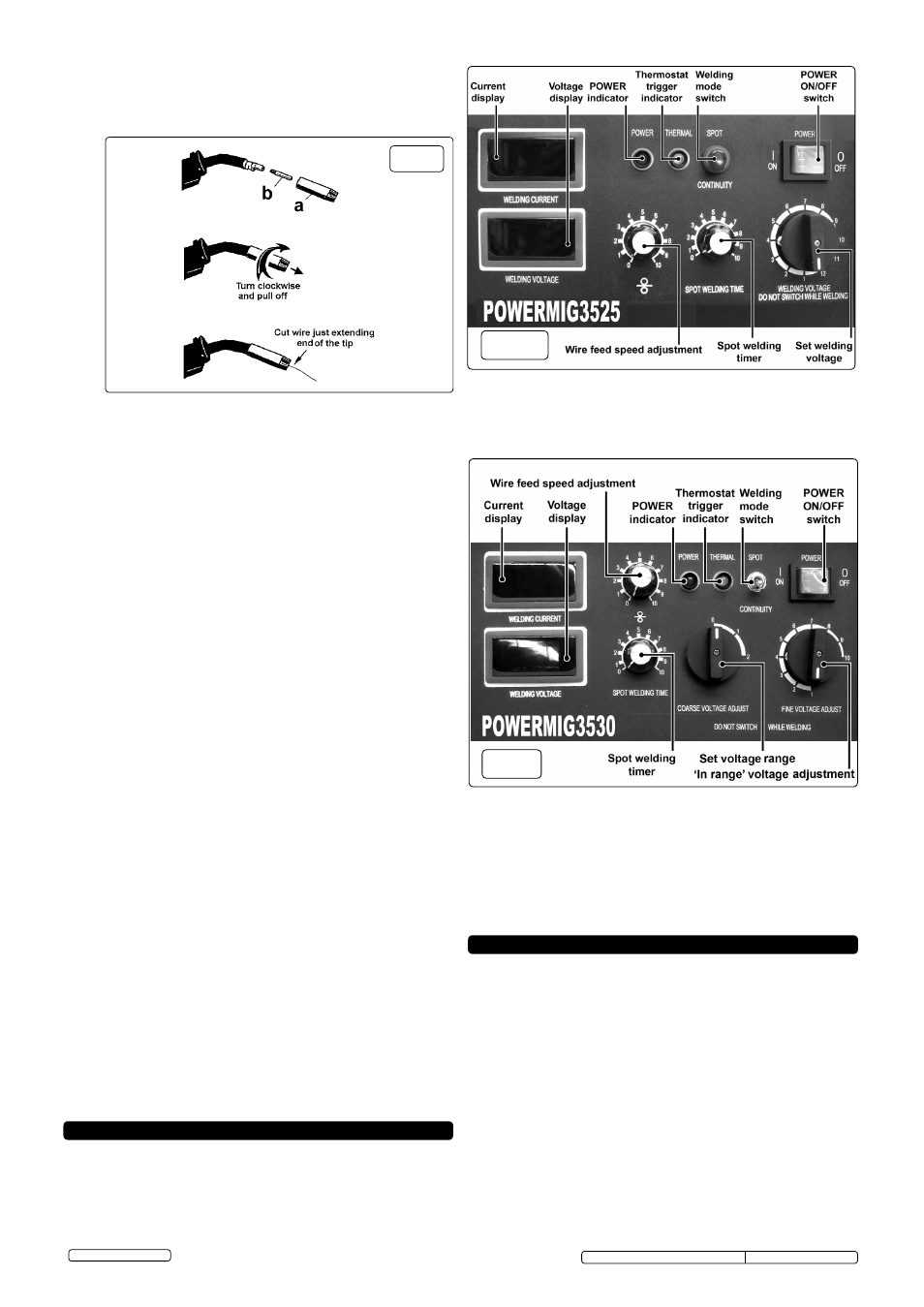
CONTROLS - POWERMIG 3525 & 3530
7.1.1 Fig.17 illustrates the main panel controls for
Powermig3525. Note that
this model has a single voltage adjustment switch and one socket on
the lower half of the front panel for the connection of the welding current
return cable (Earthing Clamp).
7.2
Fig.18 illustrates the main panel controls for
Powermig3530. Note that
this model has two voltage adjustment switches, one for coarse
adjustment and one for fine adjustment. There is a socket on the lower
half of the front panel for the connection of the welding current return
cable (Earthing Clamp).
fig.18
7.3
SYSTEM PROTECTION
To provide a level of protection against faults such as short circuits or
overheating, various safety features are incorporated into the welder
unit. The power input is protected by a 3 Amp fuse located in the
upper part of the wire feed compartment. The supply circuit is
protected by an 8 Amp fuse located on the left hand side of the rear
panel. A thermostat is built into the system to protect against
overheating. The indicator light comes on when overheating occurs
and cuts off the power supply; it will reset automatically within a few
minutes, after cooling down.
IMPORTANT.
Should you have no welding experience, we recommend you seek
training from an expert source to ensure your personal health & safety.
You must familiarise yourself with welding applications and limitations,
and specific potential hazards peculiar to welding. Good Mig welding
may be achieved only with continued, supervised practice.
8.1
Mig/Mag welding. (See fig.19 ). A reel of welding wire is placed on
the reel holder and automatically fed through an insulated liner in the
torch to its tip. The torch consist of a switch, liner, gas hose, and
control cable. The switch activates the wire feed roller and the gas
flow. Releasing the switch stops wire feed and gas flow. The weld
current is transferred to the electrode (the wire) from the contact tip at
the torch end.
Wire speed must be adjusted according to power output. The higher
the current the faster the wire speed. A gas cup fits over the contact
tip to direct gas flow towards the weld ensuring the arc welding
process is shielded from oxidising air contamination (fig.19). The
shielding gas also assists heating of the weld. The torch is connected
to the positive side of a DC rectifier, and negative clamp is attached to
the workpiece.
8. WELDING PRINCIPLES
6.3
FEEDING WIRE ThROUGh TO ThE TORCh.
6.3.1 Before feeding the wire through to the torch, the gas cup and contact tip
should be removed as shown in fig.16.
POWERMIG3525, POWERMIG3530 Issue: 3 (SP) -18/07/13