Altera Power Delivery Network User Manual
Page 11
Chapter 1: Power Delivery Network (PDN) Tool User Guide
1–7
Setting Up the PDN Tool
© March 2009
Altera Corporation
Power Delivery Network (PDN) Tool User Guide
For example, to reliably decouple a 0.9-volt power rail up to 50 MHz with 5%
AC ripple and a maximum current of 4 A, (assuming 50% of which is transcient
current), Z
TARGET
can be calculated as:
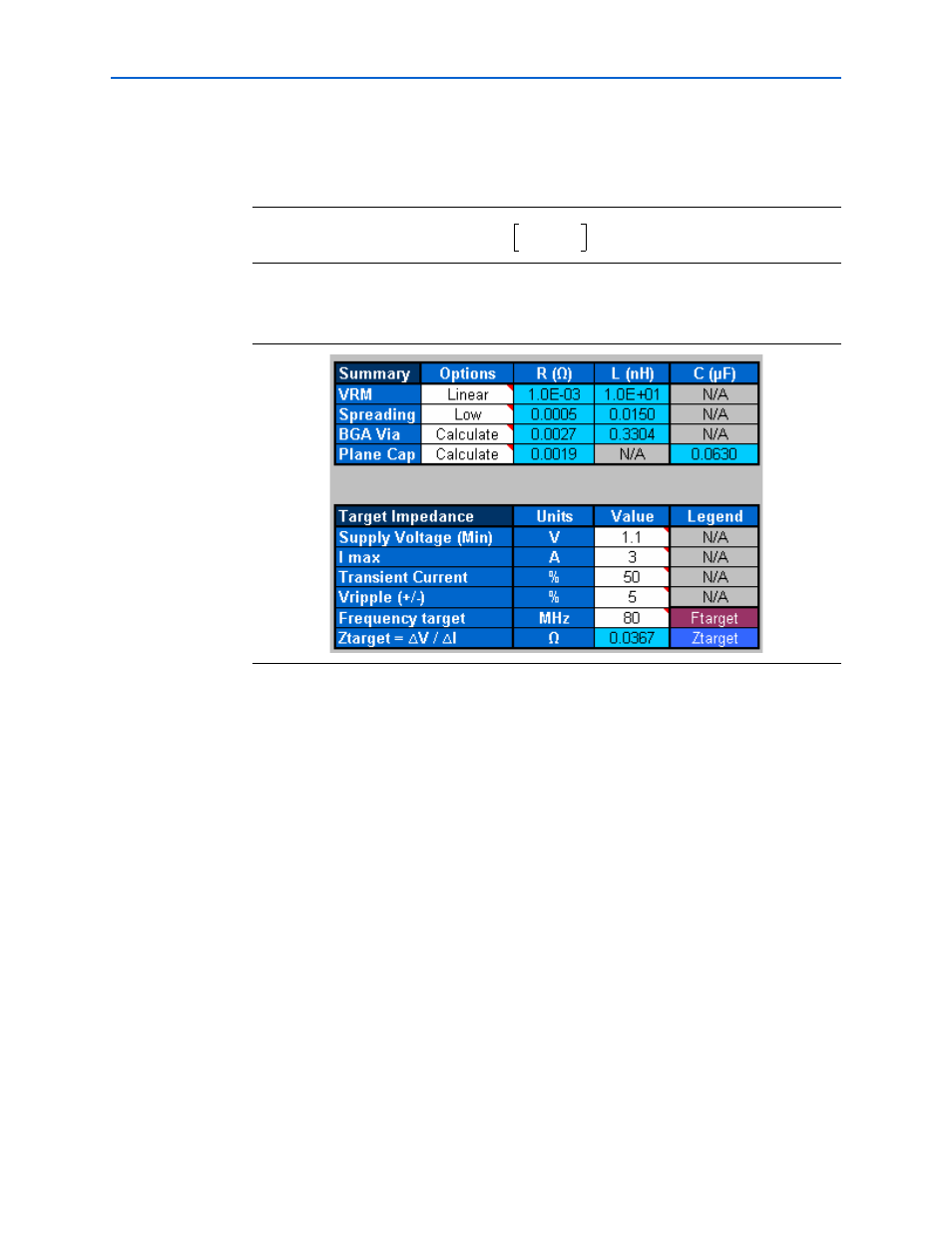
shows the Z
TARGET
calculation from the PDN tool.
To achieve a very low impedance profile (Zeff) below the target impedance (Z
TARGET
)
up to the desired frequency, the power delivery network relies on the VRM, the
on-board discrete decoupling capacitors, inter-plane capacitance, and a low value of
spreading and mounting inductances.
shows one of the capacitor combinations that you can select to ensure that
the effective impedance remains below 0.0225
Ω until the frequency range of interest
(50 MHz). There are many combinations, but the ideal solution is to minimize the
quantity and the type of capacitors required to achieve a flat impedance profile below
the target impedance.
Equation 1–2.
Figure 1–6. Z
TARGET
Calculation
Z
TARGET
(0.9)(0.05)
4x0.5
--------------------------
0.0225
=
=