Flowserve CPXVC User Manual
Page 7
CPXVC USER INSTRUCTIONS ENGLISH 26999930 03-11
Page 7 of 32
flowserve.com
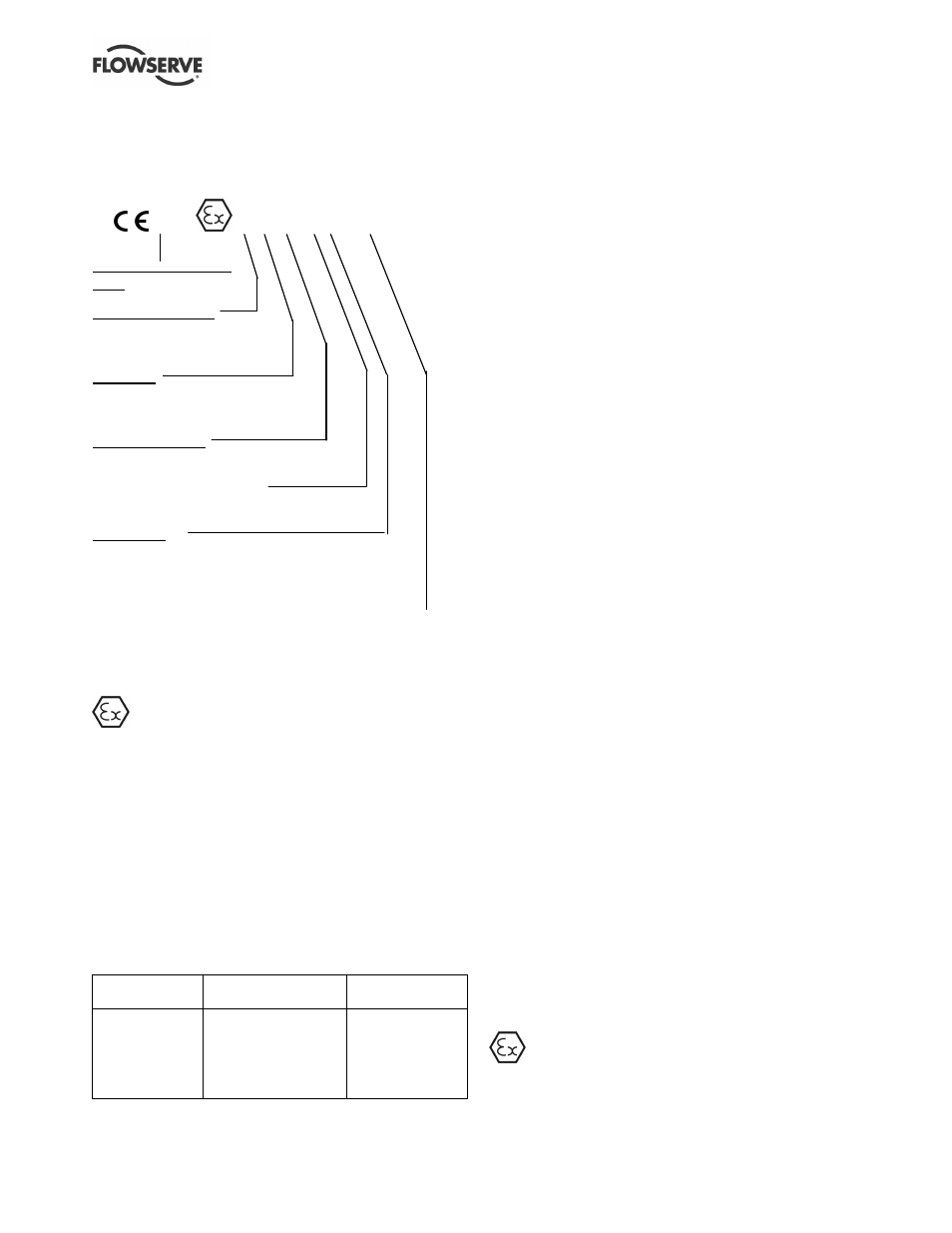
1.6.4.2
Marking
An example of ATEX equipment marking is shown
below. The actual classification of the pump will be
engraved on the nameplate.
II 2 GD c IIC 135 ºC (T4)
External examination
body *
Equipment Group
I = Mining
II = Non-mining
Category
2 or M2 = High level protection
3 = normal level of protection
Gas and/or Dust
G = Gas; D = Dust
c = Constructional safety
(in accordance with EN13463-5)
Gas Group
IIA – Propane (Typical)
IIB – Ethylene (Typical)
IIC – Hydrogen (Typical)
Maximum surface temperature (Temperature Class)
(see section 1.6.4.3.)
1.6.4.3
Avoiding excessive surface
temperatures
ENSURE THE EQUIPMENT TEMPERATURE
CLASS IS SUITABLE FOR THE HAZARD ZONE
Pumps have a temperature class as stated in the
ATEX Ex rating on the nameplate. These are based
on an ambient in the range of -80 to +55 ºC (-112 to
+131 ºF); refer to Flowserve for ambient
temperatures outside this range for this product.
The surface temperature on the pump is influenced
by the temperature of the liquid handled. The
maximum permissible liquid temperature depends on
the ATEX temperature class and must not exceed the
values in the table that follows.
Temperature class
to EN 13463-1
Maximum surface
temperature permitted
Temperature limit of
liquid handled
T6
T5
T4
T3
T2
T1
85 °C (185 °F)
100 °C (212 °F)
135 °C (275 °F)
200 °C (392 °F)
300 °C (572 °F)
450 °C (842 °F)
Consult Flowserve
Consult Flowserve
115 °C (239 °F) *
180 °C (356 °F) *
275 °C (527 °F) *
400 °C (752 °F) *
* The table only takes the ATEX temperature class into consideration.
Pump design or material, as well as component design or material,
may further limit the maximum working temperature of the liquid.
The temperature rise at the seals and bearings and
due to the minimum permitted flow rate is taken into
account in the temperatures stated.
The responsibility for compliance with the
specified maximum liquid temperature is with the
plant operator.
Temperature classification “Tx” is used when the liquid
temperature varies and when the pump is required to be
used in differently classified potentially explosive
atmospheres. In this case the user is responsible for
ensuring that the pump surface temperature does not
exceed that permitted in its actual installed location.
Do not attempt to check the direction of rotation with the
coupling element/pins fitted due to the risk of severe
contact between rotating and stationary components.
Where there is any risk of the pump being run against
a closed valve generating high liquid and casing
external surface temperatures fit an external surface
temperature protection device.
Avoid mechanical, hydraulic or electrical overload by
using motor overload trips, a temperature or power
monitor and make routine vibration monitoring checks.
In dirty or dusty environments, make regular checks
and remove dirt from areas around close clearances,
bearing housings and motors.
The equipment utilises polymer based seals and
bearing surfaces that could be corroded if they
are in contact with unsuitable liquids or gases.
These surfaces are important for the operation of
the pump. Contact Flowserve if you are uncertain
about the performance of these materials with
respect to aggressive substances that may be
present in the hazardous area.
The pump casing must be flooded with liquid to the
minimum level on the dimensional General
Arrangement (GA) drawing, at any time that the pump
is operated.
1.6.4.4 Preventing the build up of explosive
mixtures
ENSURE THE PUMP IS PROPERLY FILLED
AND VENTED AND DOES NOT RUN DRY