Configuring trill distribution trees, Configuring trill timers – H3C Technologies H3C S12500-X Series Switches User Manual
Page 19
13
Step Command
Remarks
1.
Enter system view.
system-view
N/A
2.
Enter TRILL view.
trill N/A
3.
Configure the maximum
number of TRILL unicast
equal-cost routes.
max-unicast-load-balancing
number
The default setting is 16.
Configuring TRILL distribution trees
In a TRILL network, RBs do the following:
•
Compute TRILL distribution trees according to the LSDB.
•
Use the TRILL distribution trees to guide the forwarding of multicast, broadcast, and unknown
unicast frames.
An RB with a higher priority is selected as the root bridge of a TRILL distribution tree.
An LSP carries TRILL distribution tree information that includes the following:
•
The number of TRILL distribution trees that the RB wants all RBs to compute.
•
The maximum number of TRILL distribution trees that the RB can compute (this number is fixed at 15).
•
The number of TRILL distribution trees that the RB has computed.
An RB determines the number of TRILL distribution trees to compute (n) as follows: select the lower value
between the number of TRILL distribution trees that the highest-priority RB wants all RBs to compute and
the smallest value of the maximum number of TRILL distribution trees that each RB can compute. From the
nickname list in the LSP advertised by the RB with the highest priority, the first n nicknames comprise the
root bridge list that the local RB uses to compute TRILL distribution trees.
TRILL distribution trees support Equal Cost Multiple Path (ECMP), also known as multicast ECMP. When
multicast ECMP is disabled, because the topologies of TRILL distribution trees are different, traffic can be
load shared. However, equal-cost links are not used for load sharing.
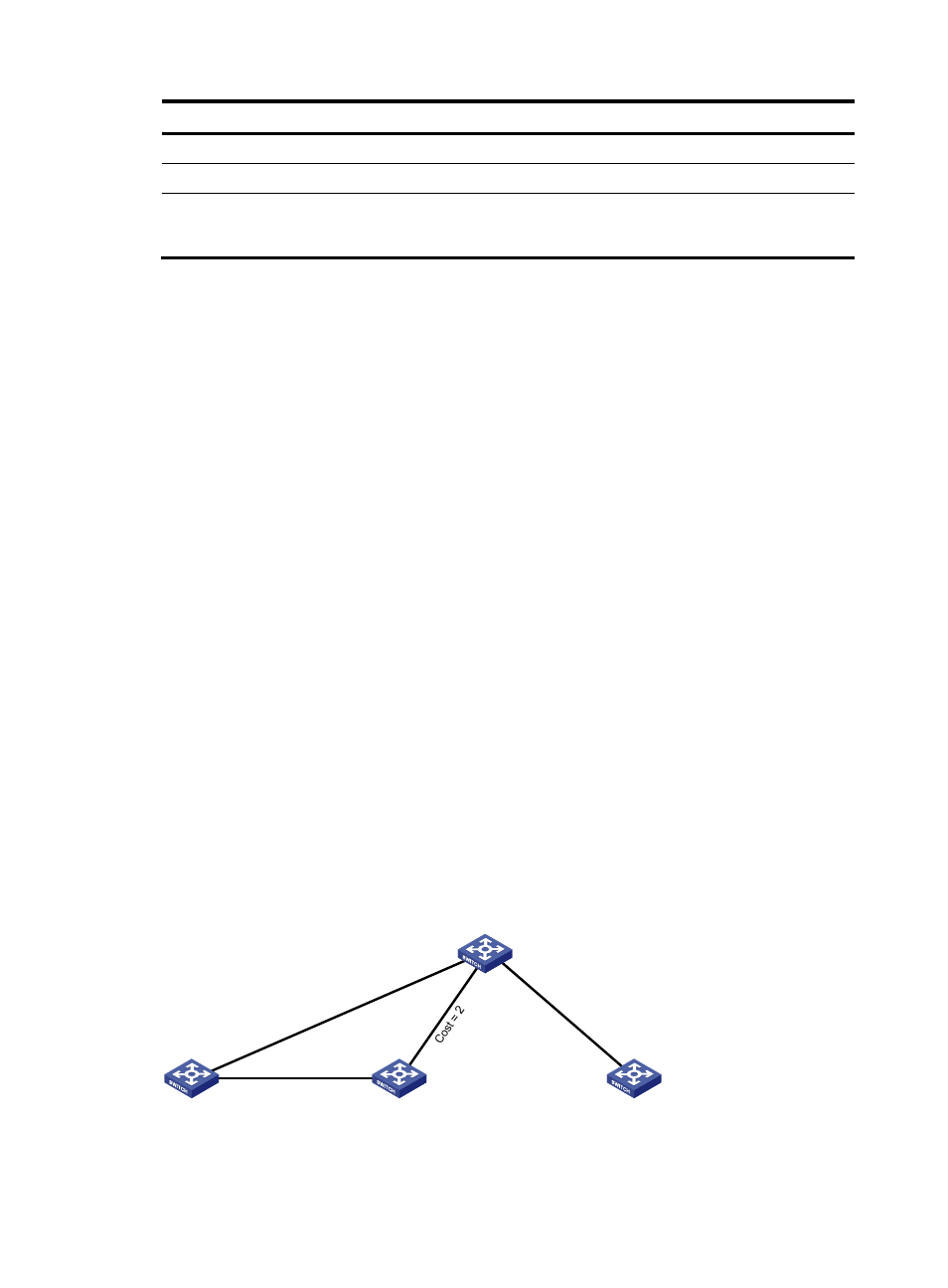
When N equal-cost links exist in the network, each TRILL distribution tree selects the link with the largest
pseudo-node ID for forwarding packets. As shown in
, two equal-cost links exist between RB 1
and RB 3. Assume the link directly connecting RB 1 to RB 3 has the largest pseudo-node ID. Both the TRILL
distribution tree rooted at RB 3 and the TRILL distribution tree rooted at RB 4 select the link.
Figure 6 Multicast ECMP
When multicast ECMP is enabled, TRILL assigns equal-cost links to different TRILL distributions trees. This
improves the load sharing performance.
RB 1
RB 2
RB 3
RB 4
Cos
t =
3
Cost = 1