Configuring evi, Overview, Layer 2 connectivity extension issues – H3C Technologies H3C S10500 Series Switches User Manual
Page 8
1
Configuring EVI
Overview
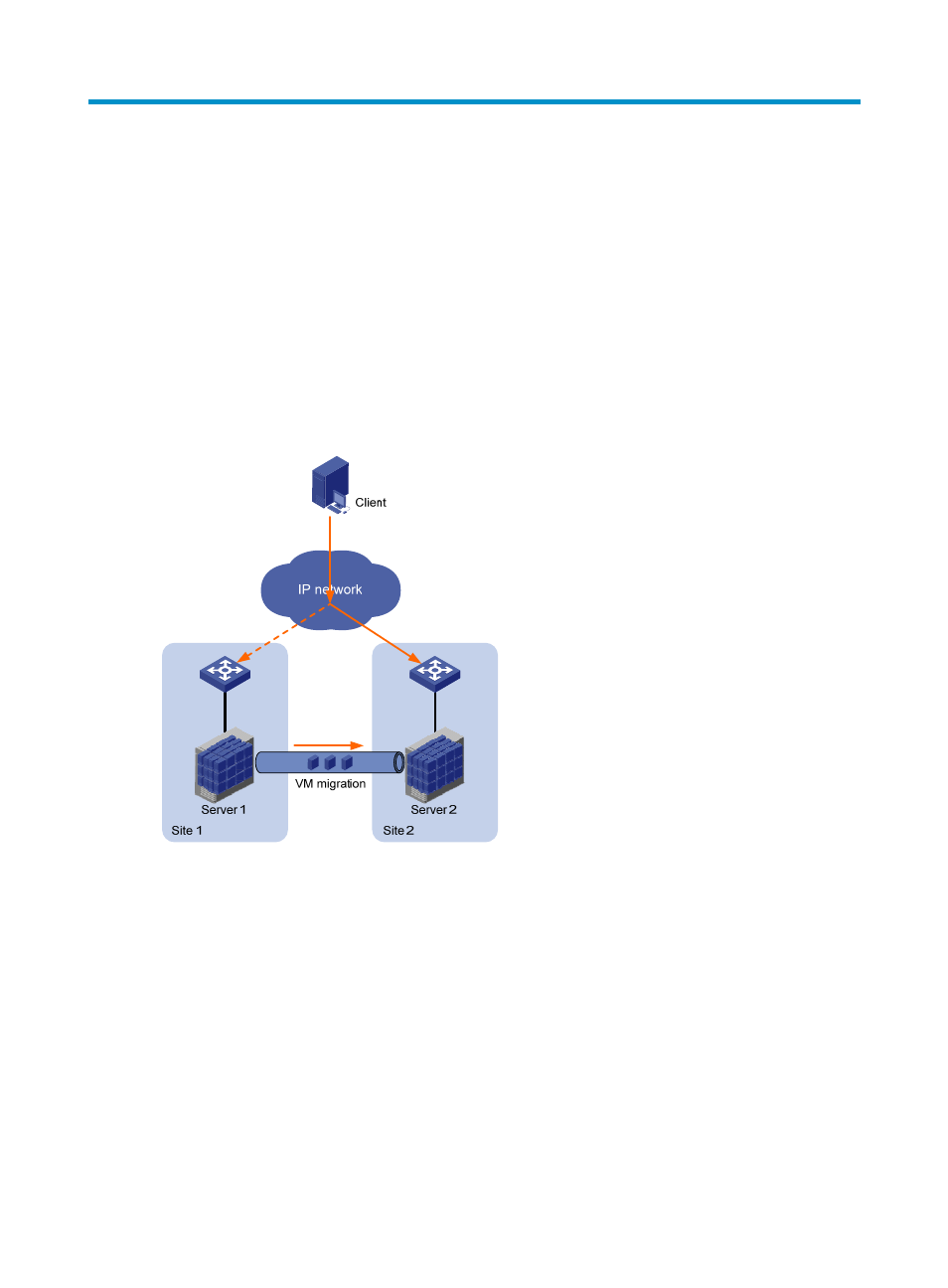
Ethernet Virtual Interconnect (EVI) is a MAC-in-IP technology that provides Layer 2 connectivity between
distant Layer 2 network sites across an IP routed network. It is used for connecting geographically
dispersed sites of a virtualized large-scale data center that requires Layer 2 adjacency (see
EVI enables long-distance virtual machine workload mobility and data mobility, disaster recovery, and
business continuity. For example, virtual machines can move between data center sites without changing
their IP addresses, so their movements are transparent to users and do not disrupt traffic.
Figure 1 Virtual machine migration
Layer 2 connectivity extension issues
EVI resolves the following Layer 2 connectivity extension issues:
•
Site independence—EVI keeps protocol failures, such as broadcast storms, from propagating
across sites.
•
Transport independence—EVI has no special requirements for site location or transport network
type, except that the transport network can forward IP packets.
•
High availability—EVI supports redundant edge devices and has a loop-free mechanism to prevent
loops for a multihomed network site.
•
Link efficiency—EVI optimizes the inter-site broadcast transmission mechanism and implements
load-sharing on redundant links.