Operation, Worcester controls – Flowserve PM15 Pneumatic Valve Positioner User Manual
Page 3
WCAIM2016
PM15 Pneumatic Valve Positioner Installation, Operation and Maintenance Instructions
3
(
Flow Control Division
Worcester Controls
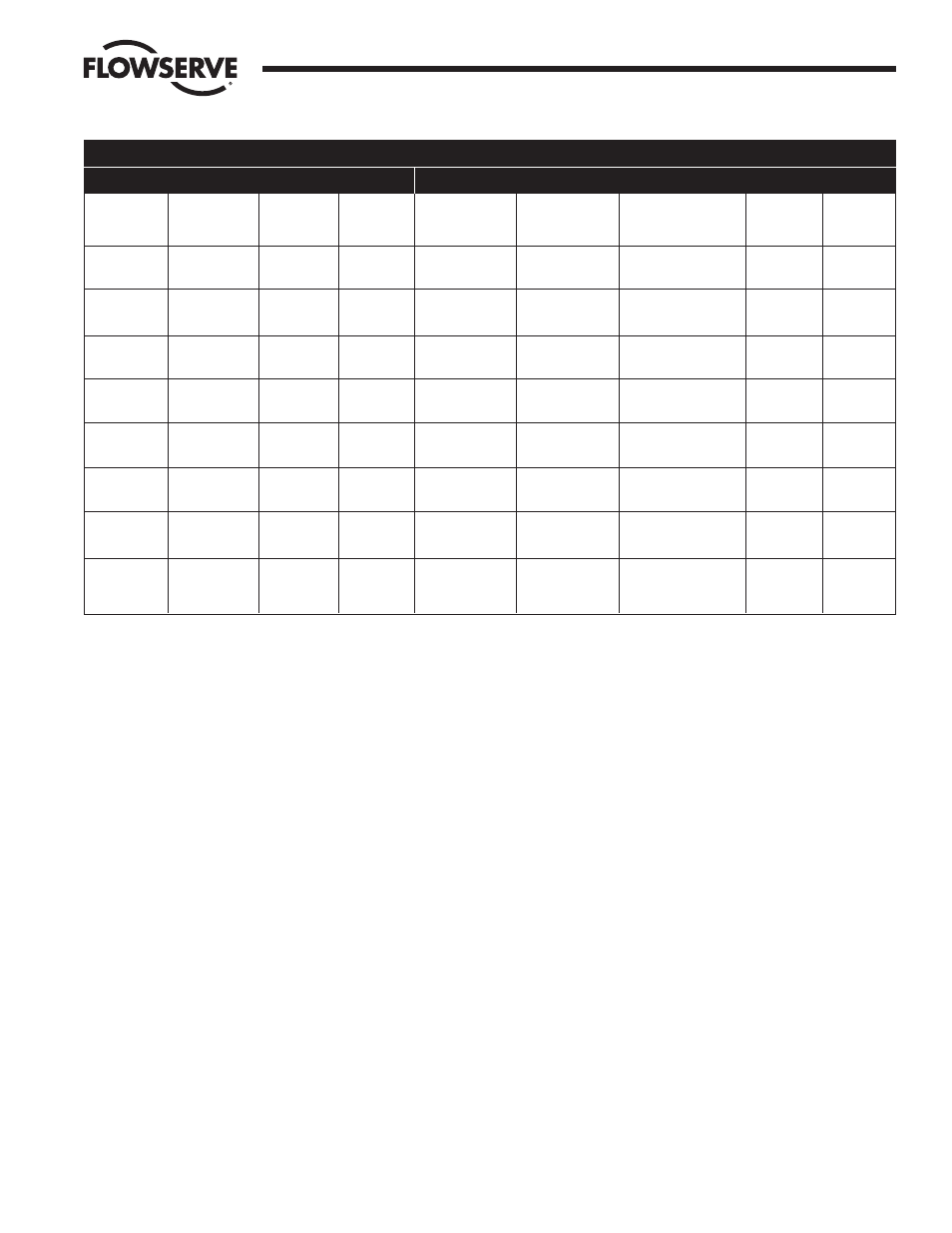
POSITIONER MOUNTING GUIDE
ACTUATOR
POSITIONER
Actuator
Mounting
(Note 1)
Inline
Inline
Cross-Line
Cross-Line
Inline
Inline
Cross-Line
Cross-Line
Failure
Mode
(Note 2)
Fail-Close
Fail-Close
Fail-Close
Fail-Close
Fail-Open
Fail-Open
Fail-Open
Fail-Open
Actuator
Position
(Note 1)
Normal
Normal
Inverted
Inverted
Inverted
Inverted
Normal
Normal
Rotation
to
Open
CCW
CCW
CW
CW
CCW
CCW
CW
CW
Positioner
Operation
Direct-Acting
Reverse-Acting
Direct-Acting
Reverse-Acting
Direct-Acting
Reverse-Acting
Direct-Acting
Reverse-Acting
Cam
(Note 3)
Direct-Acting
Reverse-Acting
Reverse-Acting
Direct-Acting
Direct-Acting
Reverse-Acting
Reverse-Acting
Direct-Acting
Cam Setting
0˚ (Min. Signal)
When Valve is Closed
90˚ (Max.Signal)
When Valve is Closed
0˚ (Min. Signal)
When Valve is Closed
90˚ (Max.Signal)
When Valve is Closed
90˚ (Max.Signal)
When Valve is Open
0˚ (Min. Signal)
When Valve is Open
90˚ (Max.Signal)
When Valve is Open
0˚ (Min. Signal)
When Valve is Open
Actuator
Supply Hoses
(Note 4)
Normal
Reverse
Reverse
Normal
Normal
Reverse
Reverse
Normal
Valve
Position at
Min. Signal
Closed
Open
Closed
Open
Closed
Open
Closed
Open
7) Align the mounting holes and then use the two
5
/
16
-18 socket
head cap screws, lockwashers, hex nuts, and rubber washers
(between bracket and positioner) supplied with the mounting
kit to fasten the positioner to the bracket.
8) Tighten the set screw at the upper end of the coupling to the
positioner shaft (seat the set screw in the positioner shaft
groove). The other two set screws will be tightened after the
actuator is cycled 90˚. Proper alignment of the positioner spindle
to the actuator shaft is very important since improper alignment
can cause excessive wear and friction to the positioner.
C. CONNECTIONS
Air connections are tapped for
1
/
4
" NPT male connectors and are
clearly marked. We recommend use of tape, Loctite
®
577 or
similar user preferred for sealing.
Port I Input instrument pneumatic signal 20–100 kPa (3–15 psi)
Port S Supply air, maximum 0.9 MPa (125 psi)
Port C1, C2 Actuator connections (0.2–0.9 MPa). C2 opening port.
Connect the air supply line to port S.
For double-acting operation, connect the right-hand and left-hand
ports of the actuator end cap (right-hand end cap when facing
actuator nameplate) to port C2 and C1 respectively.
For single-acting operation, plug port C1 for increasing signal to
open or close. Plug port C2 for decreasing (reverse) signal to
close.
3. OPERATION
The PM15 operates on a force balance principal. Force is originated
by the signal pressure transmitted through a diaphragm onto the
balance arm. The opposing force is achieved through the feedback
spring and is proportional to the position of the lower arm. The lower
arm position is determined by the position of the cam which is
secured to the spindle and connected to the actuator shaft thus
providing the feedback from the actuator/valve. When these two
forces are equal, the balance arm and the spool in the pilot valve is in
a neutral position — the complete unit is in a balanced position. Air is
supplied to the pilot valve through port S, and controls the air flow
through ports C1 and C2.
Assume an equilibrium position.
An increased control pressure will deflect the diaphragm (1) down,
compressing the feedback spring (3). The balance arm (2) moves the
spool (7) in the pilot valve (8) furnishing supply air to the actuator,
while at the same time air is exhausted from actuator and is vented to
atmosphere through the pilot valve.
With the increased supply air, the actuator rotates (or moves linearly)
moving the positioner spindle (6). The spindle and cam (5) rotate,
forcing the lower arm (4) upwards compressing the feedback spring
(3). This motion will continue until two forces are equal and the unit
is an equilibrium position.