Broadcast, Multicast – H3C Technologies H3C S3100V2 Series Switches User Manual
Page 10
2
In unicast transmission, the traffic transmitted over the network is proportional to the number of hosts that
need the information. If a large number of hosts need the information, the information source must send
a copy of the same information to each of these hosts. Sending many copies can place a tremendous
pressure on the information source and the network bandwidth.
Unicast is not suitable for batch transmission of information.
Broadcast
In broadcast transmission, the information source sends information to all hosts on the subnet, even if
some hosts do not need the information.
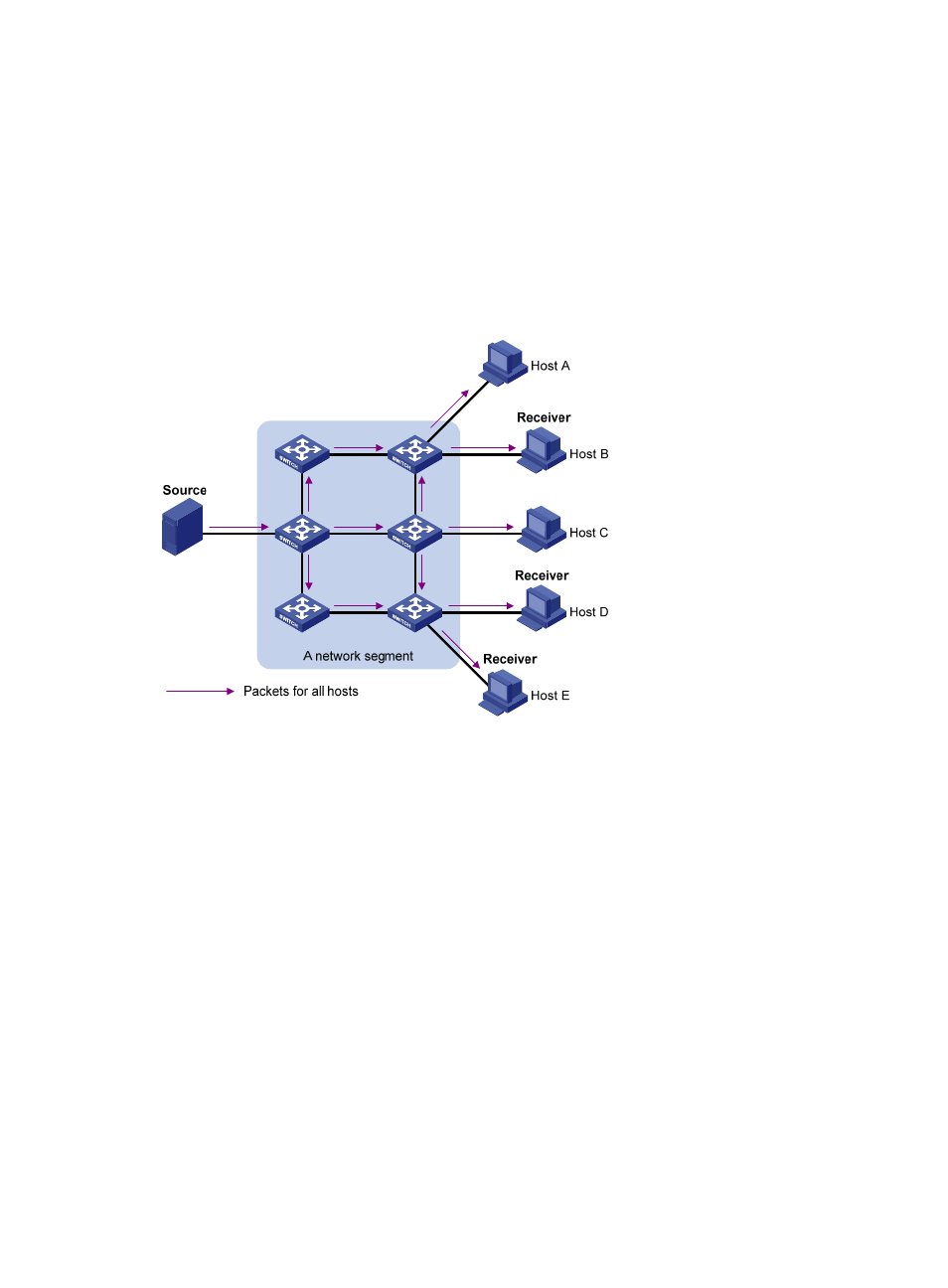
Figure 2 Broadcast transmission
In
, assume that only Host B, Host D, and Host E need the information. If the information is
broadcast to the subnet, Host A and Host C also receive it. In addition to information security issues,
broadcasting to hosts that do not need the information causes traffic flooding on the same subnet.
Broadcast is disadvantageous in transmitting data to specific hosts. Moreover, broadcast transmission is
a significant waste of network resources.
Multicast
Unicast and broadcast techniques cannot provide point-to-multipoint data transmissions with the
minimum network consumption. Multicast transmission can solve this problem. When some hosts on the
network need multicast information, the information sender, or multicast source, sends only one copy of
the information. Multicast distribution trees are built through multicast routing protocols, and the
information is replicated only on nodes where the trees branch.