Channel strip description, Level, Pre fader solo – MACKIE 802VLZ4 8-Channel Ultra-Compact Mixer User Manual
Page 16: Mute/alt 3-4, Level 22. pre fader solo 23. mute/alt 3–4, 802vlz4
802VLZ4
16
802VLZ4
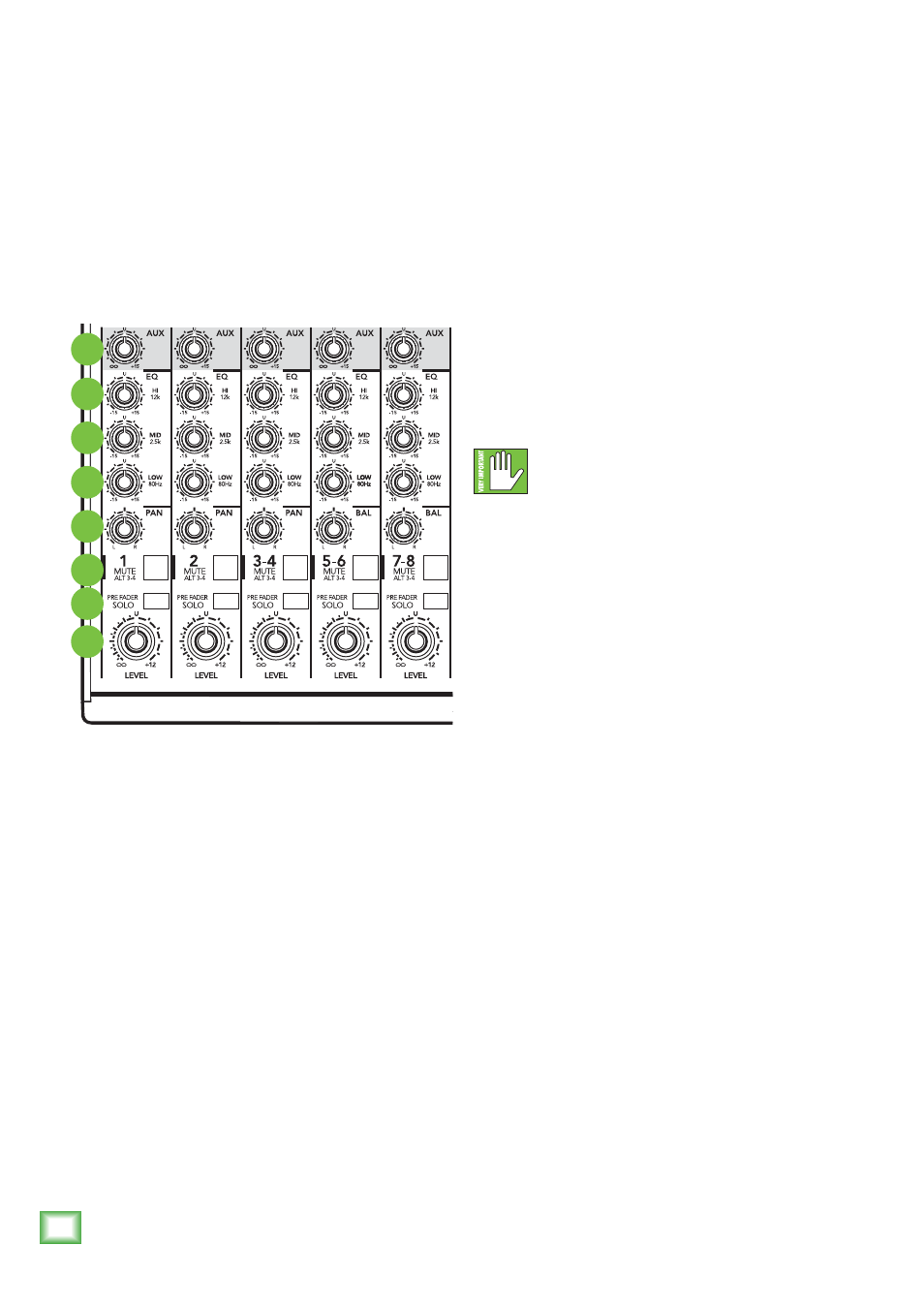
Channel Strip Description
22. Pre Fader Solo
This lovable switch allows you to hear signals
through your headphones or control room without
having to route them to the main mix or alt 3-4 mix.
You don’t even have to have the channel’s level [21]
knob turned up. Folks use solo in live work to preview
channels before they are let into the mix, or to just
check out what a particular channel is up to anytime
during a session. You can solo as many channels at a
time as you like.
Soloed channels are sent to the source mix, which
ultimately feeds your control room, phones and meter
display. Whenever solo is engaged, all source selections
(main mix, alt 3-4 and tape) are defeated, to allow the
soloed signal to do just that — solo!
WARNING:
Pre fader solo taps the
channel signal before the level knob.
If you have a channel’s level knob set below
“U” (unity gain), solo won’t know that and will send
a unity gain signal to the control room, phones and
meter display. That may result in a startling level
boost at these outputs.
23. Mute/Alt 3–4
The dual-purpose mute/alt 3–4 bus is our signature.
When Greg was designing our first product, he had to
include a mute switch for each channel. Mute switches
do just what they sound like they do. They turn off the
signal by “routing” it into oblivion. “Gee, what a waste,”
Greg reasoned. “Why not have the mute button route the
signal somewhere else useful… like a separate stereo
bus?” So mute/alt 3–4 really serves two functions —
muting (often used during a mixdown or live show), and
signal routing (for multitrack and live work) where it
acts as an extra stereo bus.
To use this as a mute switch, all you have to do is not
use the alt 3–4 [9] outputs. Then, whenever you press
this switch, you will assign a channel to these unused
outputs, disconnecting it from the main mix, and
effectively muting the channel.
To use this as an alt 3–4 switch, all you have to do
is connect the alt 3–4 outputs to whatever destination
you desire. Here are two popular examples:
When doing multitrack recording, use the alt 3–4
outputs to feed your multitrack. With most decks, you
can "mult" the alt 3–4 [9] outputs, using Y-cords or
mults, to feed multiple tracks. So, take alt output L and
send it to tracks 1, 3, 5 and 7, and alt output R and send
it to tracks 2, 4, 6 and 8. Now, tracks that are in record
or input modes will hear the alt 3–4 signals, and tracks
in playback or safe modes will ignore them.
The five channel strips look alike, and function
identically. The first two are for individual mics or mono
instruments, and have more gain available. The next
strip controls mic or stereo line-level sources, and the
last two are for either stereo or mono line-level sources.
(Each of the stereo channel strips is actually two
complete circuits. The controls are linked together to
preserve stereo.) We’ll start at the bottom and work
our way up:
“U” Like Unity Gain
VLZ4 mixers have a “U” symbol on almost every
level control. This “U” stands for “unity gain,” meaning
no change in signal level. Once you have adjusted the
input signal to line-level, you can set every control at
“U” and your signals will travel through the mixer at
optimal levels. What’s more, all the labels on our level
controls are measured in decibels (dB), so you’ll know
what you’re doing level-wise if you choose to change a
control’s settings.
21. Level
This adjusts the channel’s level, from off, to unity
gain at the center, on up to 12 dB of additional gain.
This knob is the equivalent of a channel fader,
so sometimes we lapse and say the word fader.
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21