Avery Dennison 6037 Rev. AA 3/04 Programmer Manual User Manual
Page 13
DOS Basics 2-3
It is possible to have several files with the same file name but different
extensions. ROM-DOS searches for and accesses the file name
extensions in the following order: .COM, .EXE, .BAT, and then all others.
For example, you could have an executable file named MYPROG.EXE
and a batch file call MYPROG.BAT in the current directory. When you
enter MYPROG on the command line, the file MYPROG.EXE is executed.
If you want to execute the batch file MYPROG.BAT, you must specify the
.BAT extension when entering MYPROG on the command line.
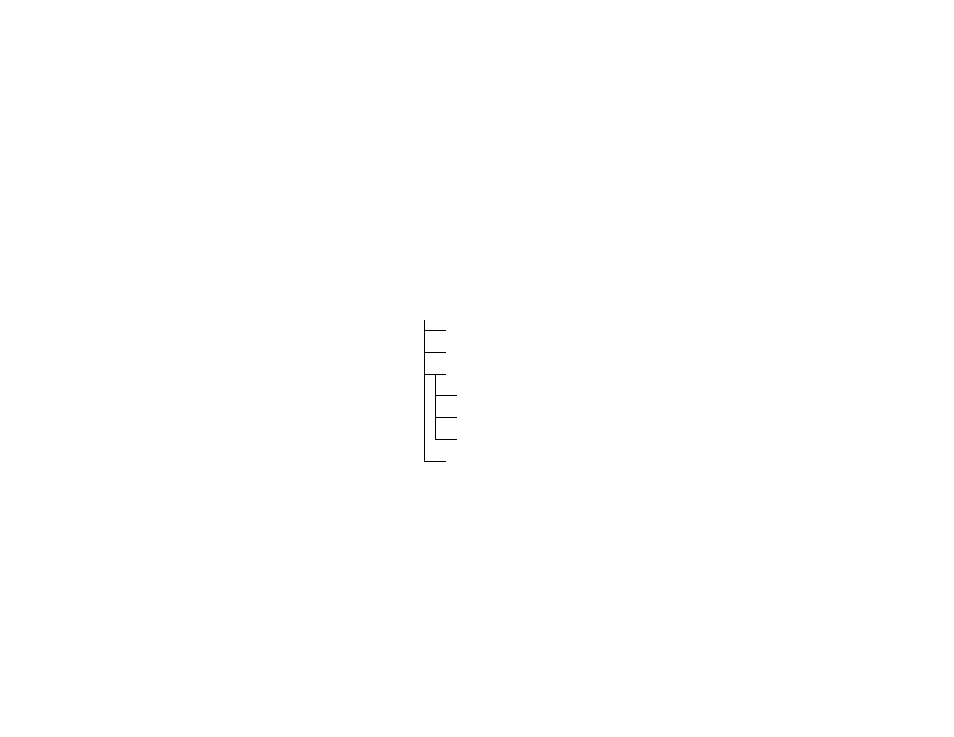
Tree-Structured Directory System
ROM-DOS uses a tree-structured directory system. In this system, each
branch of the directory, called a subdirectory, is either attached to the
main or root directory or is attached to another subdirectory. The
following diagram illustrates the directory system and shows two levels of
subdirectories under the root directory.
ROOT
SUBDIR2
SUBDIR1
SUBDIR3
SUBDIR31
SUBDIR32
SUBDIR33
SUBDIR4
Naming Subdirectories
You can create any subdirectory structure you choose, giving each
subdirectory the name of your choice. The naming of subdirectories is
similar to the naming of files. There is an eight-character limit when long
file name support is disabled, and you have the same character-choice
limitations as for file names (letters, numbers, and symbols). A
subdirectory name can also have an extension. For more information on
creating and deleting subdirectories, refer to the MD and RD descriptions
later in this manual for more information on creating and removing
directories.