Altera Avalon Tri-State Conduit Components User Manual
Page 10
2–4
Chapter 2: Generic Tri-State Controller
Parameters
Avalon Tri-State Conduit Components User Guide
May 2011
Altera Corporation
Preliminary
Refer to
“Example Read and Write Using Setup, Hold and Wait Times” on page 2–5
for an example that illustrates the use of the parameters defined in
Table 2–2
.
1
Because the Tri-State Conduit Pin Bridge registers incoming and out-going signals
you must add two cycles latency to the read latency numbers in the vendor’s data
sheet. In calculating delays, the Generic Tri-State Controller chooses the larger of the
turn around time
and (read latency + two cycles). Turn around time is measured
from the time that a command is accepted, not from the time that the previous read
returned data.
Table 2–3
allows you to specify whether a signal is asserted high or low.
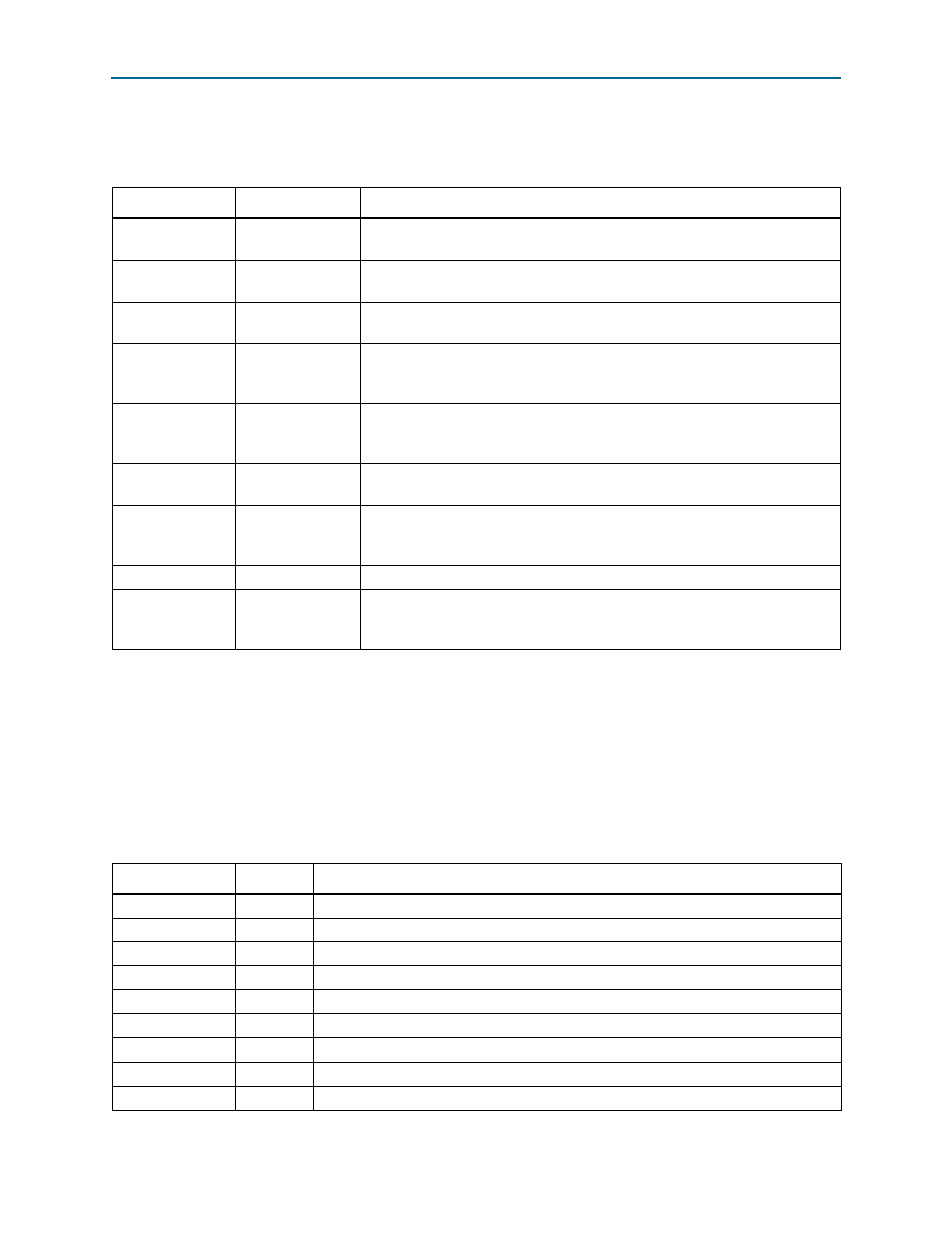
Table 2–2. Signal Timing
Parameter
Value
Description
Read wait time
0–10000
cycles
Specifies additional time in units of timing units read to be asserted to indicate a
read transfer.
Write wait time
0–10000
cycles
Specifies additional time in units of timing units for write to be asserted to
indicate a write transfer.
Setup wait time
0–10000
cycles
Specifies time in timing units between the assertion of
chipselect,
address
,
and
data
and the assertion of
read
or
write
.
Data hold time
0–1000
cycles
Specifies time in timing units between the deassertion of
write
and the
deassertion of
chipselect
,
address
, and
data
. (Only applies to write
transactions.)
Maximum
pending read
transactions
1–64
Specifies the maximum number of read transactions that can be in progress at
one time. This value controls the amount of buffering in the interconnect fabric.
Turn around time
>=0
Specifies the number of clock cycles required to change access from a read to a
write.
Timing units
cycles
,
nanoseconds
Specifies the units for setup wait time, data hold time, write wait time, and
read wait time. Use cycles for synchronous devices and nanoseconds for
asynchronous devices.
Read latency
cycles
Specifies the read latency for fixed-latency slaves.
Chip select
through read
latency
On/Off
When on,
chipselect
remains asserted until all pending read transfers have
completed; otherwise,
chipselect
is asserted for one cycle.
Table 2–3. Signal Polarities (Part 1 of 2)
Parameter
Value
Description
read
On/Off
When On,
read
is asserted low and is called
read_n
.
arbiterlock
On/Off
When On,
arbiterlock
is asserted low and is called
arbiterlock_n
.
write
On/Off
When On,
write
is asserted low and is called
write_n
.
chipselect
On/Off
When On,
chipselect
is asserted low and is called
chipselect_n
.
byteenable
On/Off
When On,
byteenable
is asserted low and is called
byteenable_n
.
outputenable
On/Off
When On,
outputenable
is asserted low and is called
outputenable_n
.
writebyteenable
On/Off
When On,
writebyteenable
is asserted low and is called
writebyteenable_n
.
waitrequest
On/Off
When On,
waitrequest
is asserted low and is called
waitrequest_n
.
begintransfer
On/Off
When On,
begintransfer
is asserted low and is called
begintransfer_n
.