Table 1–3 – Altera Nios II Custom User Manual
Page 10
1–6
Chapter 1: Nios II Custom Instruction Overview
Custom Instruction Types
Nios II Custom Instruction User Guide
January 2011
Altera Corporation
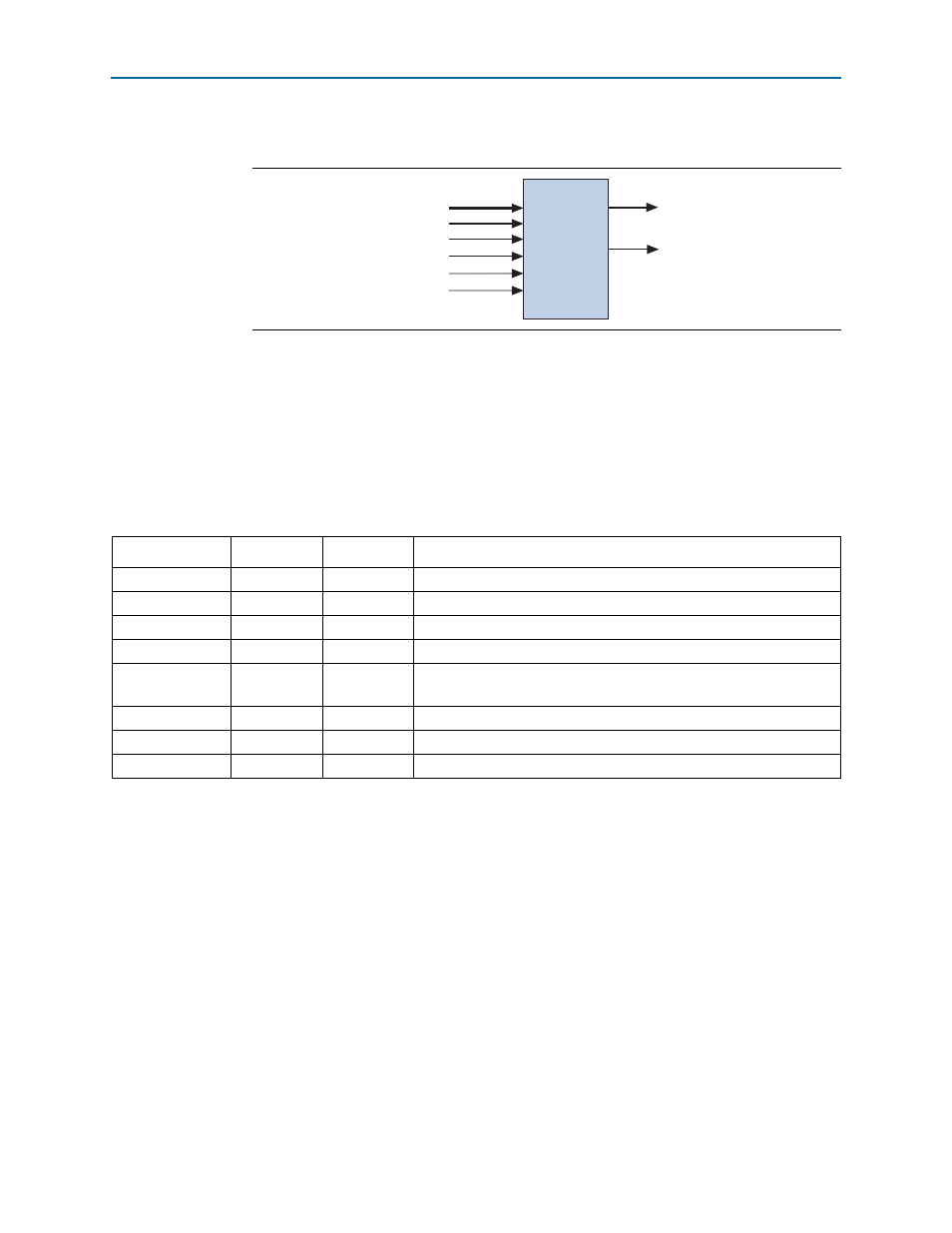
shows the multicycle custom instruction block diagram.
Multicycle custom instructions complete in either a fixed or variable number of clock
cycles. For a custom instruction that completes in a fixed number of clock cycles, you
specify the required number of clock cycles at system generation. For a custom
instruction that requires a variable number of clock cycles, you instantiate the
start
and
done
ports. These ports participate in a handshaking scheme to determine when
the custom instruction execution is complete.
describes the multicycle custom instruction ports.
As indicated in
clk
,
clk_en
, and
reset
ports are required for multicycle
custom instructions. However, the
start
,
done
,
dataa
,
datab
, and
result
ports are
optional. Implement them only if the custom instruction functionality requires them.
Figure 1–5. Multicycle Custom Instruction Block Diagram
dataa[31..0]
datab[31..0]
clk
clk_en
reset
start
Multi-cycle
done
result[31..0]
Table 1–3. Multicycle Custom Instruction Ports
Port Name
Direction
Required
Description
clk
Input
Yes System
clock
clk_en
Input
Yes
Clock enable
reset
Input
Yes
Synchronous reset
start
Input
No
Commands custom instruction logic to start execution
done
Output
No
Custom instruction logic indicates to the processor that execution is
complete
dataa[31:0]
Input
No
Input operand to custom instruction
datab[31:0]
Input
No
Input operand to custom instruction
result[31:0]
Output
No
Result of custom instruction