Altera Nios II Custom User Manual
Page 20
2–4
Chapter 2: Software Interface
Custom Instruction Assembly Software Interface
Nios II Custom Instruction User Guide
January 2011
Altera Corporation
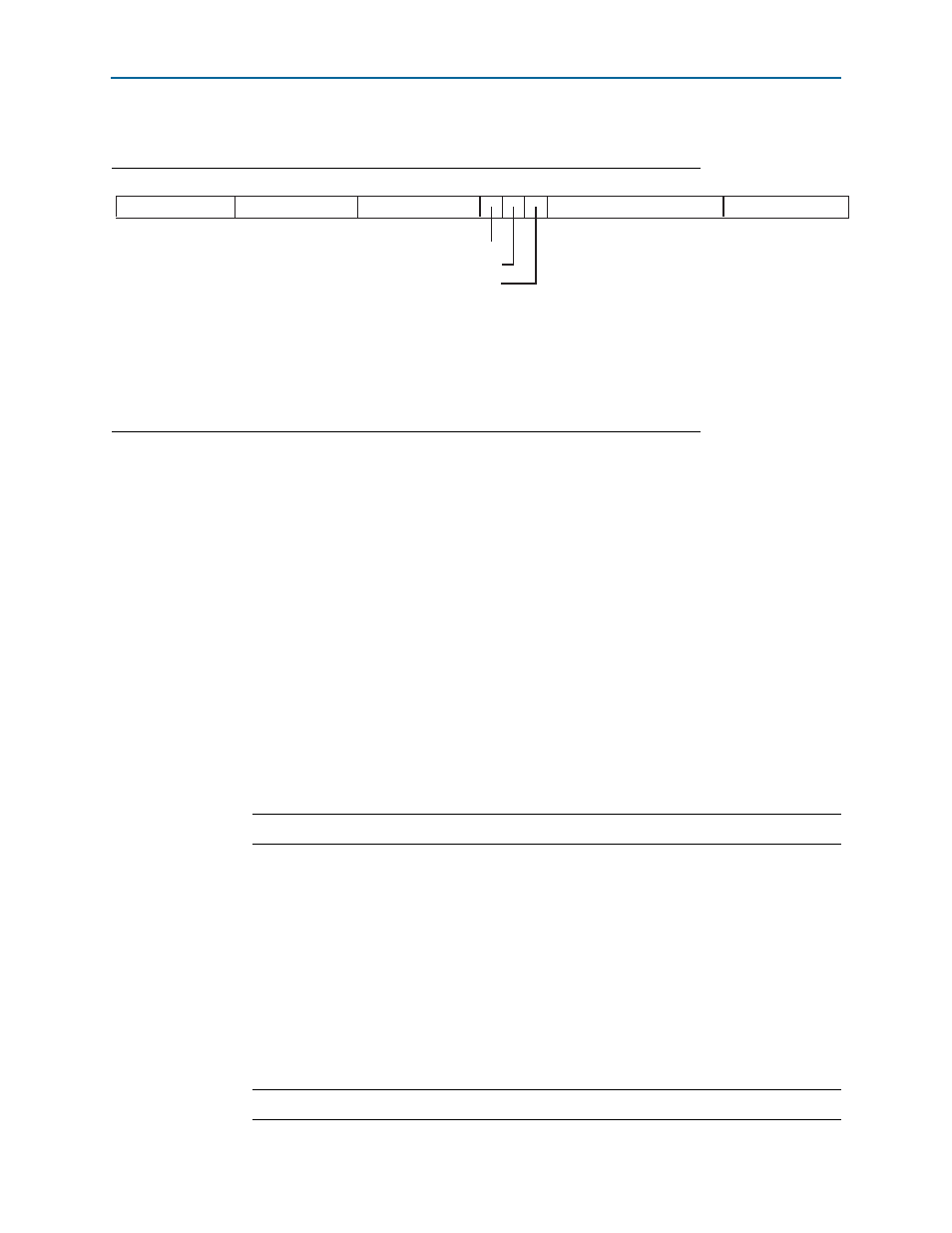
shows a diagram of the custom instruction word.
Bits 5–0 are the Nios II custom instruction opcode. The opcode for a custom
instruction is 0x32.
f
A list of opcodes appears in the “Instruction Opcodes” section in the
chapter of the Nios II Processor Reference Handbook.
The
N
field, bits 13:6, is the custom instruction index. The custom instruction index
distinguishes between different custom instructions, allowing the Nios II processor to
support as many as 256 distinct custom instructions. Depending on the type of
custom instruction, the
N
field has one of the following functions:
■
A unique custom instruction index, for logic that implements a single custom
function
■
An extended custom instruction index, for logic that implements several custom
functions
shows the assembly language syntax for the custom instruction.
In the assembly code instruction in
N
is the custom instruction index,
xC
is the destination for the
result[31:0]
port,
xA
is the
dataa
port, and
xB
is the
datab
port. To access the Nios II processor’s register file, replace
x
with
r
. To access a custom
register file, replace
x
with
c
. The use of
r
or
c
determines whether the custom
instruction has the
readra
,
readrb
, and
writerc
bits held high or low. Refer to
for the location of these three bits in the custom instruction low-level
format.
demonstrate the syntax for custom
instruction assembler calls.
Figure 2–1. Custom Instruction Format
31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
N
C
B
A
uP OPCode = Custom
writerc
readrb
readra
A = Register index of operand A
B = Register index of operand B
C = Register index of operand C
N = 8-bit number that selects instruction
readra = 1 if instruction uses processor’s register rA, 0 otherwise
readrb = 1 if instruction uses processor’s register rB, 0 otherwise
writerc = 1 if instruction provides result for processor’s register rC, 0 otherwise
Instruction Fields:
Example 2–5. Custom Instruction Assembly Syntax
custom N, xC, xA, xB
Example 2–6. Assembly Language Call to Customer Instruction I
custom 0, r6, r7, r8