Configuring nat-pt, Overview, Application scenario – H3C Technologies H3C SecPath F1000-E User Manual
Page 39: Basic concepts, Nat-pt mechanism
32
Configuring NAT-PT
NOTE:
The NAT-PT configuration is available only at the command line interface (CLI).
Overview
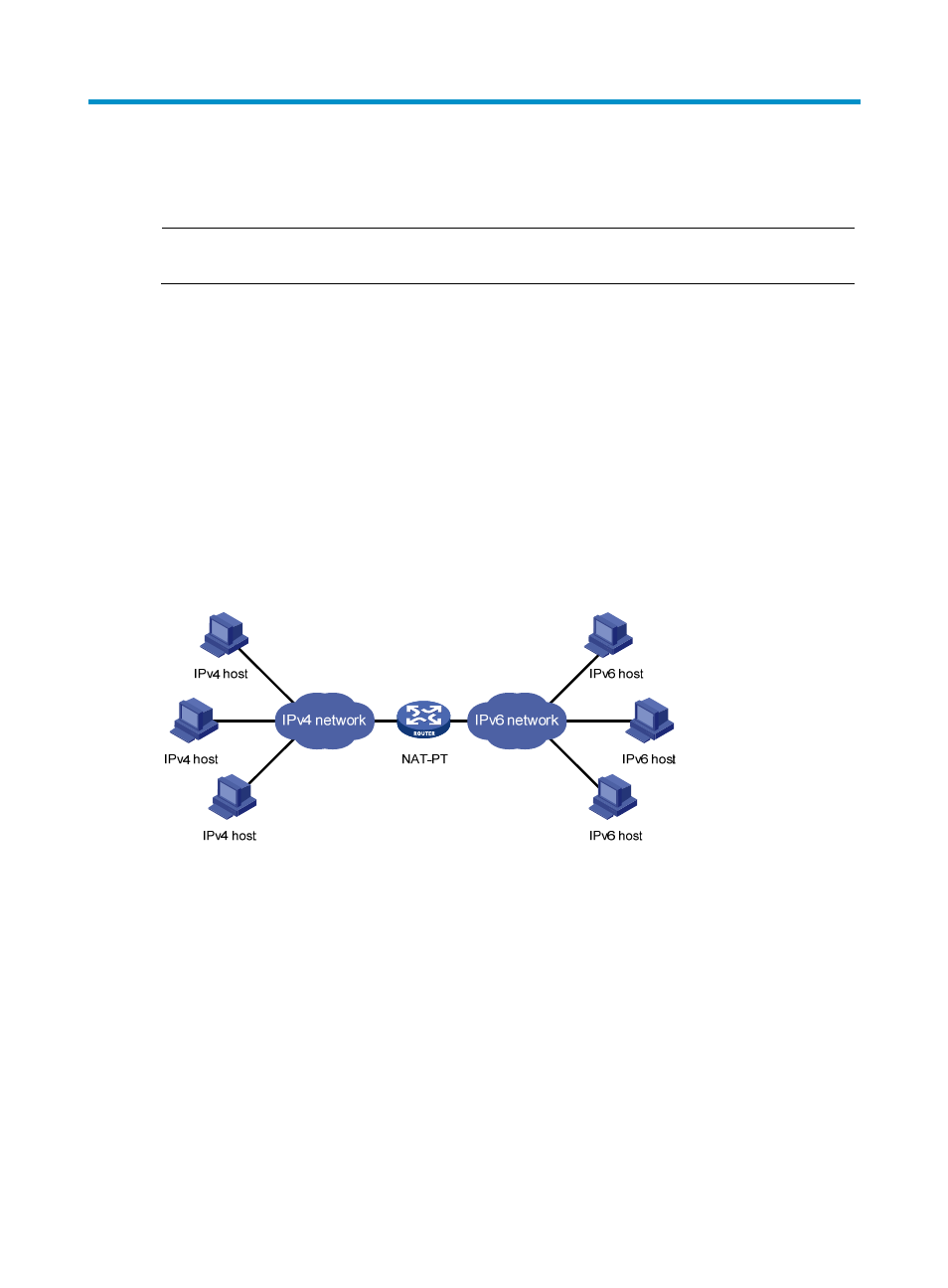
Application scenario
Because of the coexistence of IPv4 networks and IPv6 networks, Network Address Translation – Protocol
Translation (NAT-PT) was introduced to realize translation between IPv4 and IPv6 addresses. For
example, it can enable a host in an IPv6 network to access the FTP server in an IPv4 network.
As shown in
, NAT-PT runs on the device between IPv4 and IPv6 networks. The address
translation is transparent to both IPv4 and IPv6 networks. Users in the IPv6 and IPv4 networks can
communicate without changing their configurations.
Figure 29 Network diagram
Basic concepts
NAT-PT mechanism
There are three NAT-PT mechanisms to realize translation between IPv4 and IPv6 addresses:
•
Static mapping—Static mappings are manually configured for translation between IPv6 and IPv4
addresses.
•
Dynamic mapping—Dynamic mappings are dynamically generated for translation between IPv6
and IPv4 addresses. Different from static mappings, dynamic mappings are not fixed one-to-one
mappings between IPv6 and IPv4 addresses.
•
NAPT-PT—Network Address Port Translation – Protocol Translation (NAPT-PT) realizes the TCP/UDP
port number translation besides static or dynamic address translation. With NAPT-PT, different IPv6
addresses can correspond to one IPv4 address. Different IPv6 hosts are distinguished by different