Nat-pt prefix, Implementing nat-pt, Session initiated by an ipv6 host – H3C Technologies H3C SecPath F1000-E User Manual
Page 40
33
port numbers so that these IPv6 hosts can share one IPv4 address to accomplish the address
translation and save IPv4 addresses.
NAT-PT prefix
The 96-bit NAT-PT prefix in the IPv6 address prefix format is used in the following cases:
•
Upon receiving a packet from an IPv6 host to an IPv4 host, the NAT-PT device detects the prefix of
the destination IPv6 address in the packet. If the prefix is the same as the configured NAT-PT prefix,
the device will translate source and destination IPv6 addresses of the packet into IPv4 addresses.
•
After a packet from an IPv4 host to an IPv6 host is translated through NAT-PT, the prefix of the
translated source IPv6 address is the configured NAT-PT prefix.
Implementing NAT-PT
Session initiated by an IPv6 host
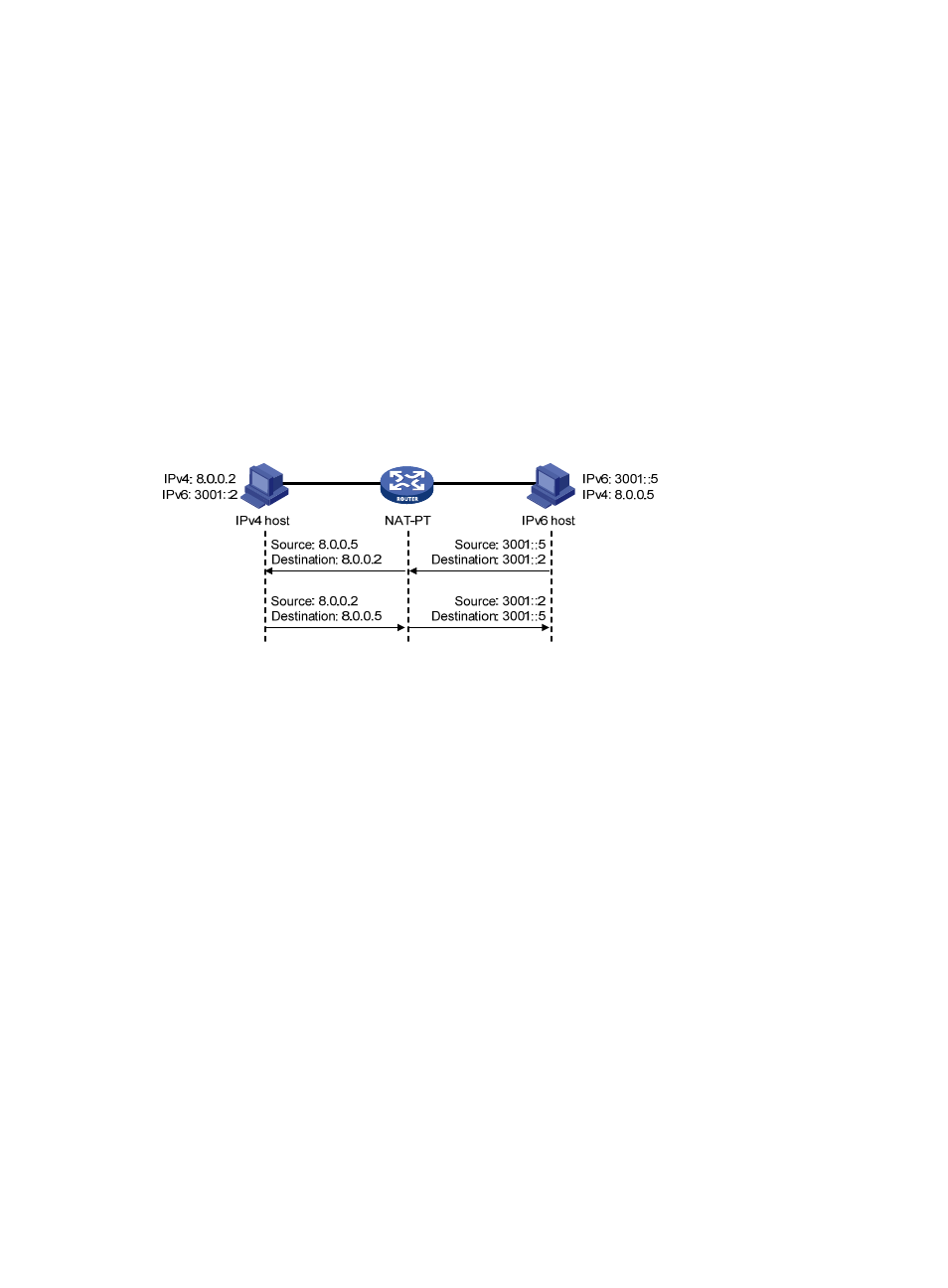
Figure 30 NAT-PT implementation (session initiated by an IPv6 host)
NAT-PT works as follows:
1.
Determines whether to perform NAT-PT or not.
Upon receiving a packet from an IPv6 host to an IPv4 host, the NAT-PT device detects the prefix of
the destination IPv6 address in the packet. If the prefix is the same as the configured NAT-PT prefix,
the device considers that the packet needs to be forwarded to the IPv4 network and NAT-PT needs
to be performed.
2.
Translates the source IP address.
The NAT-PT device translates the source IPv6 address of the packet into an IPv4 address according
to the static or dynamic mapping on the IPv6 side.
3.
Translates the destination IP address.
The NAT-PT device translates the destination IPv6 address of the packet into an IPv4 address
according to the static mapping, if configured, on the IPv4 network side. Without any static
mapping configured on the IPv4 network side, if the lowest 32 bits of the destination IPv6 address
in the packet can be directly translated into a valid IPv4 address, the destination IPv6 address is
translated into that IPv4 address. Otherwise, the translation fails.
4.
Forwards the packet and stores the mappings.
After the source and destination IPv6 addresses of the packet are translated into IPv4 addresses,
the NAT-PT device forwards the packet to the IPv4 host. Meanwhile, the IPv4/IPv6 address
mappings are stored in the NAT-PT device.
5.
Forwards the reply packet according to the stored mappings.