7 final shaft alignment check, 8 electrical connections – Flowserve L Worthington Simpson User Manual
Page 16
L and U USER INSTRUCTIONS ENGLISH 85392721 07-12
Page 16 of 36
flowserve.com
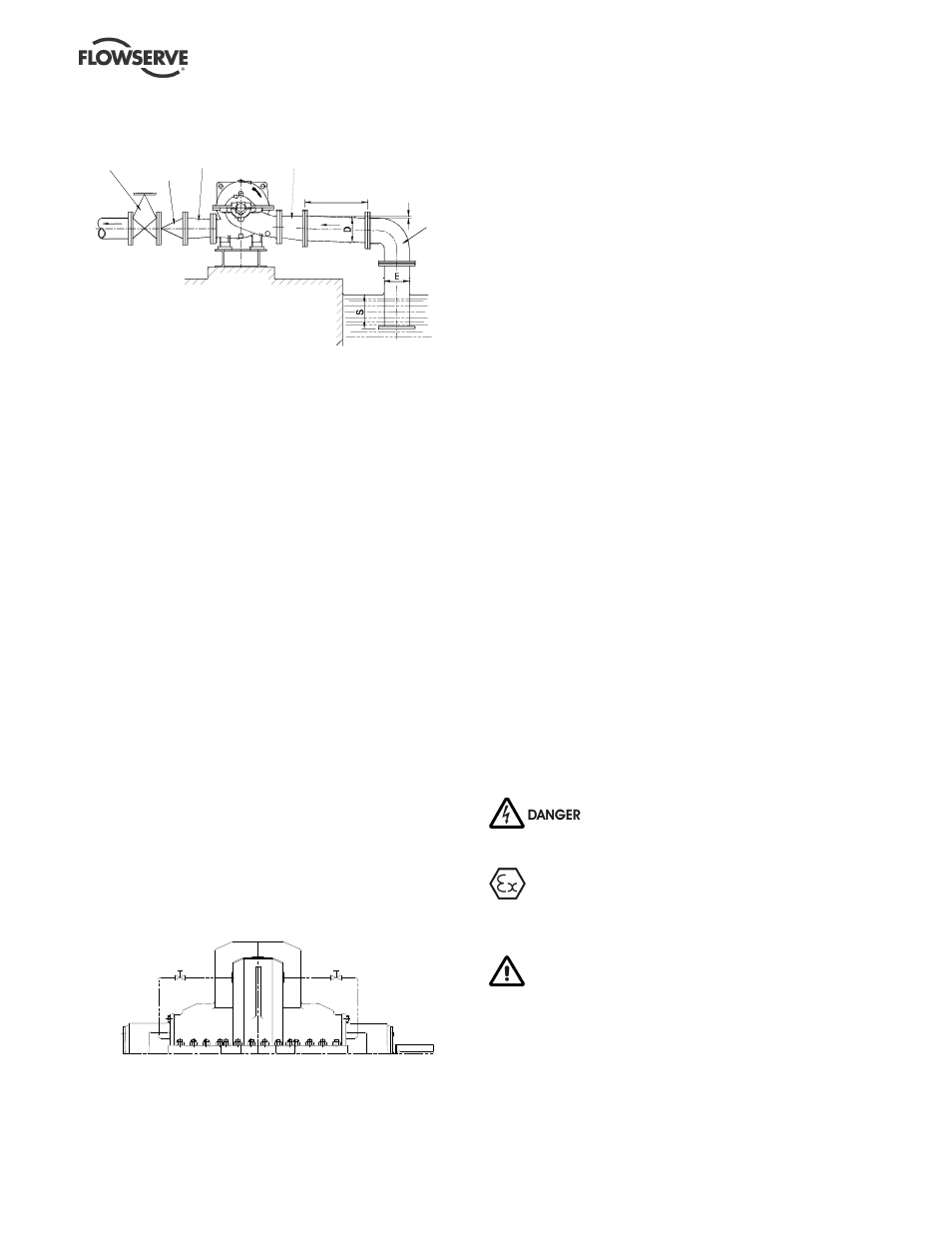
Typical design – suction lift
Notes:
1. S = Minimum submergence >3E.
2. Ideally reducers to be limited to one pipe diameter change,
i.e. 150 mm (6 in.) to 200 mm (8 in.). Must have a maximum
total angle of
divergence of 15 degrees.
4.6.4
Discharge piping
See section 4.6.3 for typical pipework design.
A non-return valve should be located in the discharge
pipework to protect the pump from excessive back
pressure and hence reverse rotation when the unit is
stopped.
Pipework reducers should have a maximum total
angle of divergence of 9 degrees.
Fitting an isolation valve will allow easier maintenance.
4.6.5
Auxiliary piping
4.6.5.1
Drains
Pipe pump casing drains and gland leakage to a
convenient disposal point.
4.6.5.2
Pumps fitted with packed gland
When suction pressure is below ambient pressure it
is necessary to feed the gland packing with liquid to
provide lubrication and prevent the ingress of air.
This is normally achieved with a supply from the
pump discharge volute to the stuffing box. A control
valve or orifice plate may have been fitted into the
supply line to control the pressure to the
gland/stuffing box.
If the pumped liquid is dirty and cannot be used for
sealing, a separate clean compatible liquid supply to
the gland at 1 bar (15 psi) above suction pressure is
recommended.
4.6.5.3
Pumps fitted with mechanical seals
Single seals requiring re-circulation will normally be
provided with the auxiliary piping from pump casing
already fitted.
If the seal requires an auxiliary quench then a
connection must be made to a suitable source of
liquid flow, low pressure steam or static pressure from
a header tank. Recommended pressure is 0.35 bar
(5 psi) or less. Check General arrangement drawing.
Special seals may require different auxiliary piping to
that described above. Consult separate User
Instructions and or Flowserve if unsure of correct
method or arrangement.
For pumping hot liquids, to avoid seal damage, it is
recommended that any external flush/cooling supply
be continued after stopping the pump.
4.6.6
Final checks
Check the tightness of all bolts in the suction and
discharge pipework. Check also the tightness of all
foundation bolts.
4.7 Final shaft alignment check
After connecting piping to the pump, rotate the shaft
several times by hand to ensure there is no binding
and all parts are free.
Recheck the coupling alignment, as previously
described, to ensure no pipe strain. If pipe strain
exists, correct piping.
4.8 Electrical connections
Electrical connections must be made
by a qualified Electrician in accordance with relevant
local, national and international regulations.
It is important to be aware of the EUROPEAN
DIRECTIVE on potentially explosive areas where
compliance with IEC60079-14 is an additional
requirement for making electrical connections.
It is important to be aware of the EUROPEAN
DIRECTIVE on electromagnetic compatibility when
wiring up and installing equipment on site. Attention
must be paid to ensure that the techniques used during
wiring/installation do not increase electromagnetic
emissions or decrease the electromagnetic immunity of
the equipment, wiring or any connected devices. If in
any doubt contact Flowserve for advice.
Discharge
isolating
valve
Non
return
valve
Concentric
conical
reducer
Eccentric
conical
reducer
>5D
Long
radius
bend
Slope down
from pump
suction