General information, 1 introduction – Fluke Biomedical 30-471 User Manual
Page 5
General Information
Introduction
1
1-1
Section 1
General Information
This device is intended for use only by persons who
have been trained in the proper interpretation of its
readings and in the appropriate safety procedures
to be followed in the presence of radiation.
These detectors are not designed, nor are they
recommended for use in primary calibration.
1.1 Introduction
The VeriDose Detectors, Models 30-471 through 30-475 and 30-471-8000 through 30-475-8000, are n-
type diodes utilizing a p-n junction and are designed for use as radiation detection devices. These diodes
are encased within a FDA approved polystyrene material. A low noise coaxial cable is used to connect
the diode to an electrometer. In this configuration, these diodes provide enhanced sensitivity,
instantaneous response time and are very rugged. With advantages such as large signal and fast
response, these diodes are ideal for relative measurements in areas of steep dose gradients and relative
absorbed dose in electron beam fields.
The Solid State Radiation Detector Diodes are constructed using a "parallel plate" geometry with planar
electrodes opposing each other at a given spacing. This configuration has many advantages over the
commonly used coaxial cylindrical geometry which have the electrodes being inner and outer shells.
The most obvious advantage is its superior construction and ease of orientation to the radiation beam.
Unlike the cylindrical style diodes where the alignment of the diode's sensitive volume is critical in
relationship to the radiation beam, the sensitive volume of the VeriDose Diode is the entire diode, which
allows for a less stringent alignment to the radiation beam. The hemispherical shape also allows for
easier attachment to the patient. The ideal orientation of the diode within the radiation beam is to have the
beam perpendicular to the diode's horizontal axis. As long as the beam is wider than the diode, full
collection of all ionization produced will occur regardless of the exact position in the active region.
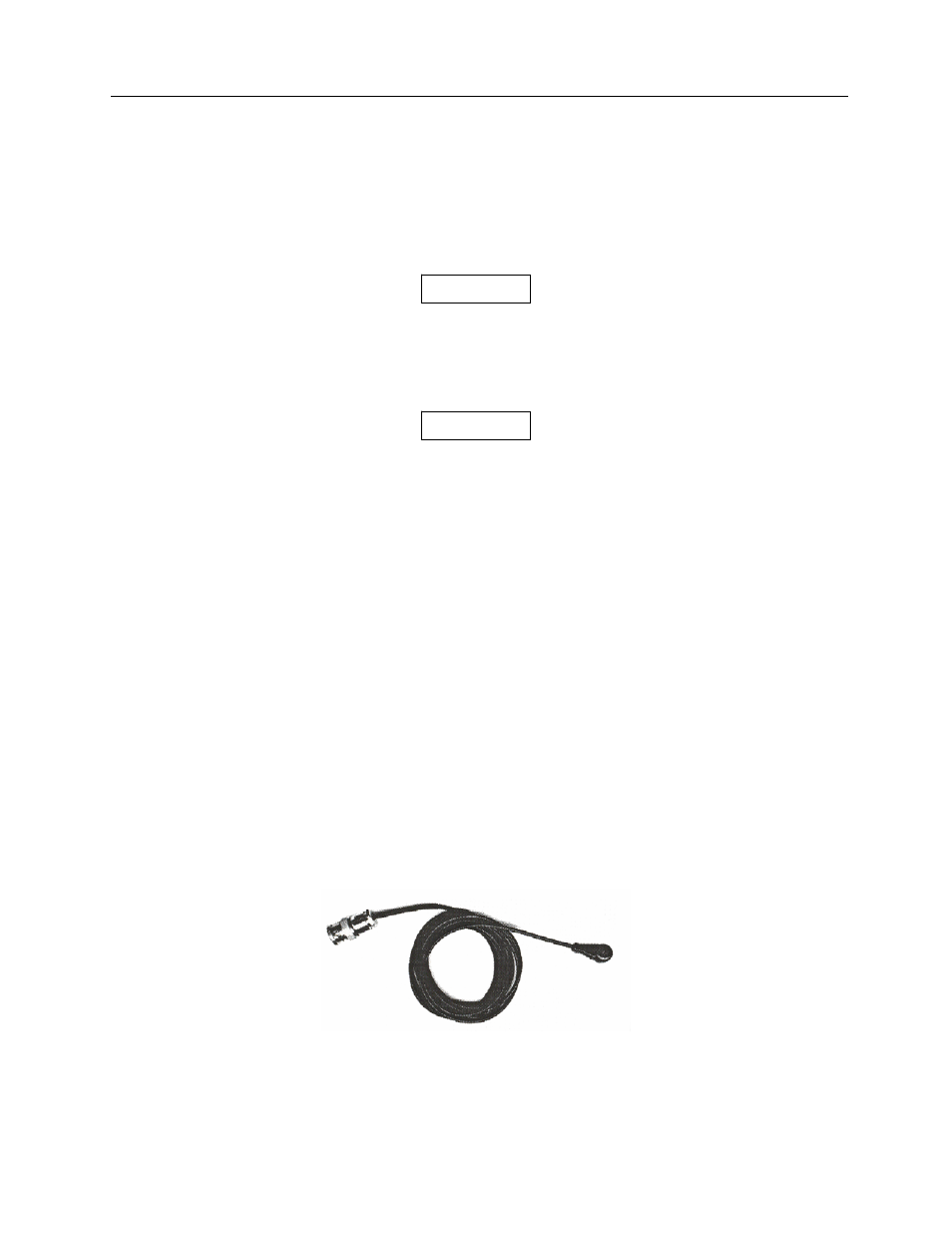
However, for ease of
alignment within a radiation
beam a raised X has been
placed on top of the diode.
Figure 1-1.
General View of the VeriDose Diode
WARNING
CAUTION