Westermo U200 Operator manal User Manual
Page 35
V4.5
www.westermo.com
U/R/T200 series
- 35 -
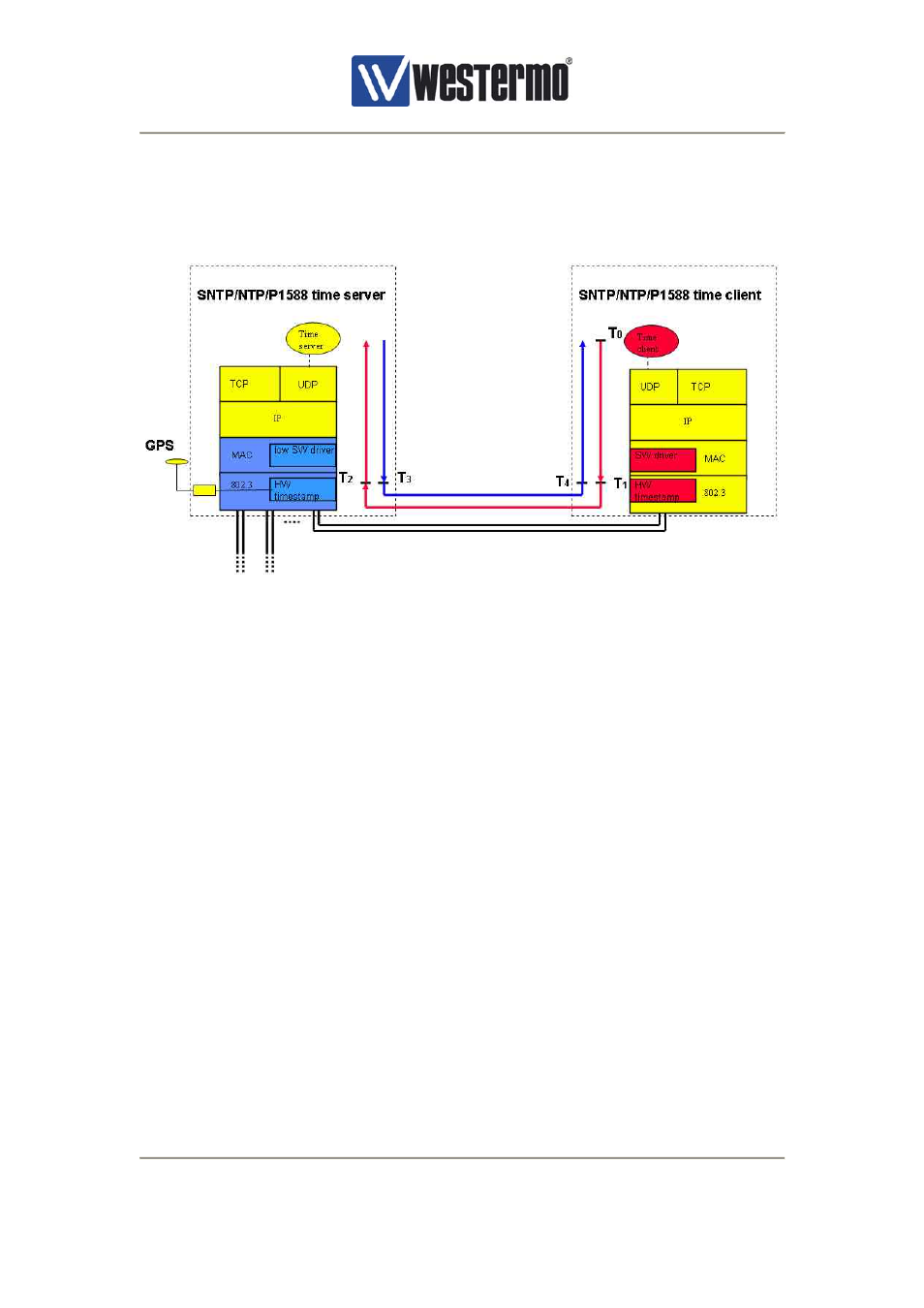
achieved if time stamping on the client is performed in hardware. Westermo OnTime networks
provide intellectual property as part of design in projects together with customers that need
highest possible accuracy. Such an implementation is shown below. This is the preferred
configuration.
Figure 15, OSI model of time server and time client
12.1 IEEE 1588 Grandmaster
The IEEE 1588 Grandmaster will periodically send SYNC and FOLLOW_UP multicast
packets with an interval of two seconds, when the switch is enabled for IEEE 1588
Grandmaster functionality, version 1. The SYNC packet contains no accurate time stamp in
the fraction part of the SYNC transmit time stamp, originTimestamp (nanoseconds), while the
corresponding FOLLOW_UP packet contains this time stamp of the SYNC packet in its
preciseOriginTimestamp
(nanoseconds), i.e. the T3 time stamp (see figure above). The
sequenceId of the SYNC packet and the associatedSequenceId parameter of the
FOLLOW_UP packet are used for pairing the SYNC and the corresponding FOLLOW_UP
packet at the IEEE 1588 Slave implementation connected to the T200. The IEEE 1588
Grandmaster will also respond with a DELAY_RESP packet when a DELAY_REQ packet is
received from an IEEE 1588 Slave. The requestingSourceSequenceId parameter of the
DELAY_RESP packet and the sequenceId parameter of the DELAY_REQ packet is used for
pairing the two packets. The delayReceiptTimestampSec and delayReceiptTimestampFrac
parameters of the DELAY_RESP packet contains the receive time stamp of the DELAY_REQ
packet , i.e. the T2 time stamp (see figure above).
12.2 IEEE1588 Transparent Clock
One of the main properties of the IEEE1588 standard is related to the handling of variable
network latency between the Grand Master clock and the Slave clocks. Thus, the network