H3C Technologies H3C S12500-X Series Switches User Manual
Page 196
182
IBGP peers must be fully meshed to maintain connectivity. If n routers exist in an AS, the number of
IBGP connections is n(n-1)/2. If a large number of IBGP peers exist, large amounts of network and
CPU resources are consumed to maintain sessions.
Using route reflectors can solve this issue. In an AS, a router acts as a route reflector, and other
routers act as clients connecting to the route reflector. The route reflector forwards routing
information received from a client to other clients. In this way, all clients can receive routing
information from one another without establishing BGP sessions.
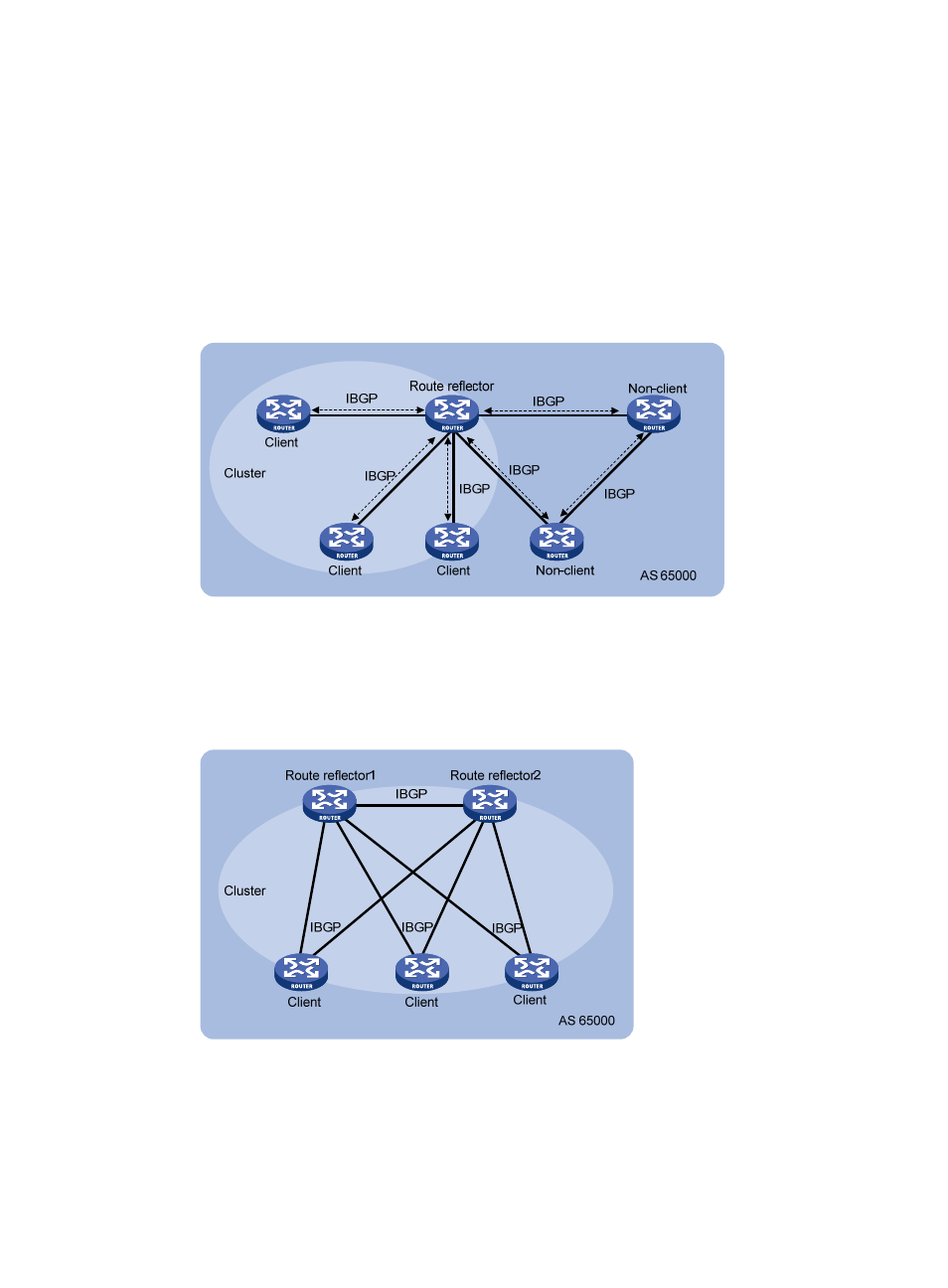
A router that is neither a route reflector nor a client is a non-client, which, as shown in
1063H
Figure 52
,
must establish BGP sessions to the route reflector and other non-clients.
Figure 52 Network diagram for a route reflector
The route reflector and clients form a cluster. Typically a cluster has one route reflector. The ID of
the route reflector is the Cluster_ID. You can configure more than one route reflector in a cluster to
improve availability, as shown in
1064H
Figure 53
. The configured route reflectors must have the same
Cluster_ID to avoid routing loops.
Figure 53 Network diagram for route reflectors
When the BGP routers in an AS are fully meshed, route reflection is unnecessary because it
consumes more bandwidth resources. You can use commands to disable route reflection instead of
modifying network configuration or changing network topology.
After route reflection is disabled between clients, routes can still be reflected between a client and
a non-client.