2 video blocks overview, 3 optical/ electrical input selection – Nevion ARC-SD-XMUX4 User Manual
Page 8
ARC-SD-XMUX4
Rev. B
nevion.com | 8
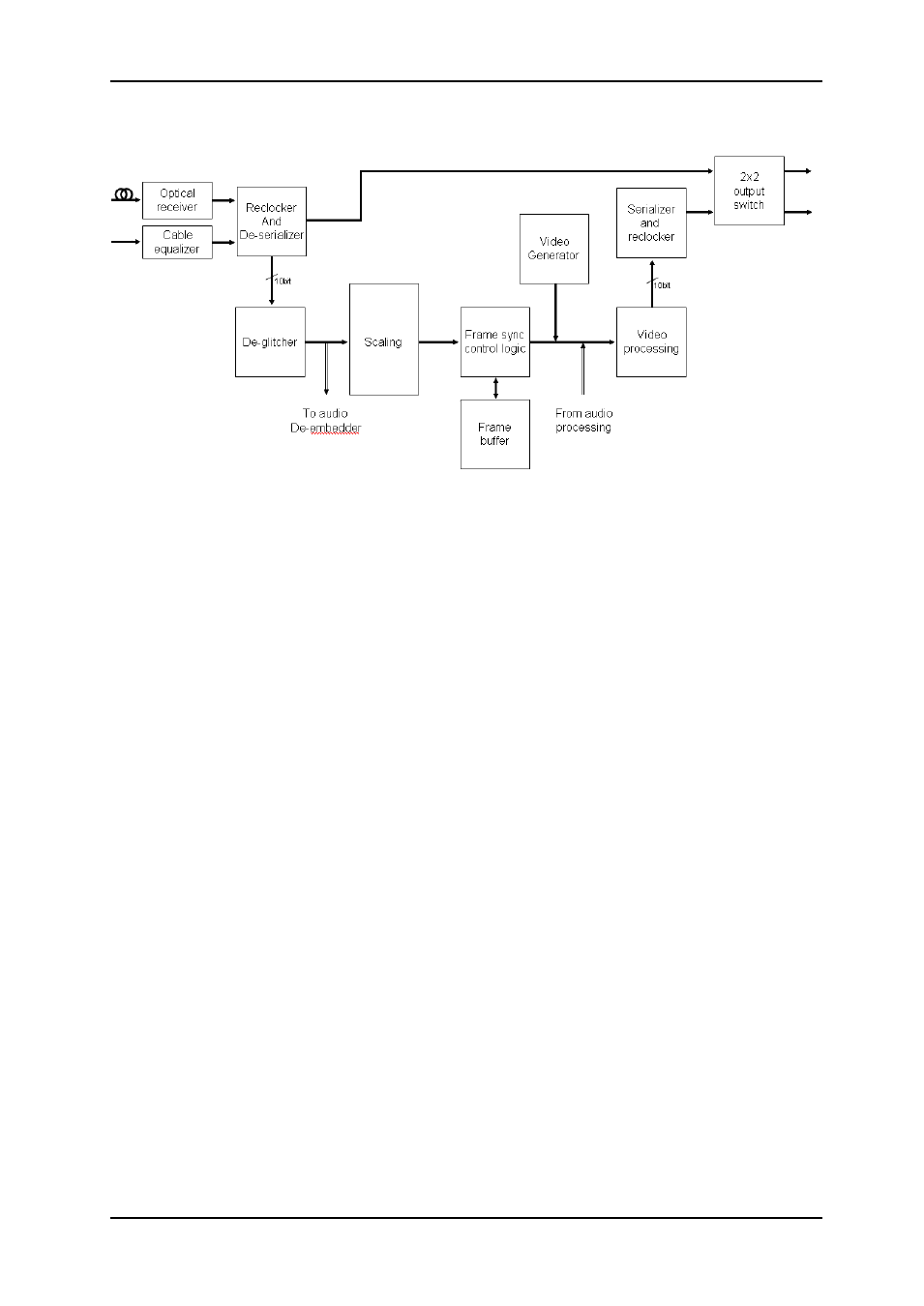
3.2 Video blocks overview
Figure 2: Video block diagram
3.3 Optical/ Electrical input selection
The ARC-SD-XMUX4-R has both an optical and an electrical input. The active input can be
selected either:
1. Automatically based on a prioritized list of inputs and a rule of switching.
2. Manually.
When controlled by DIP switches, the card will use the fall back source and generator
settings saved from the last Multicon GYDA session.
3.3.1 Automatic selection mode
Video in Mode set to auto: There are three priority levels. Each level may be assigned an
input setting; optical, electrical, video generator or mute.
The priority is the order in which the board will look for a valid input. The card will switch to
the next priority after a loss of lock to the input signal.
If the active input is either electrical or optical, and the other is selected as the first priority
(main), the module will not switch back to main unless signal is lost on the active channel, or
the user hits the Latch reset button.
Hold time determines how long a signal has to be missing/out of lock before it is considered
lost. This is useful to avoid switching when the input has intermittent faults.
Lock time determines how long a higher prioritized signal has to be locked before it again
can be considered to be present and stable. This is only active when the module has lost
both optical and electrical video inputs.
If video input disappears
Given that stable SDI input and sync input exists: If the SDI input disappears and Video in is
set to Auto, the board will hold on to the current input for the time set by Hold time whilst
frame freezing.
The board will then select the next input in the priority list (or go up to the main input, if no
fallback exists).