Timing analysis, Timing analysis at i/o, Soft cdr mode and dpa-fifo mode rx – Altera LVDS SERDES User Manual
Page 20: Non-dpa mode rx and receiver skew margin (rskm)
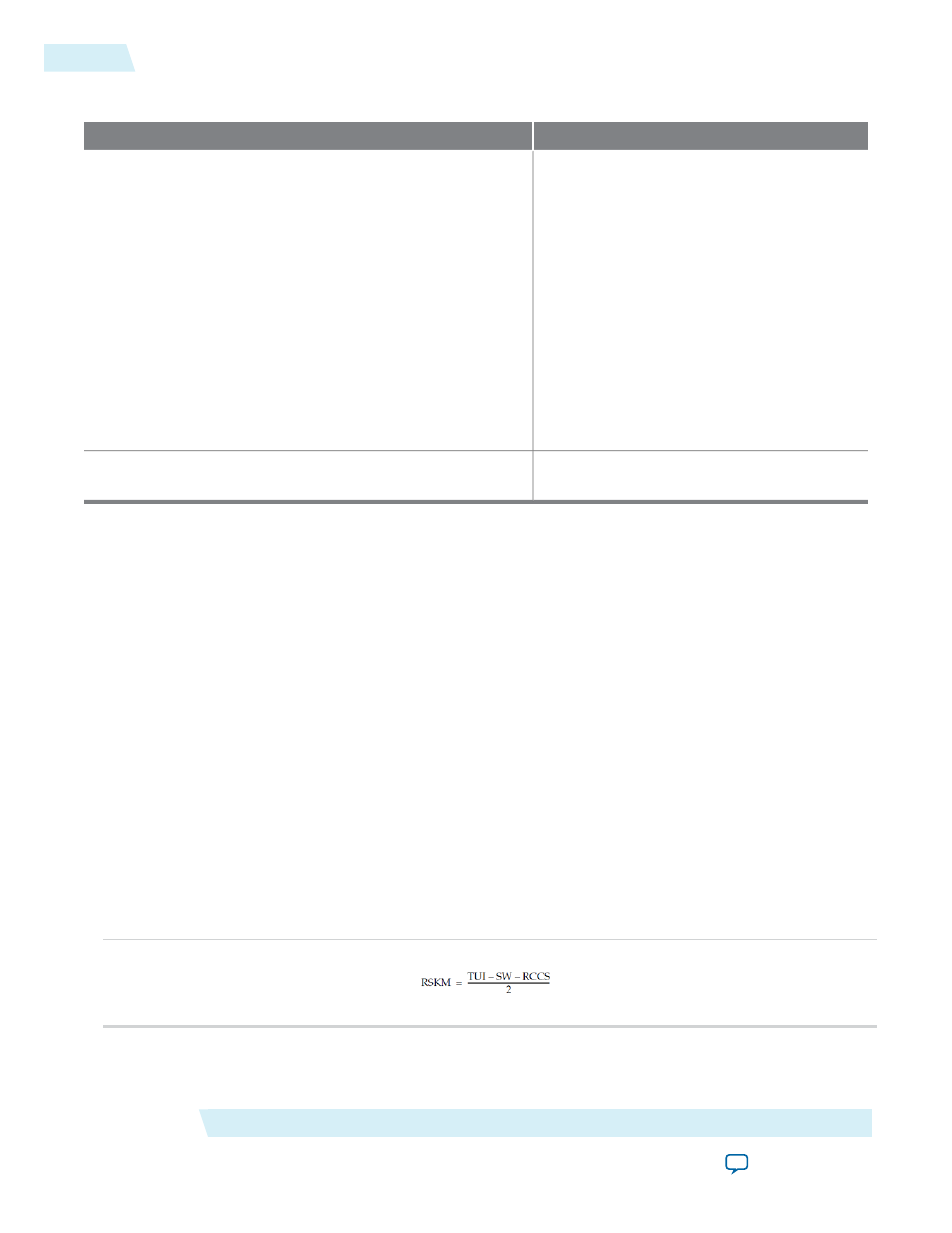
Table 7: Timing Files
Description
File
This .sdc allows the Fitter to optimize timing
margins with timing driven compilation. Also
allows the TimeQuest timing analyzer to
analyze the timing of your design.
The IP core uses the .sdc for the following
operations:
• Creating clocks on PLL inputs
• Creating generated clocks
• Calling
derive_clock_uncertainty
• Creating proper multi-cycle constraints
You can locate this file in the .qip generated
during the IP generation.
<variation_name>_altera_lvds_core20_140_<random_id>
.sdc
This .tcl file is a library of functions and
procedures that the .sdc uses.
sdc_util.tcl
Timing Analysis
Timing Analysis at I/O
This section describes the timing analysis at the I/O interfacing external devices.
Soft CDR Mode and DPA-FIFO Mode RX
In soft CDR and DPA-FIFO mode, the receiving data is captured dynamically by the DPA hardware. As a
result, the TimeQuest Timing Analyzer does not perform static timing analysis at the I/O.
Non-DPA Mode RX and Receiver Skew Margin (RSKM)
Changes in the system environment, such as temperature, media (cable, connector, or PCB), and loading,
affect the receiver's setup and hold times; internal skew affects the sampling ability of the receiver.
In non-DPA mode, use receiver skew margin (RSKM), receiver channel-to-channel skew (RCCS), and
sampling window (SW) specifications to analyze the timing for high-speed source-synchronous differential
signals in the receiver data path. The following equation shows the relationship between RSKM, RCCS, and
SW.
Figure 11: RSKM
Altera LVDS SERDES IP Core User Guide
Altera Corporation
ug_altera_lvds
Timing Analysis
20
2014.08.18