Vectronics VEC-1220K User Manual
Page 31
VEC-1220K/1230K/1240K/1280K Owner's
Manual
29
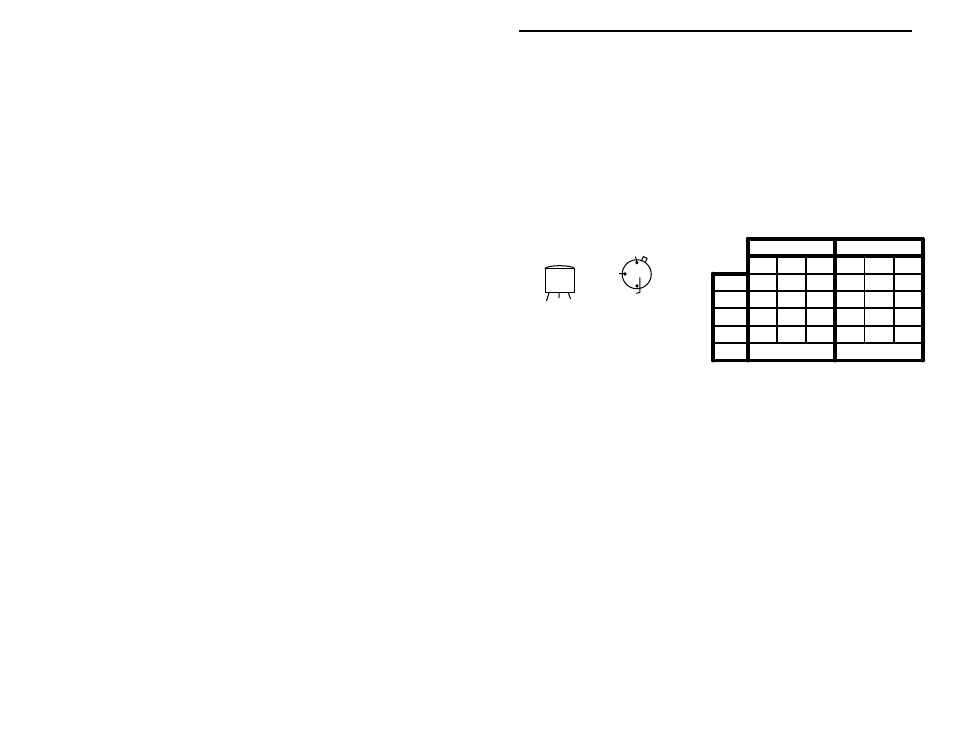
Voltage Analysis: Voltage analysis is a great way to pinpoint circuit problems.
To do this, you'll need a voltmeter or DVM. Clip the black lead (-) to ground
and use the red (+) probe to check the DC voltage at each transistor lead. Before
you begin, disable oscillator Q2 by switching the crystal select switch "in". This
will remove the crystal from the oscillator circuit and prevent the transmitter
from generating RF while you're attempting to make DC voltage measurements.
Compare your readings against the chart below. They should agree to within 10-
15%. If you observe one or more "bad" readings, this may mean the device
you're checking is blown--or that an incorrectly-installed part is lurking near-by.
Try using the transmitter's schematic diagram to trace out the exact cause of the
problem.
E B C
E
B
C
(Collector is on Case)
(Emitter is grounded)
2N3053
Top View
2N3906-Q1
2N3904-Q2
PN2222-Q3
Front View
Q1
Q2
Q3
Q4
E
B
C
E
B
C
Standby
Key-Down
D2
13.8
13.2
0
13.8
13.0
13.6
0
0
0
5.7
6.3
12.6
0
0
13.8
0
.7
7.5
0
0
13.8
0
0
13.8
(banded end) 2.2
(banded end) 12.9
VOLTAGE CHART
Important Note: Crystal Select Switch MUST be
pushed in to disable oscillator. Unit must not
generate RF during these checks!
Q4
If these checks fail to uncover the problem, repeat the "QC" check one more
time. Service records show that, for most malfunctioning kits, outright
component failure is relatively rare. In most cases, the culprit is a misplaced
part, reverse-polarized capacitor or diode, improperly installed transistor, or a
faulty solder connection! If, despite your best effort, you cannot solve a problem
with your radio, kit repair services are available through Vectronics. See the
warranty on the inside front cover for complete instructions.