4 gimbal angle y (0x2044 = 3), 5 explanatory example – ifm electronic JN2301 User Manual
Page 15
UK
Inclination sensor JN
15
be detected by the inclination sensor� In this condition the "inclination value lateral"
is insignificant� In practice, the "inclination value lateral" will vary very strongly
when it is close to this condition even if there is only little movement�
9.4 Gimbal angle Y (0x2044 = 3)
This setting corresponds to the setting described in 9�3 with the difference that the
order of the two rotations is now inverted�
In this option the measured object is first rotated about its X axis with the angle
[°] "inclination value lateral"� The measured object is then rotated about the Y axis
(which is now inclined) with the angle value [°] indicated by the "inclination value
longitudinal" of the sensor�
As a result of this the measured values of the gimbal angle X and the gimbal angle
Y are identical as long as the measured object is only rotated about one of the
sensor's axes� The measured values of the two options do not differ until a general
rotation is made about the two sensitivity axes�
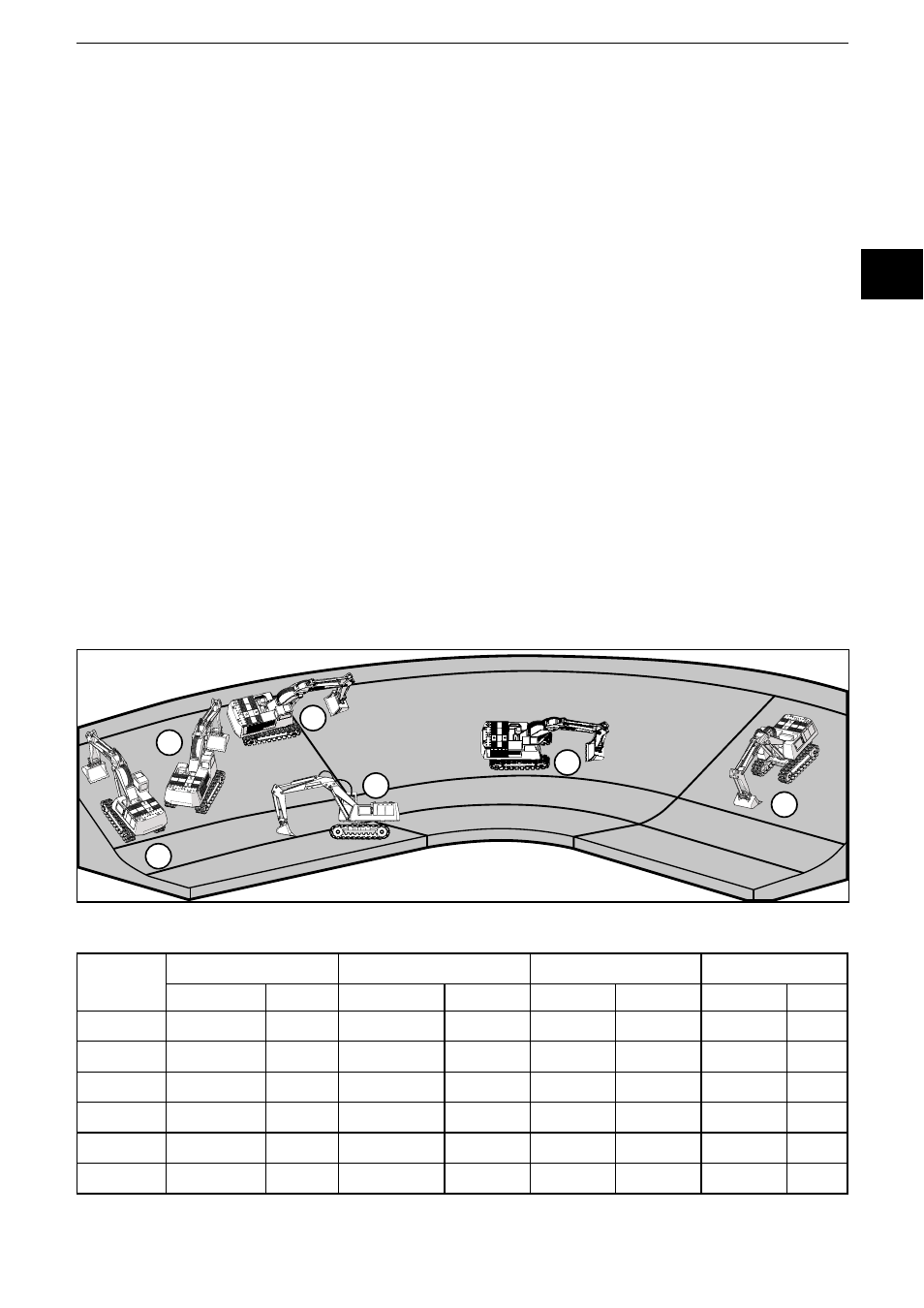
9.5 Explanatory example
The different angle definitions will be illustrated using a simple example� An
excavator moves up and down an embankment (illustration)� The embankment is
angled at 30°� The inclination sensor is installed so that the positive Y axis of the
sensor shows in driving direction of the excavator�
1
2
3
4
5
6
Excavator
position
Perpendicular angle
Euler
Gimbal X
Gimbal Y
Longitudinal
Lateral
Longitudinal
Lateral
Longitudinal
Lateral
Longitudinal
Lateral
1
0°
0°
0°
Undefined
0°
0°
0°
0°
2
0°
-30°
30°
0°
0°
-30°
0°
-30°
3
20°
-20°
30°
45°
20°
-22°
22°
-20°
4
30°
0°
30°
90°
30°
0°
30°
0°
5
30°
0°
30°
90°
30°
0°
30°
0°
6
0°
30°
30°
180°
0°
30°
0°
30°