5 functional description, 1 data path, 2 video input selection – Nevion FRS-HD-XMUX4 User Manual
Page 15
FRS-HD-XMUX4
Rev. C
nevion.com | 15
5 Functional description
5.1 Data path
HD/SD-SDI input is selected from either optical or electrical input and equalized, re-
clocked and de-serialized and transferred to a processing unit called an FPGA. In the
FPGA the signal is first sent through a de-glitcher that cleans up errors that might
appear on the video lines, for instance due to switching. After the video is de-glitched, it
is sent along two different paths; it is sent to a frame-store buffer, and to the audio de-
embedder.
The 16 audio channels coming from the de-embedder are bundled in pairs and sent to
an audio buffer. The audio is fetched from the audio buffer according to a user
specified delay and sent to an Audio cross point. The audio from the Audio cross point
can be any pair of audio channels de-embedded from the incoming video stream, AES
inputs, an internal 1
kHz sine or a muted signal. “Muted signal” means that even
though there’s silence, there’s still a legal audio stream present, which makes it
different from Delete (for embedded channels) and Outputs Off (for AES outputs). From
the cross point outputs each channel pair enters an Audio Processing Block, where the
paired channels may be shuffled. After the audio processing block the audio enters the
Audio Embedder.
The video (with audio still inserted) is fetched from the frame buffer with the user
specified delay and sent to a Video processing block followed by an EDH processing
block. After the EDH block the video and audio is embedded according to the user
settings and the video is sent from the FPGA to a serializer that re-clocks the data and
output the SDI to a buffered output switch.
The buffered output switch is a 2x2 cross point with input 1 being the equalized and re-
clocked input (non-processed) and input 2 being the output of the video processing.
The two outputs are then sent to two paired sets (non-inverting and inverting) of
outputs.
There are also 4 I/O ports for AES. These can be setup to be either inputs, outputs or a
mix. The outputs are taken from the Audio cross point and can be any stereo pair of
audio channels embedded on the incoming video stream, the internal 1 kHz sine
generator or the internal “black sound” generator. The inputs are routed through
optional audio delay and sample rate converter before it goes to the audio crosspoint.
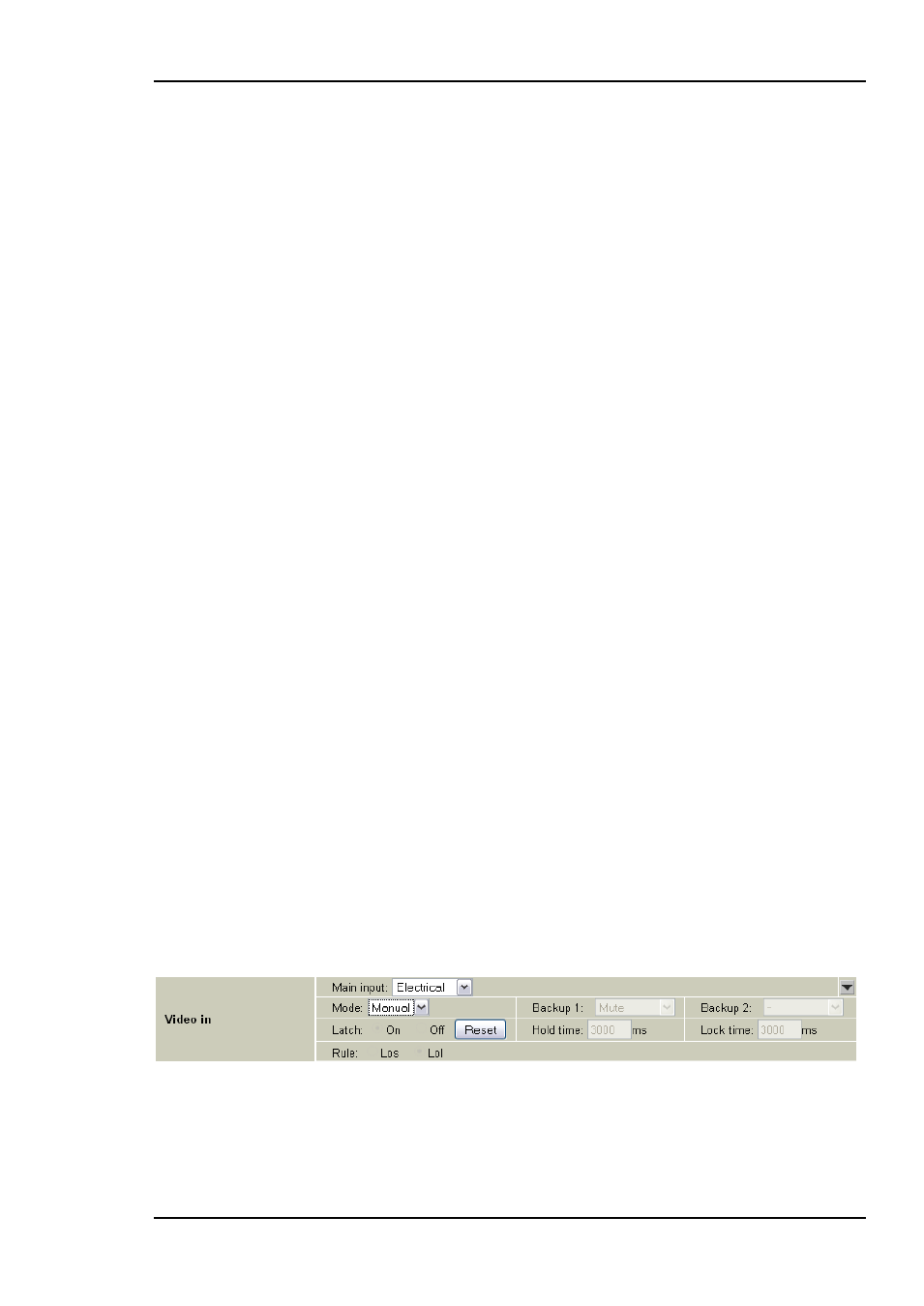
5.2 Video input selection
The FRS-HD-XMUX4 has one electrical and one optical input. The input can be chosen
either by an automatic selection with priorities and rule of switching, or by manual
selection.
Manual selection mode
Figure 5: Multicon GYDA view of electrical input selected in manual mode.