H3C Technologies H3C MSR 50 User Manual
Page 4
1-3
l)
Active scanning is used by clients to scan surrounding wireless networks and locate a compatible one.
Active scanning falls into two modes according to whether a specified SSID is carried in a probe
request.
z
A client sends a probe request (with the SSID null): The client prepares a list of channels and
broadcasts a probe request frame on each of them. APs that receive the probe request send a
probe response. The client associates with the AP with the strongest signal. This active scanning
mode enables a client to know whether an AP can provide wireless services.
Figure 1-2 Active scanning (the SSID of the probe request is nul
AP 2
Client
AP 1
Prob
e Re
ques
t
(SSI
D=n
ull)
ProbeR
equest
(SSID=
null)
Probe R
espons
e
z
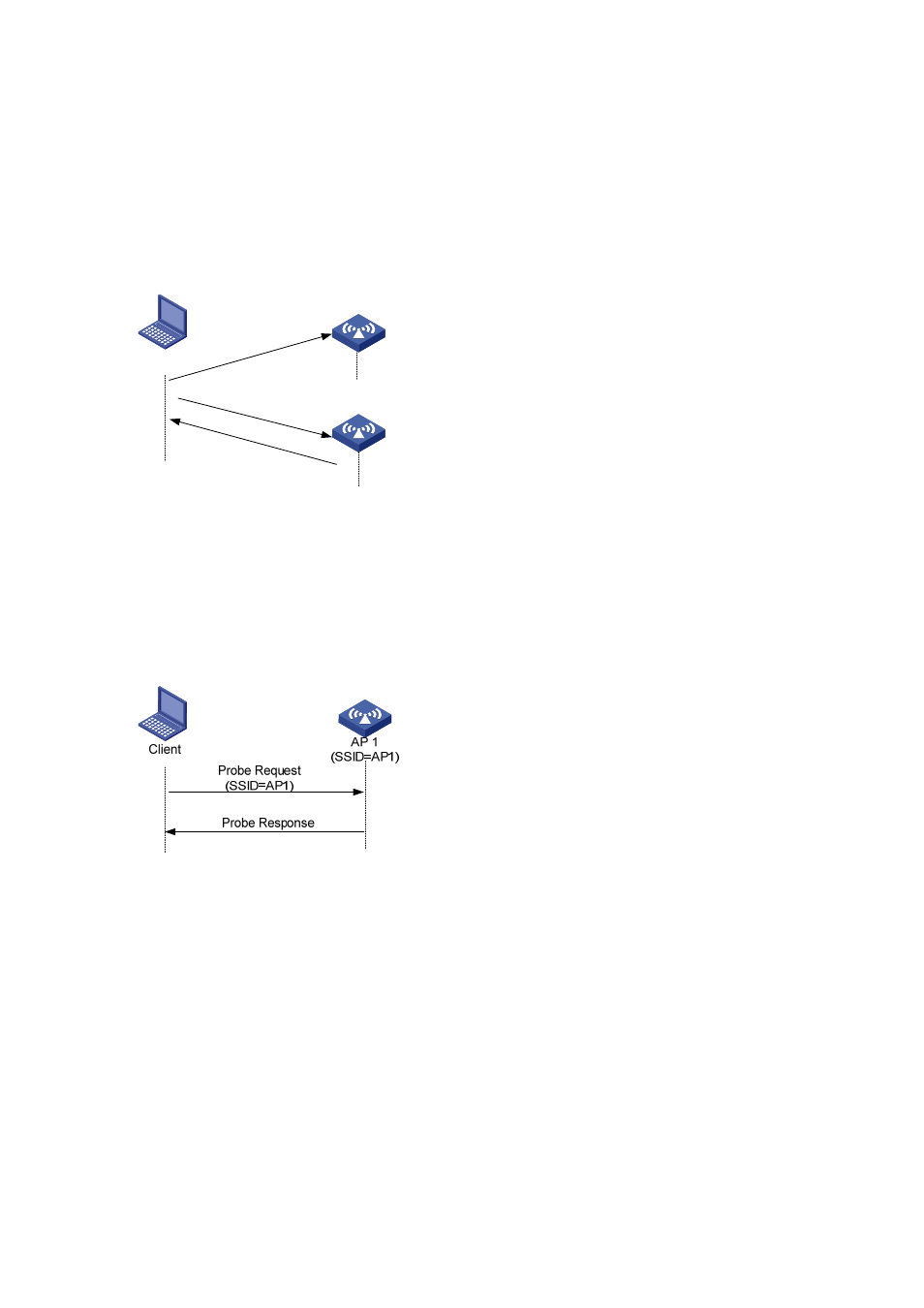
A client sends a probe request (with a specified SSID): In this case, the client only unicasts a probe
request because the probe request it sends carries the specified SSID. When an AP receives the
probe request, it sends a probe response. This active scanning mode enables a client to access a
specified wireless network.
Figure 1-3 Active scanning (the probe request carries the specified SSID)
2) Passive
scanning
Passive scanning is used by clients to discover surrounding wireless networks through listening to the
beacon frames periodically sent by an AP. The client prepares a list of channels and listens to beacons
on each of these channels. In this case, the AP needs to periodically broadcast beacon frames. Passive
scanning is used by a client when it wants to save battery power. Typically, VoIP clients adopt the
passive scanning mode.