Raid 6 – Avago Technologies 3ware SAS 9750-4i User Manual
Page 19
Understanding RAID Levels and Concepts
www.lsi.com/channel/products
11
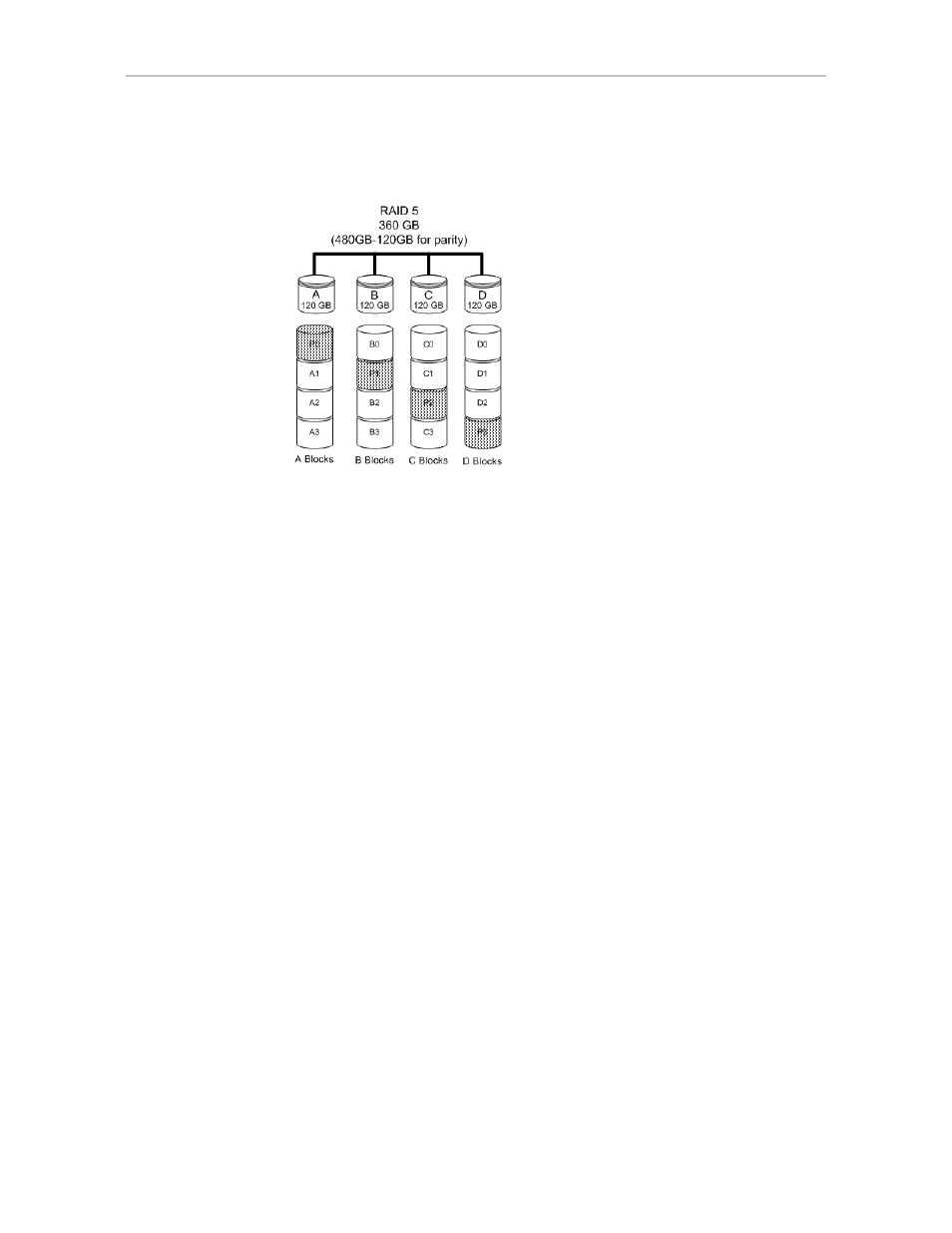
RAID 5 is able to tolerate 1 drive failure in the unit.
Figure 3. RAID 5 Configuration Example
RAID 6
RAID 6 provides greater redundancy and fault tolerance than RAID 5. It is
similar to RAID 5, but has two blocks of parity information (P+Q) distributed
across all the drives of a unit, instead of the single block of RAID 5.
Due to the two parities, a RAID 6 unit can tolerate two hard drives failing
simultaneously. This also means that a RAID 6 unit may be in two different
states at the same time. For example, one sub-unit can be degraded, while
another may be rebuilding, or one sub-unit may be initializing, while another
is verifying.
The 3ware implementation of RAID 6 requires a minimum of five drives.
Performance and storage efficiency also increase as the number of drives
increase.