Flowserve MARK 3 GROUP 4 User Manual
Page 36
MARK 3 GROUP 4 USER INSTRUCTIONS ENGLISH 71569286 08-12
Page 36 of
48
flowserve.com
®
d) Bearing seals are not totally leak free devices.
Oil from these may cause staining adjacent to
the bearings.
6.9.6
Installed pump
Complete pump installed.
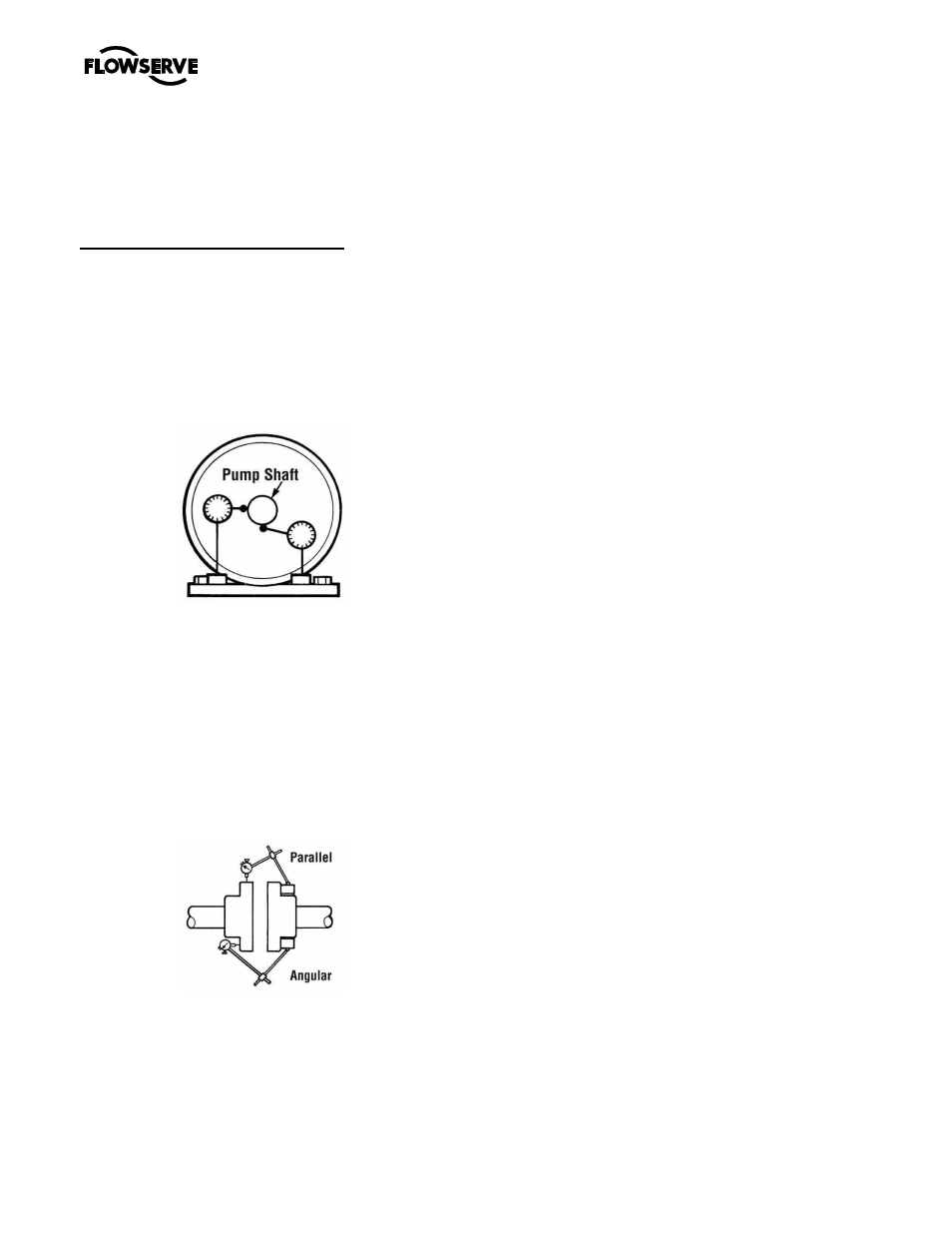
Shaft movement caused by pipe strain
Pipe strain is any force put on the pump casing by
the piping. Pipe strain should be measured as shown
below. Install the indicators as shown before
attaching the piping to the pump. The suction and
discharge flanges should now be bolted to the piping
separately while continuously observing the
indicators. Indicator movement should not exceed
0.05 mm (0.002 in.).
Pipe strain movement
Alignment
Misalignment of the pump and motor shafts can
cause the following problems:
•
Failure of the mechanical seal
•
Failure of the motor and/or pump bearings
•
Failure of the coupling
•
Excessive vibration/noise
The schematics below show the technique for a
typical rim and face alignment using a dial indicator.
It is important that this alignment be done after the
flanges are loaded, and at typical operating
temperatures.
Many companies today are using laser alignment
which is a more sophisticated and accurate
technique. With this method a laser and sensor
measure misalignment. This is fed to a computer with
a graphic display that shows the required adjustment
for each of the motor feet.
See section 4.8 for recommended final shaft
alignment limits.
Vibration analysis
Vibration analysis is a type of condition monitoring
where a pump’s vibration “signature” is monitored on
a regular, periodic basis. The primary goal of
vibration analysis is extension on MTBPM. By using
this tool Flowserve can often determine not only the
existence of a problem before it becomes serious,
but also the root cause and possible solution.
Modern vibration analysis equipment not only detects
if a vibration problem exists, but can also suggest the
cause of the problem. On a centrifugal pump, these
causes can include the following: unbalance,
misalignment, defective bearings, resonance,
hydraulic forces, cavitation and recirculation. Once
identified, the problem can be corrected, leading to
increased MTBPM for the pump.
Flowserve does not make vibration analysis
equipment, however Flowserve strongly urges
customers to work with an equipment supplier or
consultant to establish an on-going vibration analysis
program. See 5.7.5 regarding acceptance criteria.
6.10 Assembly
To assemble the pump consult the sectional
drawings, see section 8,
Parts list and drawings
.
Ensure threads, gasket and O-ring mating faces are
clean. Apply thread sealant to non-face sealing pipe
thread fittings.
6.10.1 Bearing housing
a) Lubricate the internal bores of the bearing frame
[3130] with the same oil or grease used to
lubricate the bearings.
b) Install the thrust bearing housing [3240] in the
bearing frame [3130] to ensure a good sliding fit.
Remove the thrust bearing housing from the
frame.
c) Install the oil sight gauge [3856] and the drain lug
in the bearing frame [3130] using Teflon pipe
thread sealant. Install the vent plug [6521].
6.10.2 Line bearing
a) Pack the line bearing with grease if the bearings
are being grease lubricated.
b) Lightly lubricate the shaft [2110] at the line
bearing position. Install the line bearing [3011]
on the shaft. Use an induction heated or hot oil
bath to first heat the bearing [250
°
F