Configuring congestion management, Overview, Causes, impacts, and countermeasures of congestion – H3C Technologies H3C WX3000E Series Wireless Switches User Manual
Page 46: Congestion management policies
37
Configuring congestion management
Overview
Causes, impacts, and countermeasures of congestion
Congestion occurs on a link or node when traffic size exceeds the processing capability of the link or
node. It is typical of a statistical multiplexing network and can be caused by link failures, insufficient
resources, and various other causes.
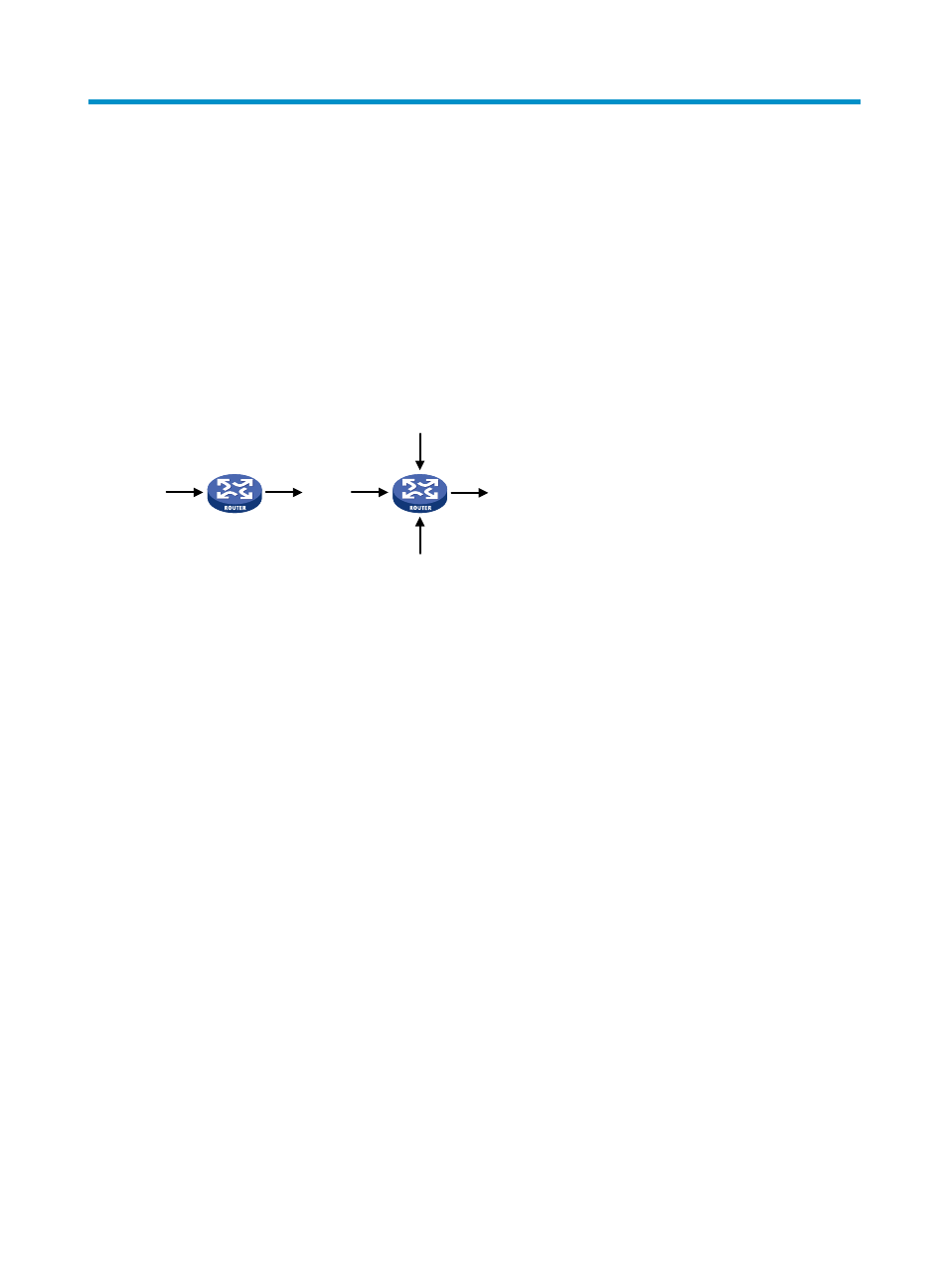
shows two common congestion scenarios:
Figure 10 Traffic congestion causes
Congestion may bring these negative results:
•
Increased delay and jitter during packet transmission
•
Decreased network throughput and resource use efficiency
•
Network resource (memory in particular) exhaustion and even system breakdown
Congestion is unavoidable in switched networks or multi-user application environments. To improve the
service performance of your network, you must take measures to manage and control it.
One major issue that congestion management deals with is how to define a resource dispatching policy
to prioritize packets for forwarding when congestion occurs.
Congestion management policies
Queuing is a common congestion management technique. It classifies traffic into queues and picks out
packets from each queue by using a certain algorithm. Various queuing algorithms are available, and
each addresses a particular network traffic problem. Your choice of algorithm affects bandwidth
assignment, delay, and jitter significantly.
Congestion management involves queue creating, traffic classification, packet enqueuing, and queue
scheduling. Queue scheduling treats packets with different priorities differently to transmit high-priority
packets preferentially.
This section briefly describes several common queue-scheduling mechanisms.
100M > 10M
(100M + 10M + 50M) > 100M
100M
100M
100M
50M
10M
10M
(1)
(2)