Irf split, Irf merge, Member priority – H3C Technologies H3C S12500 Series Switches User Manual
Page 15: Master election
7
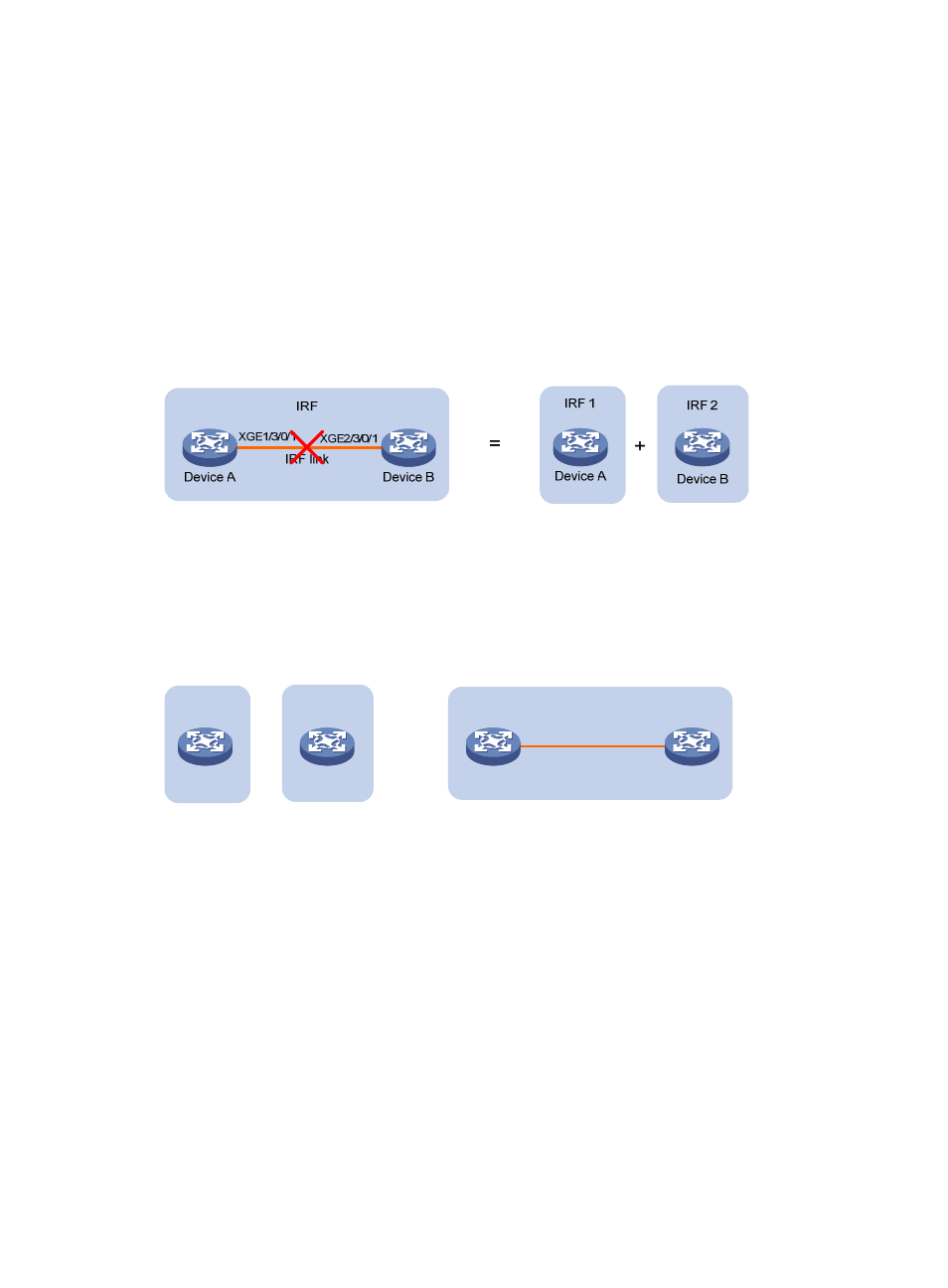
IRF split
IRF split occurs when an IRF fabric breaks up into two or more IRF fabrics because of IRF link failures, as
shown in
. The split IRF fabrics operate with the same IP address and cause routing and
forwarding problems on the network.
When you install the card where a physical IRF port resides, IRF split might occur. When you remove this
kind of card, make sure there are at least two physical IRF ports in UP state on the member device, and
they are not on the same card.
To quickly detect a multi-active collision, configure at least one MAD mechanisms (see "
").
Figure 5 IRF split
IRF merge
IRF merge occurs when two split IRF fabrics reunite or when you configure and connect two independent
IRF fabrics to be one IRF fabric, as shown in
.
Figure 6 IRF merge
Member priority
Member priority determines the possibility of a member device to be elected the master. A member with
higher priority is more likely to be elected the master.
The default member priority is 1. You can change the member priority of a member device to affect the
master election result.
Master election
Master election is held each time the IRF fabric topology changes, for example, when the IRF fabric is
established, the master device fails or is removed, or the IRF fabric splits, or IRF fabrics merge. Master
election does not occur when two split IRF fabrics merge.
Master election uses the following rules in descending order:
IRF link
XGE1/3/0/1
XGE2/3/0/1
Device A
Device B
Device A
Device B
IRF 1
IRF 2
IRF
+
=