2 general information on the data interfaces, 1 rs-232-c/v.24 interface, 1 hardware – HEIDENHAIN SHB Data Interfaces for HEIDENHAIN User Manual
Page 6: 2 signal levels, General information on the data interfaces, Rs-232-c/v.24 interface 2.1.1, Hardware, Signal levels
June 2011
2 – 7
2 General Information on the Data Interfaces
2.1 RS-232-C/V.24 Interface
RS-232-C is the designation of a serial interface for transfer rates of up to 19,200 bps based on
the American EIA standard of the same name. Data transfer is executed asynchronously, with a
start bit before each character and one or two stop bits after each character.
The interface is designed for transmission distances of up to 30 meters.
The RS-232-C interface has been adopted with slight modifications and introduced into Europe
as the V.24 interface. The relevant German standard is DIN 66020.
2.1.1 Hardware
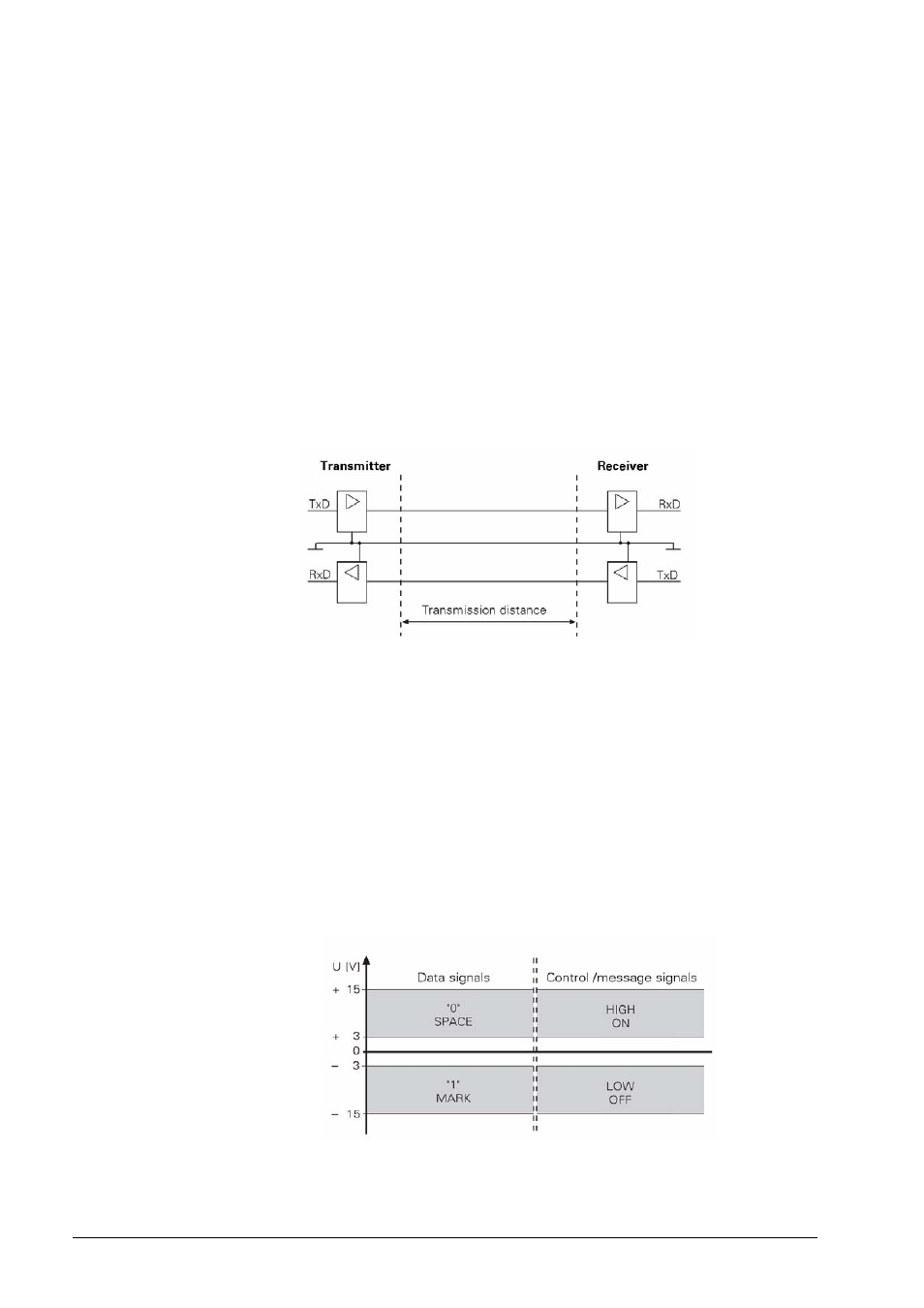
The physical connection between two RS-232-C/V.24 interfaces is an asymmetrical line, i.e. the
common ground connection between transmitter and receiver is used as a return wire.
Physical connections:
2.1.2 Signal levels
With the RS-232-C/V.24 interface one must differentiate between two different signal lines and
their levels.
Data lines:
The data signals are defined as being logical one (MARK) over the range –3 V to +15 V and
logical zero (SPACE) over the range +3 V to +15 V.
Control and signal lines:
These signals are defined as being ON (High) over the range +3 V to +15 V and as OFF (Low)
over the range –3 V to –15 V.
For all of the signals, the voltage range from –3 V to +3 V is not defined as a logic level and can
therefore not be evaluated.