Theory of operation, Module description – Linx Technologies TRM-915-R250 User Manual
Page 6
– –
– –
6
7
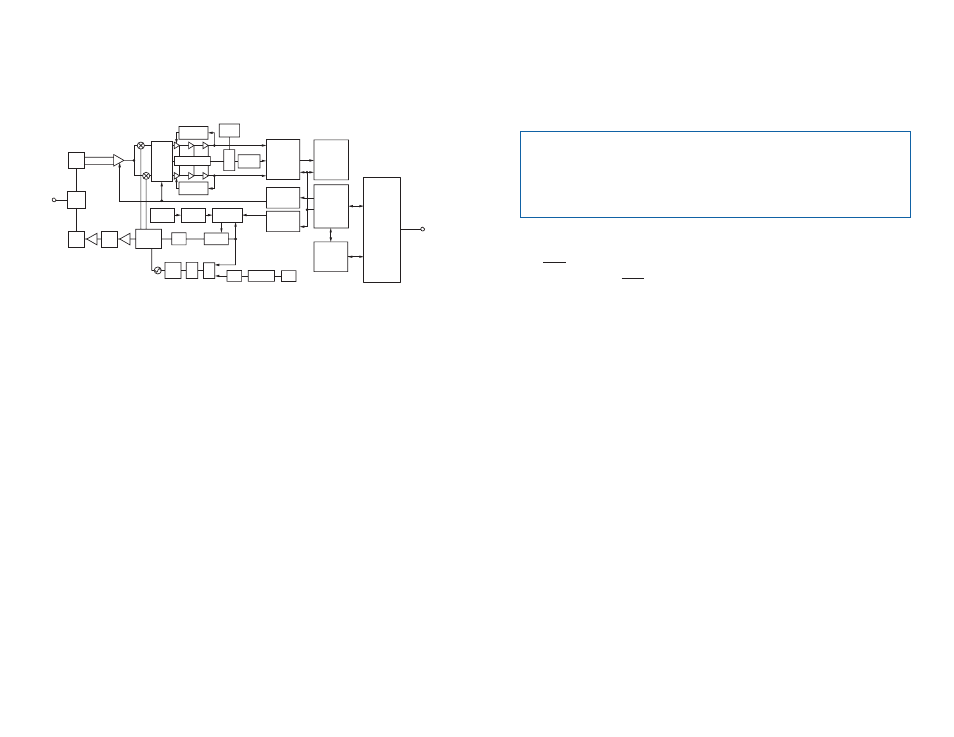
Theory of Operation
The 250 Series transceiver is a low-cost, high-performance synthesized
FSK transceiver. Its wideband operation gives it outstanding range while
still meeting regulatory requirements. Figure 7 shows a block diagram for
the module.
The 250 Series transceiver is designed for operation in the 902 to 928MHz
frequency band. The RF synthesizer contains a VCO and a low-noise
fractional-N PLL. The receive and transmit synthesizers are integrated,
enabling them to be automatically configured to achieve optimum phase
noise, modulation quality and settling time.
The transmitter output power is programmable from +8dBm to +23.5dBm
with automatic PA ramping to meet transient spurious specifications.
The ramping and frequency deviation are optimized to deliver the highest
performance over a wide range of data rates.
The receiver incorporates highly efficient low-noise amplifiers that provide
up to –105dBm sensitivity.
An onboard controller performs the radio control and management
functions. A processor performs the higher level protocol functions and
controls the serial and hardware interfaces.
Σ-Δ
Tx/Rx
CONTROL
AGC
CONTROL
FSK/ASK
DEMODULATOR
DATA
SYNCHRONIZER
RSSI
7-BIT ADC
GAIN
DIV R
SERIAL
PORT
OFFSET
CORRECTION
OFFSET
CORRECTION
LNA
VCO
PFD
CP
AFC
CONTROL
DIVIDERS/
MUXING
N/N + 1
DIV P
MUX
TEMP
SENSOR
OSC
CLK
DIV
FSK MOD
CONTROL
GAUSSIAN
FILTER
MODULATOR
IF FILTER
PROCESSOR
UART /
INTERFACE
FILTER
FILTER
FILTER
FILTER
SWITCH
PA
ANTENNA
Figure 7: 250 Series Transceiver Block Diagram
Module Description
The 250 Series RF transceiver module has a Universal Asynchronous
Receiver Transmitter (UART) serial interface and is designed to create
a complete UART-to-antenna wireless solution capable of direct wire
replacement in most embedded RS-232/422/485 applications.
The module is designed to interface directly to a host UART. Three lines are
used to transfer data between the module and the host UART: TXD, RXD,
and CTS. TXD is the data output from the module. RXD is the data input
to the module. The CTS output indicates if the module is ready to accept
data. The UART interface is capable of operating in full duplex at baud
rates from 2.4 to 115.2kbps.
The module has a built-in protocol that automatically transmits the data
input on the UART. All encoding, transmitting, receiving and decoding
functions are handled by the internal processor, so no overhead is required
by an external processor. The networking modes in the protocol allow
for point-to-point and broadcast transmissions as well as allowing for the
creation of subnets and more complicated network topologies.
The module can be put into a Sleep mode through serial commands. In
Sleep mode, the RF section is completely shut down and the protocol
processor is in an idle state. Once the module has been placed in the sleep
mode, it can be awakened by sending a power-up sequence through the
serial port.
If the current draw in sleep mode is too high for a particular application,
power to the module can be switched through an external FET to turn off
the module when it is not needed. If this technique is used, the volatile
registers are reset to the values in their non-volatile mirrors, so any changes
from the default will have to be reloaded.
Every module has a 32-bit GUID address that can be used by the host
application to uniquely identify each module. This address can be read
through the serial interface.
Note:
Although the module is capable of supporting the serial data
communications required by RS-232, RS-422, and RS-485 networks,
it is not compatible with the electrical interfaces for these types of
networks. The module has CMOS inputs and outputs and requires an
appropriate converter for the particular type of network being used.