14 audio cross point matrix – Nevion FRS-HD-CHO User Manual
Page 26
FRS-HD-CHO
Rev. 9
nevion.com | 26
The negative audio delay is limited by the positive video delay. Since the audio delay is
always relative to the video, the only way to give the audio a negative delay is to delay the
video by a positive amount. To go beyond this limit would require the audio to be re-
embedded before it had even been de-embedded from the incoming video, and that is of
course impossible.
The positive audio delay is limited by the fact that the sum of the video delay and the relative
audio delay cannot be larger than 32000 audio samples (approx. 0.67 ms with 48 kHz audio).
If the video delay is set to minimum, the full 32000 audio samples will be available, but if the
video delay is set to
– say – 5 frames, the maximum relative audio delay is reduced to 20000
audio samples (assuming 25 frames per second, 5 frames equals 0.2 seconds, which in turn
equals 12000 audio samples, and 32000-12000=20000). When doing these calculations,
remember that if a sync reference is present, a video delay setting of N frames means that
the actual video delay can vary continuously between N and (N+1) frames. The calculations
should therefore be based on (N+1) frames.
Dolby-E delay handling
The FRS-HD-CHO can re-align Dolby-E with video. Dolby-E processing equipment typically
causes one frame delay for the audio.
The positive video delay needs to be set higher than the desired negative relative audio
delay. Then set a negative relative audio delay that corresponds to a whole number of full
frames of audio samples
6
. A delay example setting is shown in Figure 21. The audio
embedder settings should be as in Figure 22.
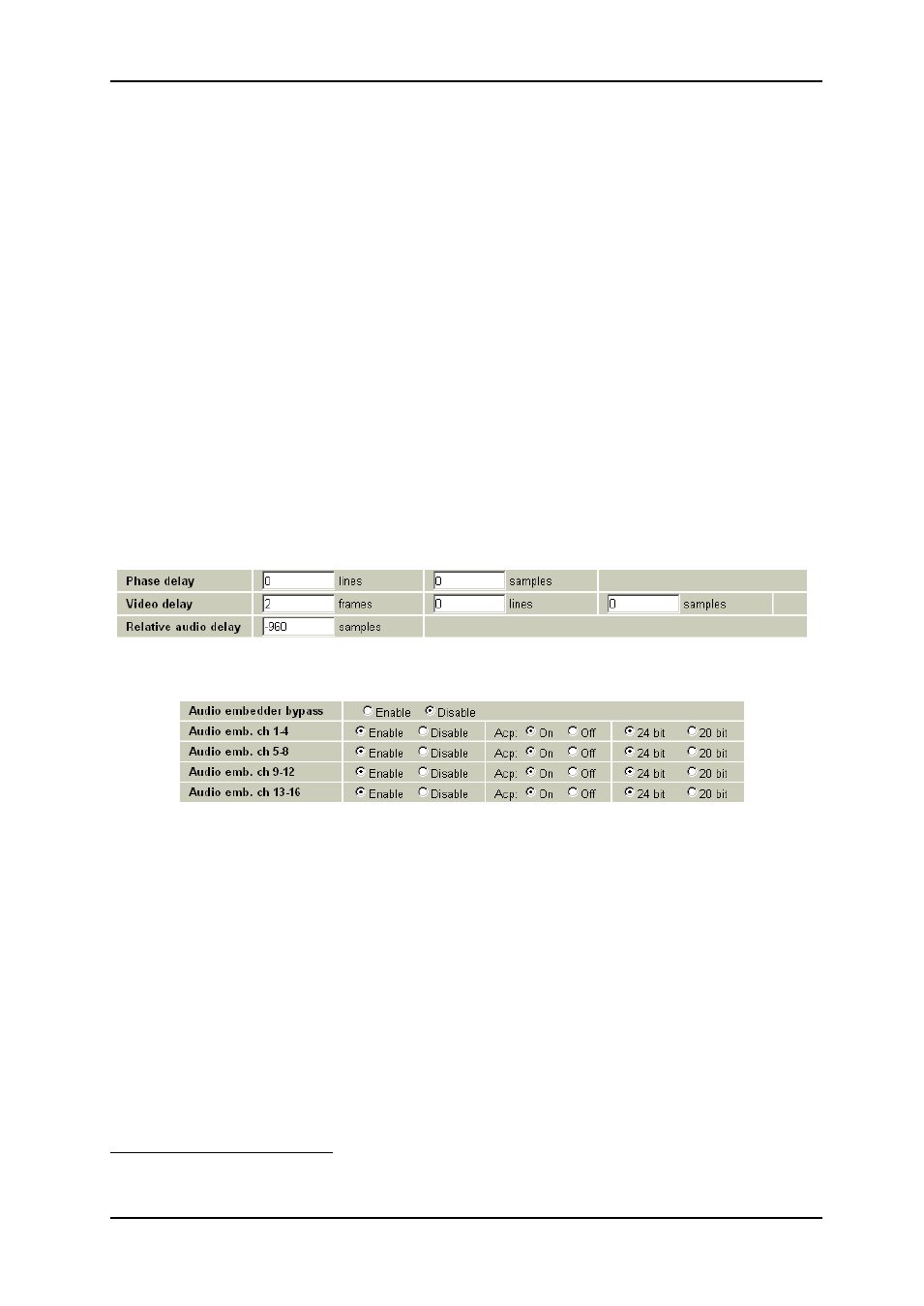
Figure 21: Gyda view of the delay settings. The video is delayed 1 frames compared with the
audio for a 50Hz signal.
Figure 22: Gyda view of the audio embedder settings
5.14 Audio cross point matrix
The audio cross point matrix is an 8x10 cross point with inputs and outputs as shown in
Figure 20. The 8 de-embedded channels, a 1 kHz sine and
“black sound” are selectable
inputs.
“Black sound” is explained in Chapter 5.2. The outputs of the cross points are 8
stereo channels for re-embedding.
6
To calculate number of audio samples/frame simply divide 48000 with frame rate (24Hz, 25Hz,
29.97Hz, 30Hz, 50Hz, 59.94Hz or 60Hz)