Installation procedures – Pinnacle Systems DR User Manual
Page 22
15
Installation Procedures
DIN-rail Controller Module
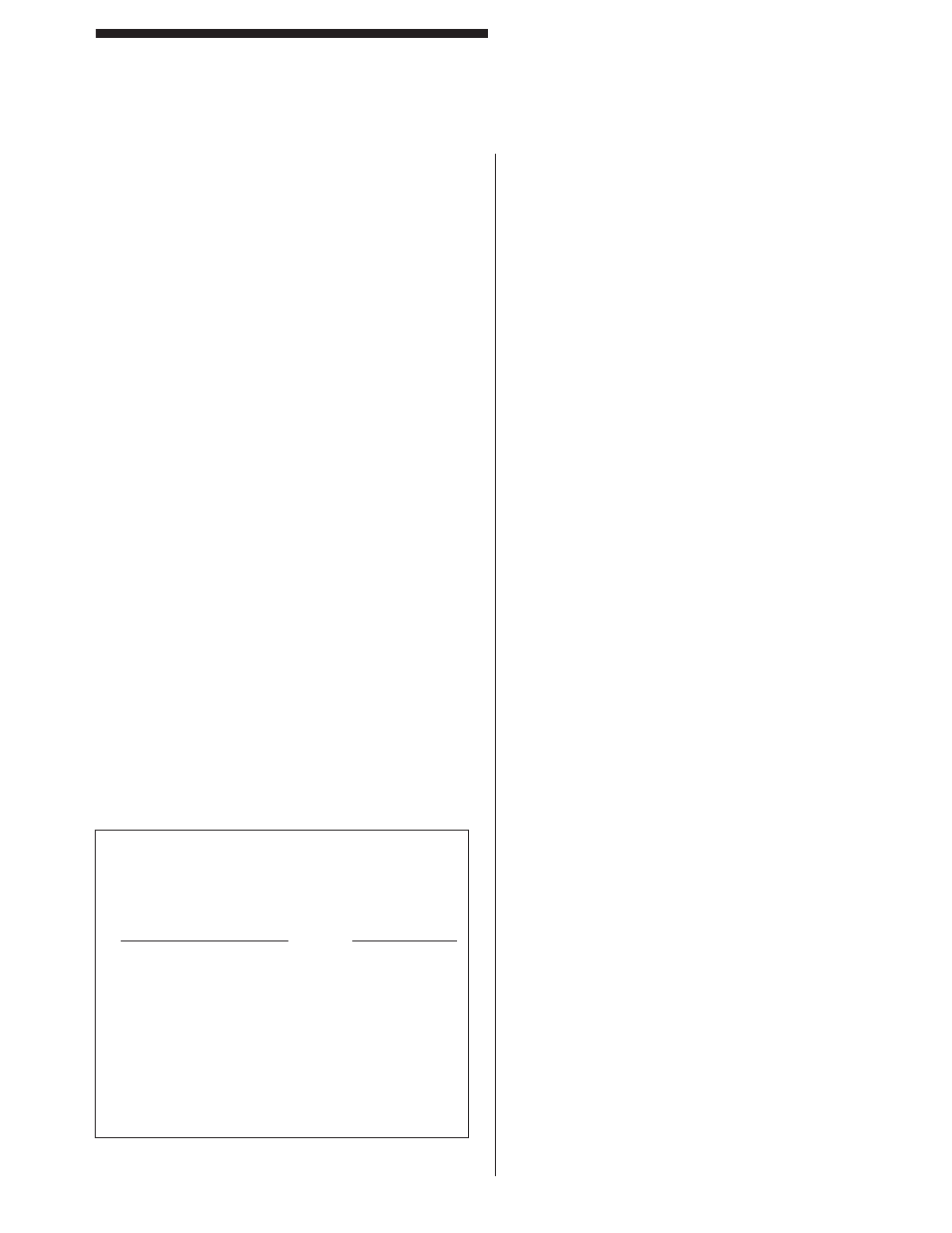
Table 4: Mechanical Guards
Distance of opening
Maximum width
from point of operation
of opening
hazard
(inches)
(inches)
1/2 to 1-1/2
1/4
1-1/2
to
2-1/2
3/8
2-1/2
to
3-1/2
1/2
3-1/2
to
5-1/2
5/8
5-1/2
to
6-1/2
3/4
6-1/2
to
7-1/2
7/8
7-1/2
to 12-1/2
1-1/4
12-1/2
to
15-1/2
1-1/2
15-1/2
to
17-1/2
1-7/8
17-1/2
to
31-1/2
2-1/8
Light Curtain Test Procedure
Use a dowel rod (or similar object) with a diameter equal
to the M.O.S. (Minimum Object Sensitivity) of the guard
you are testing. Move the rod through the fi eld of the cur-
tain (i.e. top to bottom for vertically mounted curtains).
Repeat this test close to the Emitter pylon, close to the
Receiver pylon, in the middle between the pylons, and
most importantly in front of the operator position.
Make sure the curtain indicates a “Blocked” condition
(RED light) when the rod is in the fi eld of the curtain.
Check and make sure the machine cannot move when
the curtain shows “Blocked”. If the machine can oper-
ate while the curtain shows a “Blocked” condition, then
re-examine your wiring.
NOTE: Always use both safety relays in your STOP
circuit(s).
If the curtain does not show “Blocked” when the rod is
in the fi eld: Check to make sure the rod is truly in the
curtain’s fi eld, and re-check the curtain’s Minimum Ob-
ject Sensitity (including AutoBlank and Floating blank
options that change the M.O.S.).
Infrared light from the curtain may be refl ecting around
the rod due to refl ective material too close to the curtain’s
fi eld. In this case, you will have to move the curtain py-
lons back away from the refl ective material and repeat
the test over again. The curtain’s power level can also
be reduced by the factory.
12
Installation Procedures
DIN-rail Controller Module
Safeguarding with Mechanical Guards
When a light system is used to protect the operator or
passerby from penetration, it must be mounted and
properly sized (grid length) so it is impossible to reach
under, around, or over into the hazardous point of
operation zone. Infrared light systems normally guard
the front or feed area of a machine. The sides or the
areas where the light screen does not guard must be
guarded by some other means.
If the position of the safety light curtain will allow the
operator or others to place themselves between the
sensing fi eld and the hazardous area, auxiliary guards or
devices such as safety mats, barrier guards, or devices
should be used in conjunction with the safety light
curtain to prevent the operator or others from exposure
to the hazardous area. If mechanical guards such as
polyurethane, expanded or perforated metal, hairpins,
etc. are used to guard these areas, the opening must
comply with the OSHA safety distance in relationship
to the openings.
After installation of point of operation guards and before
a job is released for operation, a check should be made
to verify that the guard will prevent the operators hands
from reaching into the point of operation or any hazard
zone.
Table 4 outlines the distances that guards should be
positioned from the nearest point-of-operation hazards.
The various openings are such that for average-sized
hands, an operator’s fi ngers will not reach the point of
operation.
After installation of point-of-operation guards and before
a job is released for operation, a check should be made
to verify that the guard will prevent the operator’s hands
or other body parts from reaching the point of operation.