Amprobe Multitest-1000 Continuity-Tester User Manual
Page 65
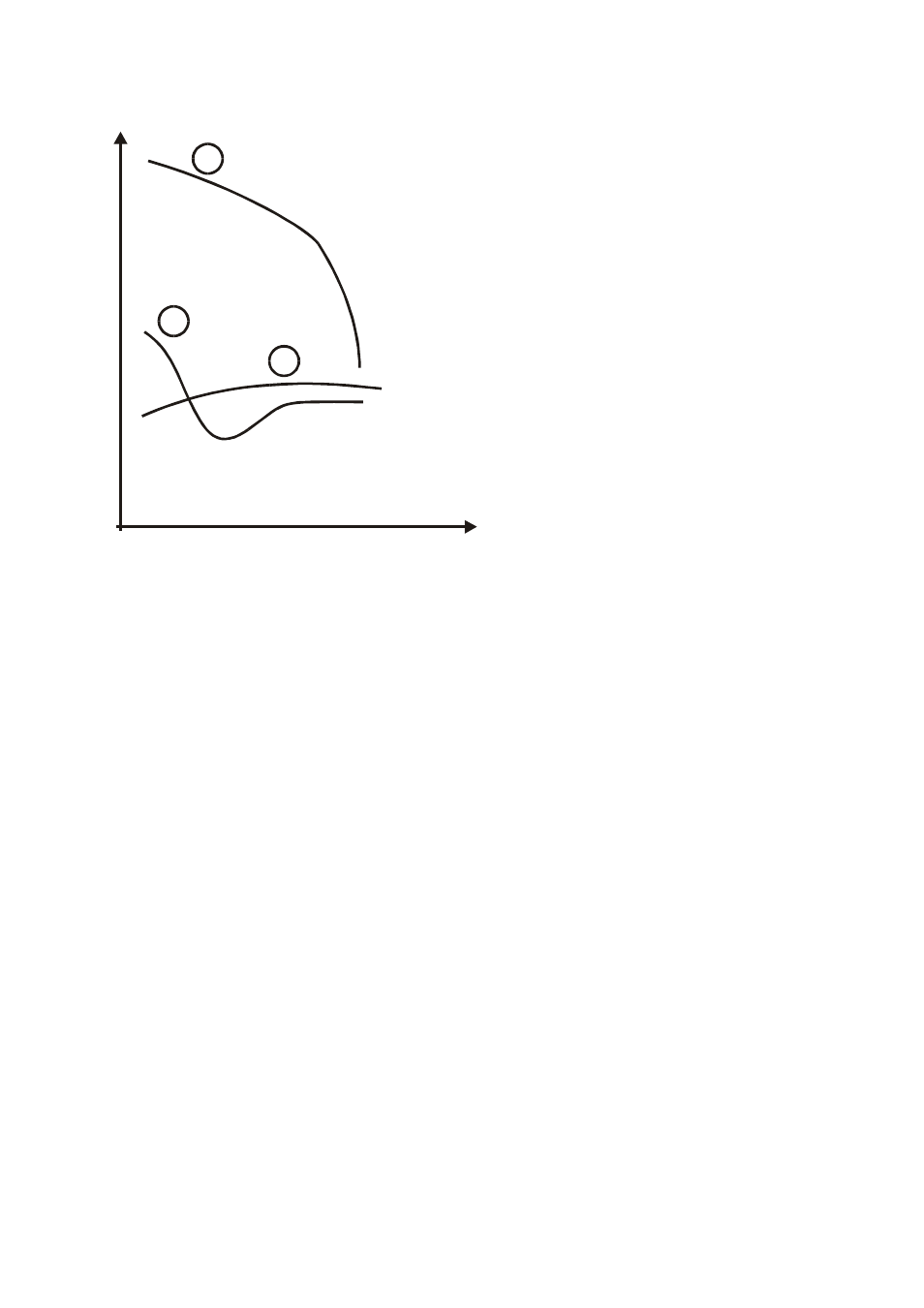
Distance between the rods a(m)
Sp
e
c
ifi
c
re
si
st
iv
ity
o
f
th
e
g
ro
u
nd
E
(
m
)
ρ
Ω
3
2
1
Curve 1: as
ρ decreases only in
depth, it’s possible to use only a
rod in depth.
Curve 2: as
ρ decreases only
until the depth A, it’s not useful to
increase the depth of the rod
beyond A.
Curve 3: even at a superior
depth,
ρ does not decrease,
therefore a ring rod must be
used.
APPROXIMATE EVALUATION OF INTENTIONAL RODS CONTRIBUTION (64-12 2.4.1)
The resistance of a rod Rd can be calculated with the following formulas (
ρ = medium
resistivity of the ground).
a) Resistance of a vertical rod
Rd =
ρ / L
L= length of the element touching the ground
b) Resistance of a horizontal rod
Rd = 2
ρ / L
L= length of the element touching the ground
c) Resistance of linked elements
The resistance of a complex system with more elements in parallel is always greater
than the resistance that could result from a simple calculation of elements in parallel,
especially if those elements are close and therefore interactive. For this reason, in
case of a linked system the following formula is quicker and more effective than the
calculation of the single horizontal and vertical elements:
Rd =
ρ / 4r
r= radius of the circle which circumscribes the link