Address resolution, Neighbor reachability detection – H3C Technologies H3C S7500E Series Switches User Manual
Page 126
13-7
ICMPv6 message
Number
Function
Used to respond to an RS message
Router advertisement (RA)
message
134
With the RA message suppression disabled, the router
regularly sends an RA message containing information such
as prefix information options and flag bits.
Redirect message
137
When a certain condition is satisfied, the default gateway
sends a redirect message to the source host so that the host
can reselect a correct next hop router to forward packets.
The NDP mainly provides the following functions:
Address resolution
Similar to the ARP function in IPv4, a node acquires the link-layer addresses of neighbor nodes on the
same link through NS and NA messages.
shows how node A acquires the link-layer
address of node B.
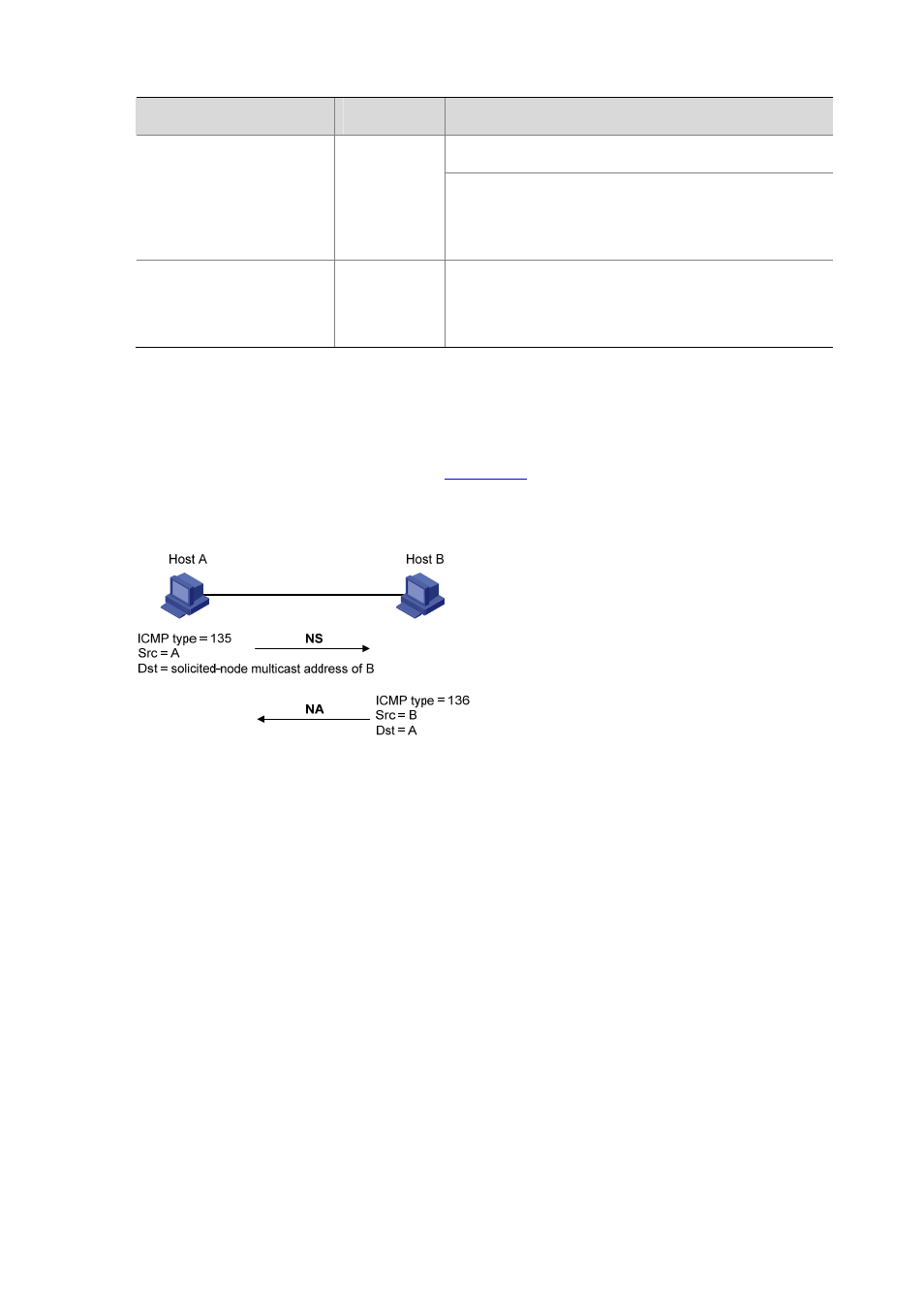
Figure 13-3 Address resolution
The address resolution procedure is as follows:
1) Node A multicasts an NS message. The source address of the NS message is the IPv6 address of
the sending interface of node A and the destination address is the solicited-node multicast
address of node B. The NS message contains the link-layer address of node A.
2) After receiving the NS message, node B judges whether the destination address of the packet is
its solicited-node multicast address. If yes, node B learns the link-layer address of node A, and
then unicasts an NA message containing its link-layer address.
3) Node A acquires the link-layer address of node B from the NA message.
Neighbor reachability detection
After node A acquires the link-layer address of its neighbor node B, node A can verify whether node B
is reachable according to NS and NA messages.
1) Node A sends an NS message whose destination address is the IPv6 address of node B.
2) If node A receives an NA message from node B, node A considers that node B is reachable.
Otherwise, node B is unreachable.