Basler Electric BE1-87B User Manual
Page 36
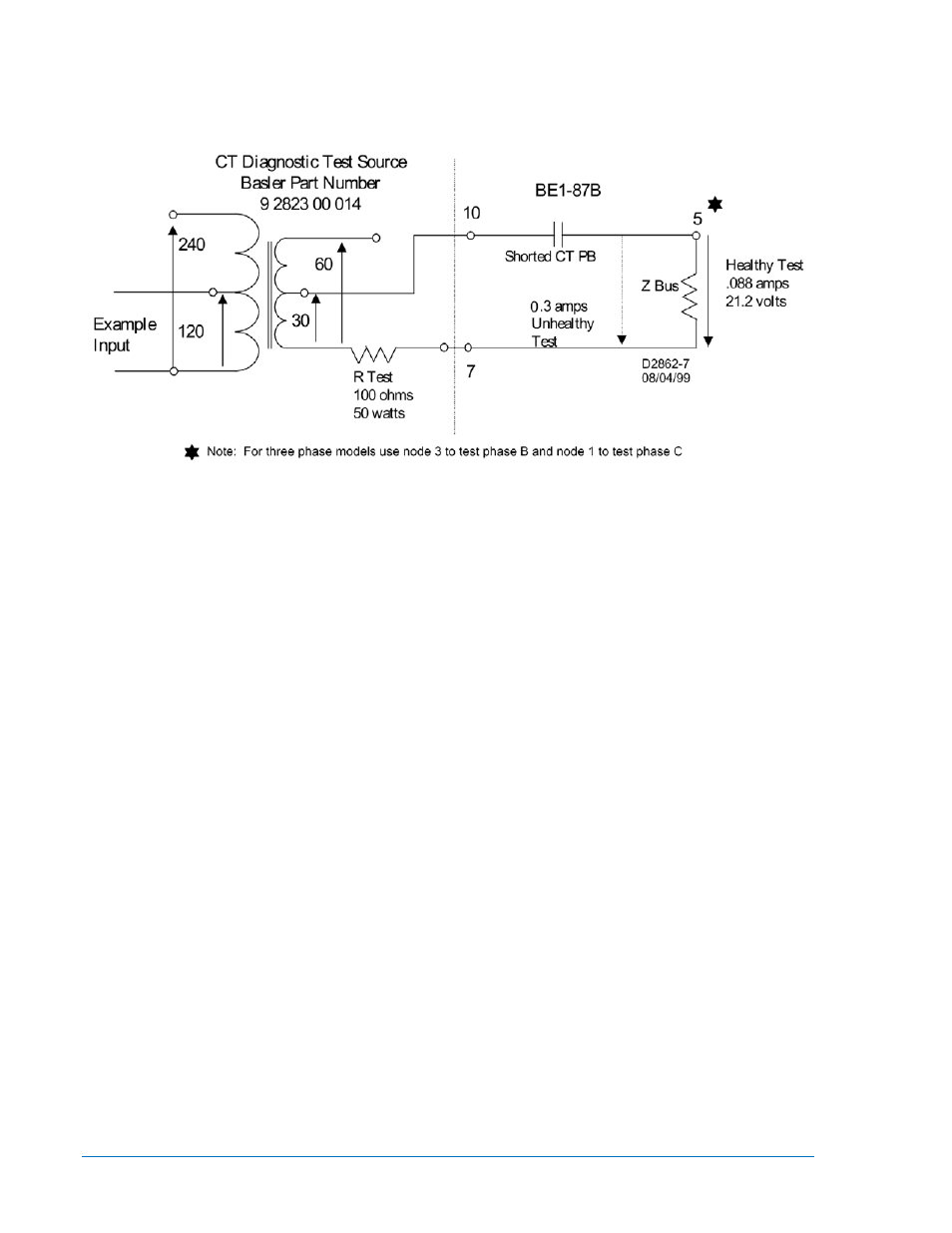
1. From a CT excitation curve, find Ie at 30 volts for full ratio. At 30 volts on the 240 /1 curve, Ie is
approximately equal to .017 amps:
CTZ = V Test / Ie or 30 / .017 = 1765 ohms/CT (ignoring any reactive component)
Figure 2-10. Voltage Appearing Across Full Winding of CT
2. In our example case, 7 CTs are in parallel with a relay input impedance of 5k ohms resulting in an
equivalent impedance of 240 ohms (refer to Figure 2-9).
Z Bus = CTZ / nCTs or 1765/7 = (252 X 5000) / (252 + 5000) = 240 ohms
3. Find the total current for a healthy CT test using V Test = 30 volts and R Test = 100 ohms.
Z Total = R Test + Z Bus or 100 + 240 = 340 ohms.
I HT = V Test / Z Total or 30/340 = 0.088 amp.
4. Find the total current for an unhealthy CT circuit (Z Bus shorted out):
I UHT = V Test / R Test or 30/100 = 0.3 amp.
5. To guarantee security of the relay during the Shorted CT Test, set the relay Pickup Current to 0.5
amperes (For additional information see the paragraph in Section 3 entitled Shorted CT Test Circuit.)
6. Check the voltage drop across R Test and Z Bus:
V R Test = 100 X .088 = 8.8 volts and V Z Bus = 240 X .088 = 21.2 volts.
7. Verify that the ratio between V Z Bus and V Alarm is 110% or higher:
% V Alarm = V Z Bus / V Alarm X 100 or 21.2/15 X 100 = 141%.
8. If the %V Alarm is below 110%, raise V Test to 60 volts and repeat all calculation steps. A %V Alarm
less than 110% may result in indication of an unhealthy CT circuit when in fact there is nothing wrong.
2-18
BE1-87B Application
9282300990 Rev P