3 scsi concepts – OpenEye GraniteRack 3U User Manual
Page 16
Introduction
1-10
1.3 SCSI Concepts
Before configuring the subsystem, you must first understand some basic
SCSI concepts so that the subsystem and SCSI devices will function
properly.
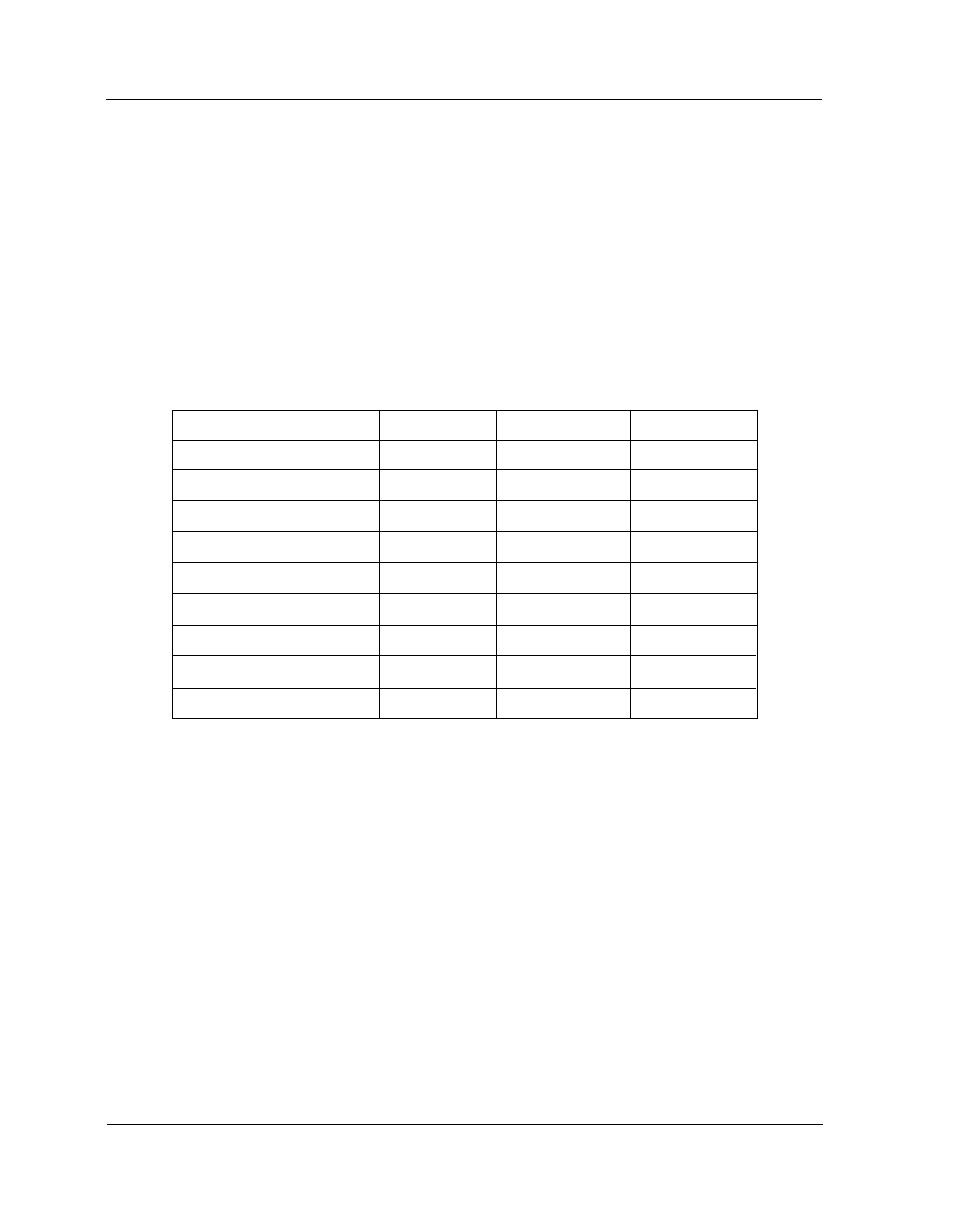
1.3.1 Multiple SCSI Format Support
The subsystem support the SCSI interface standards listed below. Note that
the data bit and cable length restrictions must be followed.
SCSI Type
SCSI-1
Fast SCSI
Fast Wide SCSI
Ultra SCSI
Ultra Wide SCSI
Ultra 2 SCSI
Ultra 2 Wide SCSI
Ultra 160 Wide LVD
Ultra 320 LVD
Data Bit
8 Bits
8 Bits
16 Bits
8 Bits
16 Bits
8 Bits
16 Bits
16 Bits
16 Bits
Data Rate
5 MB/Sec
10 MB/Sec
20 MB/Sec
20 MB/Sec
40 MB/Sec
40 MB/Sec
80 MB/Sec
160MB/Sec
320MB/Sec
Cable Length
6 m
3 m
3 m
1.5 m
1.5 m
12 m
12 m
12 m
12 m
1.3.2 Host SCSI ID Selection
A SCSI ID is an identifier assigned to SCSI devices which enables them to
communicate with a computer when they are attached to a host adapter via
the SCSI bus. Each SCSI device, and the host adapter itself, must have a
SCSI ID number (Ultra 320 Wide SCSI = 0 to 15). The ID defines each SCSI
device on the SCSI bus. If there are more than one SCSI adapter in the Host
subsystem, each adapter forms a separate SCSI bus. SCSI IDs can be re-
used as long as the ID is assigned to a device on a separate SCSI bus.
Refer to the documentation that came with your peripheral device to deter-
mine the ID and how to change it. The subsystem must be assigned a
unique SCSI ID ranging from 0 to 15 for the Ultra 320 LVD SCSI host system.
The default value is ID 0.