Flowserve Mark 3 Sealed Metallic Durco User Manual
Page 54
MARK 3 USER INSTRUCTIONS ENGLISH 71569102 01-13
Page 54 of 72
flowserve.com
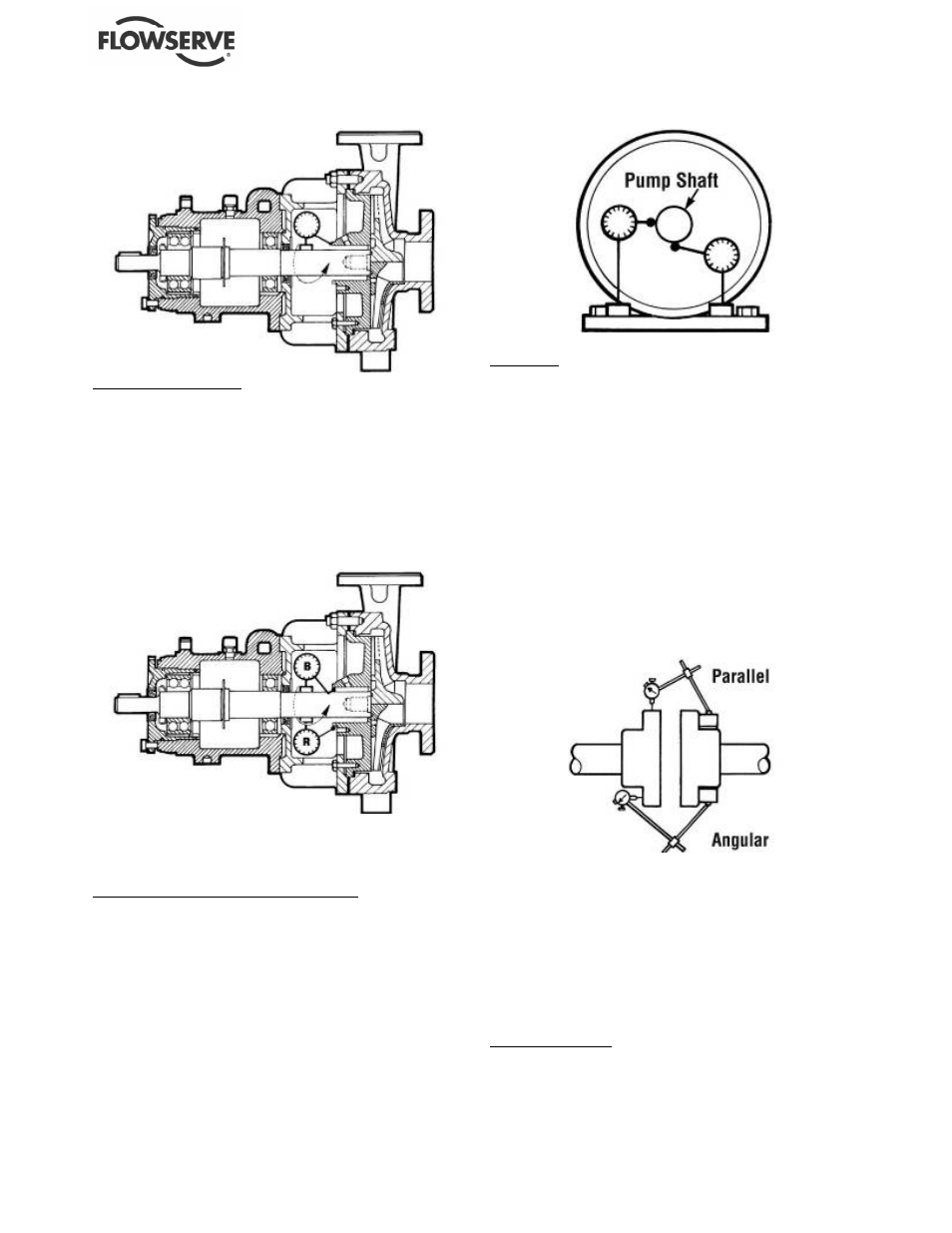
Figure 6.24 Face squareness
Register concentricity
An eccentric seal chamber bore or gland register can
interfere with the piloting and centering of the seal
components and alter the hydraulic loading of the
seal faces, resulting in reduction of seal life and
performance. The seal chamber register
concentricity should be less than 0.13 mm (0.005 in.).
The diagram below shows how to measure this
concentricity.
Figure 6.25 Concentricity
Installed pump
6.8.4.7
Complete pump installed.
Shaft movement caused by pipe strain
Pipe strain is any force put on the pump casing by
the piping. Pipe strain should be measured as shown
below. Install the indicators as shown before
attaching the piping to the pump. The suction and
discharge flanges should now be bolted to the piping
separately while continuously observing the
indicators. Indicator movement should not exceed
0.05 mm (0.002 in.).
Figure 6.26 Pipe strain movement
Alignment
Misalignment of the pump and motor shafts can
cause the following problems:
•
Failure of the mechanical seal
•
Failure of the motor and/or pump bearings
•
Failure of the coupling
•
Excessive vibration/noise
The schematics below show the technique for a
typical rim and face alignment using a dial indicator.
It is important that this alignment be done after the
flanges are loaded, and at typical operating
temperatures. If proper alignment cannot be
maintained a C-flange motor adapter and/or
stilt/spring mounting should be considered.
Figure 6.27 Alignment
Many companies today are using laser alignment
which is a more sophisticated and accurate
technique. With this method a laser and sensor
measure misalignment. This is fed to a computer
with a graphic display that shows the required
adjustment for each of the motor feet.
See section 4.8 for recommended final shaft
alignment limits.
Vibration analysis
Vibration analysis is a type of condition monitoring
where a pump’s vibration “signature” is monitored on
a regular, periodic basis. The primary goal of
vibration analysis is extension on MTBPM. By using