Flowserve ValveSight Diagnostics User Manual
Page 53
ValveSight Diagnostics for HART User Manual FCD VSENSF0001-02-AQ 03/15
53
flowserve.com
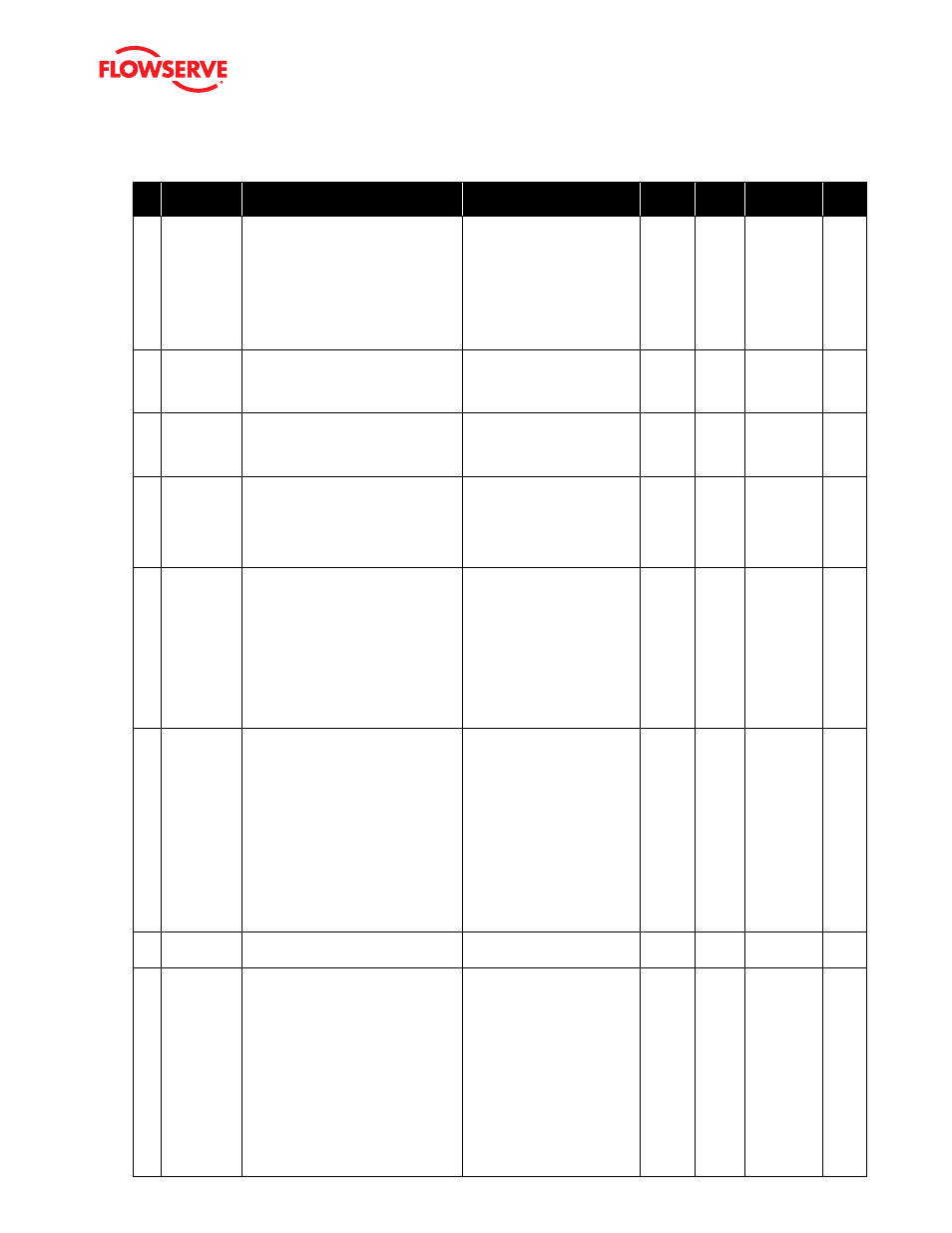
#
Indicator
Implications
Possible Solutions
Default
Settings
Enable/
Disable
Refer to DTM
Screen
Blink
Code
13
MPC Active
Mode
Indicates that tight shutoff (MPC) is
active. The command is beyond the user
set limit for tight shutoff feature. This
is a normal condition for all valves when
closed. The factory default setting triggers
this at command signals below 1%. This
indication may also occur on 3 way valves
at both ends of travel if the high MPC
value has been set.
If tight shutoff is not desired,
reset the tight shutoff limits to
the correct values or adjust the
command signal inside of the
specified MPC value.
110%
and 1%
No
Configuration
> Custom
> Position
Cutoff
GGGY
14
Local Inter-
face Enabled/
Disabled
Indicates PC software has been used to
disable the local interface. This code is
only present for a short time when the
QUICK-CAL button is pressed.
If local control is desired then
the local interface must be
re-enabled from the remote
software.
N/A
No
Configura-
tion> Basic/
Local Inter-
face
GGYG
15
Error History
Reset Alert
Indicates that a flag has been set for the
position to clear its internal history. The
positioner will automatically reset the flag
once the history has been cleared.
N/A
No
Alarms >
Alarm Status
None
16 Actuation Ra-
tio Warning
Indicates a decreased ability of the system
to actuate the valve. It is based on the
ratio of available force to required force to
actuate. It is affected by the process load,
friction, spring force, and available supply
pressure.
Increase the supply pressure.
Reduce the friction. Check the
actuator spring. Re size the
actuator, Adjust user set limits.
Start
90%
End
100%
Yes
Health >
Actuator
Health
YYYY
17
Pneumatic In-
ability to Fail
Safe Warning
Indicates that upon loss of air supply,
the valve may not move to the fail-safe
position. The spring alone is not adequate
to overcome the friction and process load
in the system. The system is relying on
pneumatic force to actuate in the direction
the spring is pushing. The fail-safe spring
may have failed or was not sized properly
for the application. Friction or process
load may have increased.
Check for high friction. Repair or
replace actuator spring. Reduce
process load.
N/A
Yes
Health >
Actuator
Health
YRRR
18
Friction High
Warning
Indicates the valve/actuator friction has
passed the user-set limit. High friction
can cause loop oscillations, poor position
control, jerky motion, or valve sticking.
It can be caused by build-up from the
process on the stem, trim or seat by
a failing bearing or guides in the valve
and actuator, galling of the trim or stem,
excessively tightened packing, linages or
other valve/actuator mechanical issues.
Determine if the friction is
significantly interfering with the
valve control. If not, consider
increasing the friction warning
limit. Consider the following to
reduce friction: Stroke the valve
to clear off build up. Clear any
external mechanical obstruc-
tion, loosen the packing, clean
the stem, repair or replace the
actuator. Highly localized friction
or very jerky travel can indicate
internal galling. Repair or replace
internal valve components.
10,000
lbs
Yes
Health >
Valve Health
YRYG
19
Friction Low
Warning
Indicates the friction has passed below
the user-set limit.
Check for packing leak. Tighten
or replace the valve packing.
0 lbs.
Yes
Health >
Valve Health
YRGY
20
Friction High
Alarm
Indicates the valve/actuator friction has
passed the user-set limit. The alarm
indicates a more severe condition than
the warning. High friction can cause
loop oscillations, poor position control,
jerky motion, or valve sticking. It can be
caused by build-up from the process on
the stem, trip, or seat by a failing bearing
or guides in the valve and actuator, calling
of the trim or stem, excessively tightened
packing, linkages, or other valve/actuator
mechanical issues.
Determine if the friction is
significantly interfering with the
valve control. If not, consider
increasing the friction warning
limit. Consider the following to
reduce friction: Stroke the valve
to clear off build up. Clear any
external mechanical obstruc-
tion, loosen the packing, clean
the stem, repair or replace the
actuator. Highly localized friction
or very jerky travel can indicate
internal galling. Repair or replace
internal valve components.
10,000
lbs.
Yes
Health >
Valve Health
RRGR