Traffic policing – H3C Technologies H3C S12500 Series Switches User Manual
Page 49
40
•
Peak information rate (PIR)—Rate at which tokens are put into bucket E, which specifies the average
packet transmission or forwarding rate allowed by bucket E.
•
Excess burst size (EBS)—Size of bucket E, which specifies the transient burst of traffic that bucket E
can forward.
CBS is implemented with bucket C, and EBS with bucket E. In each evaluation, packets are measured
against the following bucket scenarios:
•
If bucket C has enough tokens, packets are colored green.
•
If bucket C does not have enough tokens but bucket E has enough tokens, packets are colored
yellow.
•
If neither bucket C nor bucket E has sufficient tokens, packets are colored red.
Traffic policing
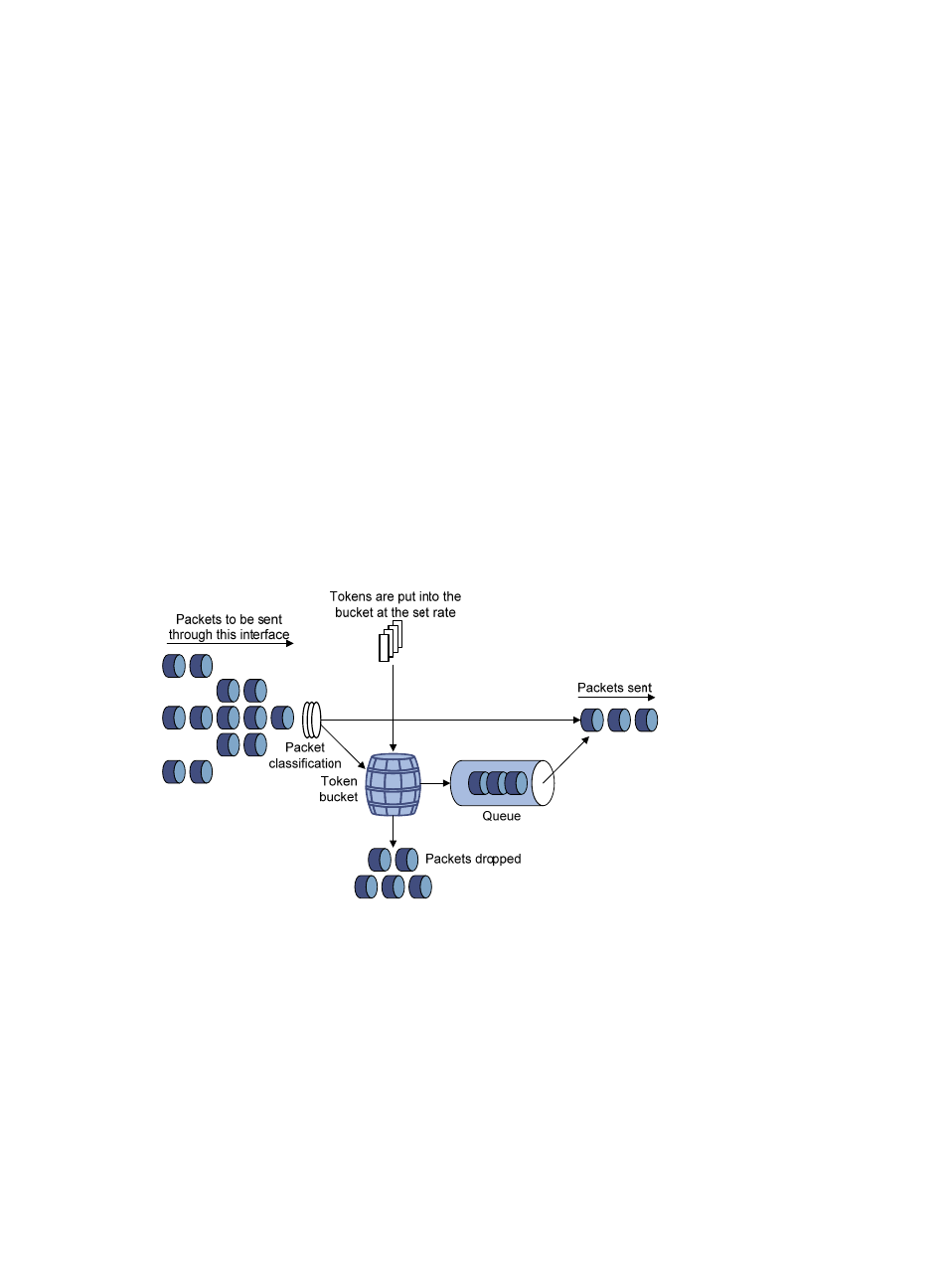
A typical application of traffic policing is to supervise the specification of certain traffic entering a
network and limit it within a reasonable range, or to "discipline" the extra traffic to prevent aggressive
use of network resources by a certain application. For example, you can limit bandwidth for HTTP
packets to less than 50% of the total. If the traffic of a certain session exceeds the limit, traffic policing can
drop the packets or reset the IP precedence of the packets.
shows an example of policing
outbound traffic on an interface.
Figure 7 Traffic policing
Traffic policing is widely used in policing traffic entering the networks of internet service providers (ISPs).
It can classify the policed traffic and take pre-defined policing actions on each packet depending on the
evaluation result:
•
Forwarding the packet if the evaluation result is "conforming."
•
Dropping the packet if the evaluation result is "excess."
•
Forwarding the packet with its IP precedence re-marked if the evaluation result is "conforming."
•
Delivering the packet to next-level traffic policing with its IP precedence re-marked if the evaluation
result is "conforming."
•
Entering the next-level policing (you can set multiple traffic policing levels each focused on specific
objects).