Tint effect tritone effect, Tint effect, Tritone effect – Adobe After Effects User Manual
Page 631
Shadow Tonal Width and Highlight Tonal Width
Shadow Radius and Highlight Radius
Color Correction
Note:
Midtone Contrast
Black Clip, White Clip
Blend With Original
The range of adjustable tones in the shadows and highlights. Lower values restrict the
adjustable range to only the darkest and lightest regions, respectively. Higher values expand the adjustable range. These controls are useful for
isolating regions to adjust. For example, to lighten a dark area without affecting the midtones, set a low Shadow Tonal Width value so that when
you adjust the Shadow Amount, you’re lightening only the darkest areas of an image. Specifying a value that is too large for a given image may
introduce halos around strong dark to light edges. The default settings attempt to reduce these artifacts. These halos may occur if the Shadow or
Highlight Amount value is too large; they can also be reduced by decreasing these values.
The radius (in pixels) of the area around a pixel that the effect uses to determine whether the pixel
resides in a shadow or a highlight. Generally, this value should roughly equal the size of the subject of interest in the image.
The amount of color correction that the effect applies to the adjusted shadows and highlights. For example, if you increase the
Shadow Amount value, you bring out colors that were dark in the original image; you may want these colors to be more vivid. The higher the Color
Correction value, the more saturated these colors become. The more significant the correction that you make to the shadows and highlights, the
greater the range of color correction available.
If you want to change the color over the whole image, use the Hue/Saturation effect after applying the Shadow/Highlight effect.
The amount of contrast that the effect applies to the midtones. Higher values increase the contrast in the midtones alone, while
concurrently darkening the shadows and lightening the highlights. A negative value reduces contrast.
How much of the shadows and highlights are clipped to the new extreme shadow and highlight colors in the image.
Setting the clipping values too high reduces detail in the shadows or highlights. A value in the range from 0.0% to 1% is recommended. By default,
shadow and highlight pixels are clipped by 0.1%—that is, the first 0.1% of either extreme is ignored when identifying the darkest and lightest pixels
in the image, which are then mapped to output black and output white. This method ensures that input black and input white values are based on
representative rather than extreme pixel values.
Tint effect
The Tint effect tints a layer by replacing the color values of each pixel with a value between the colors specified by Map Black To and Map White
To. Pixels with luminance values between black and white are assigned intermediate values. Amount To Tint specifies the intensity of the effect.
For more complex tinting, use the Colorama effect.
This effect works with 8-bpc, 16-bpc, and 32-bpc color.
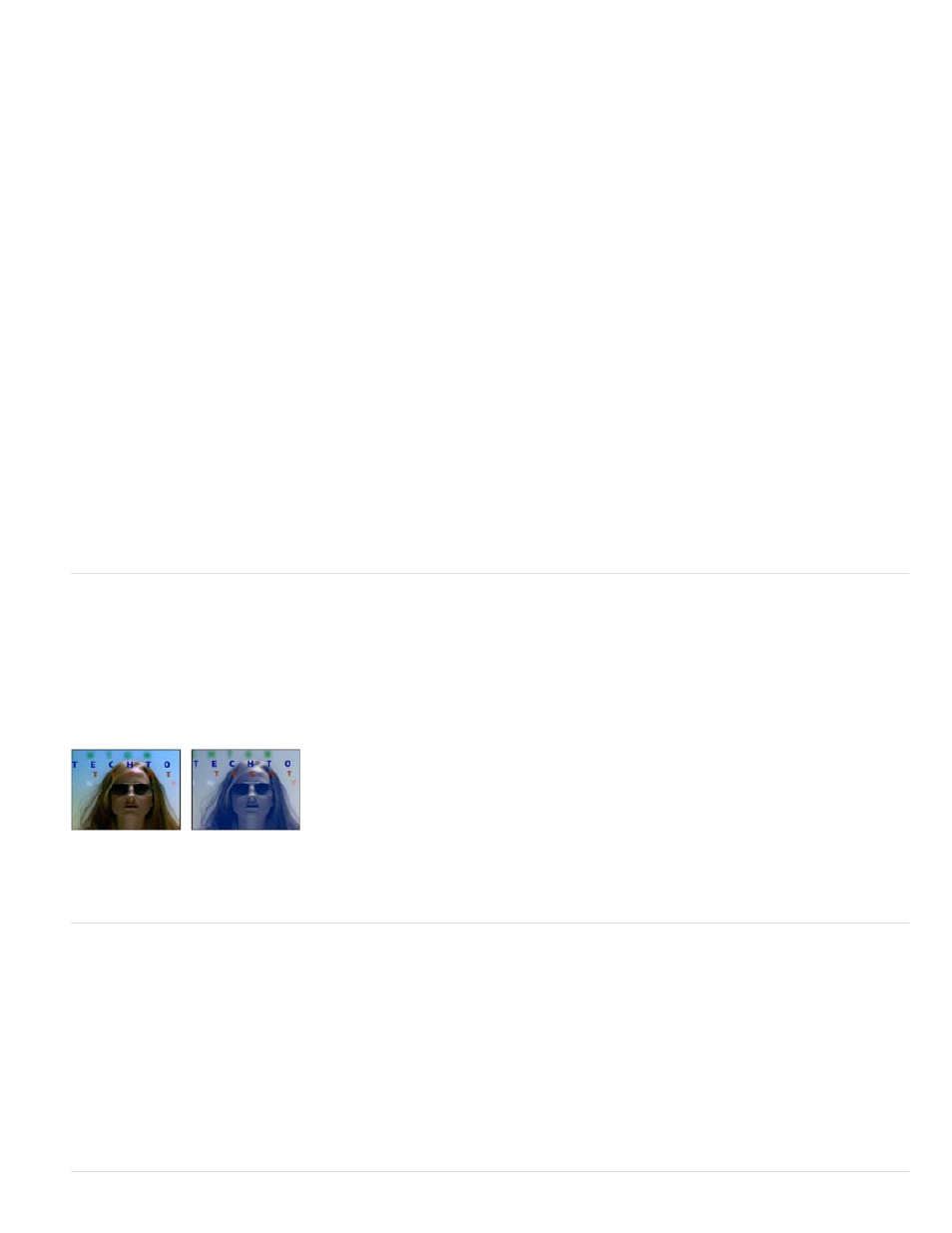
Original (left), and with effect applied (right)
Tritone effect
The Tritone effect alters the color information of a layer by mapping bright, dark, and midtone pixels to colors that you select. The Tritone effect is
like the Tint effect, except with midtone control.
This effect works with 8-bpc, 16-bpc, and 32-bpc color.
The transparency of the effect. The result of the effect is blended with the original image, with the effect result composited
on top. The higher you set this value, the less the effect affects the layer. For example, if you set this value to 100%, the effect has no visible result
on the layer; if you set this value to 0%, the original image doesn’t show through.
627