Vrrp configuration, Vrrp overview – H3C Technologies H3C S10500 Series Switches User Manual
Page 133
124
VRRP configuration
NOTE:
•
The term
router in this document refers to both routers and Layer 3 switches.
•
The term
interface in the VRRP feature refers to Layer 3 interfaces, including VLAN interfaces and
route-mode (or Layer 3) Ethernet ports. You can set an Ethernet port to operate in route mode by using
the port link-mode route command (see
Layer 2—LAN Switching Configuration Guide).
•
VRRP cannot be configured on an interface of an aggregation group.
VRRP overview
, you can configure a default route with the gateway as the next hop for
every host on a network segment. All packets destined to other network segments are sent over the
default route to the gateway, which then forwards the packets. However, when the gateway fails, all the
hosts that use the gateway as the default next-hop router fail to communicate with external networks.
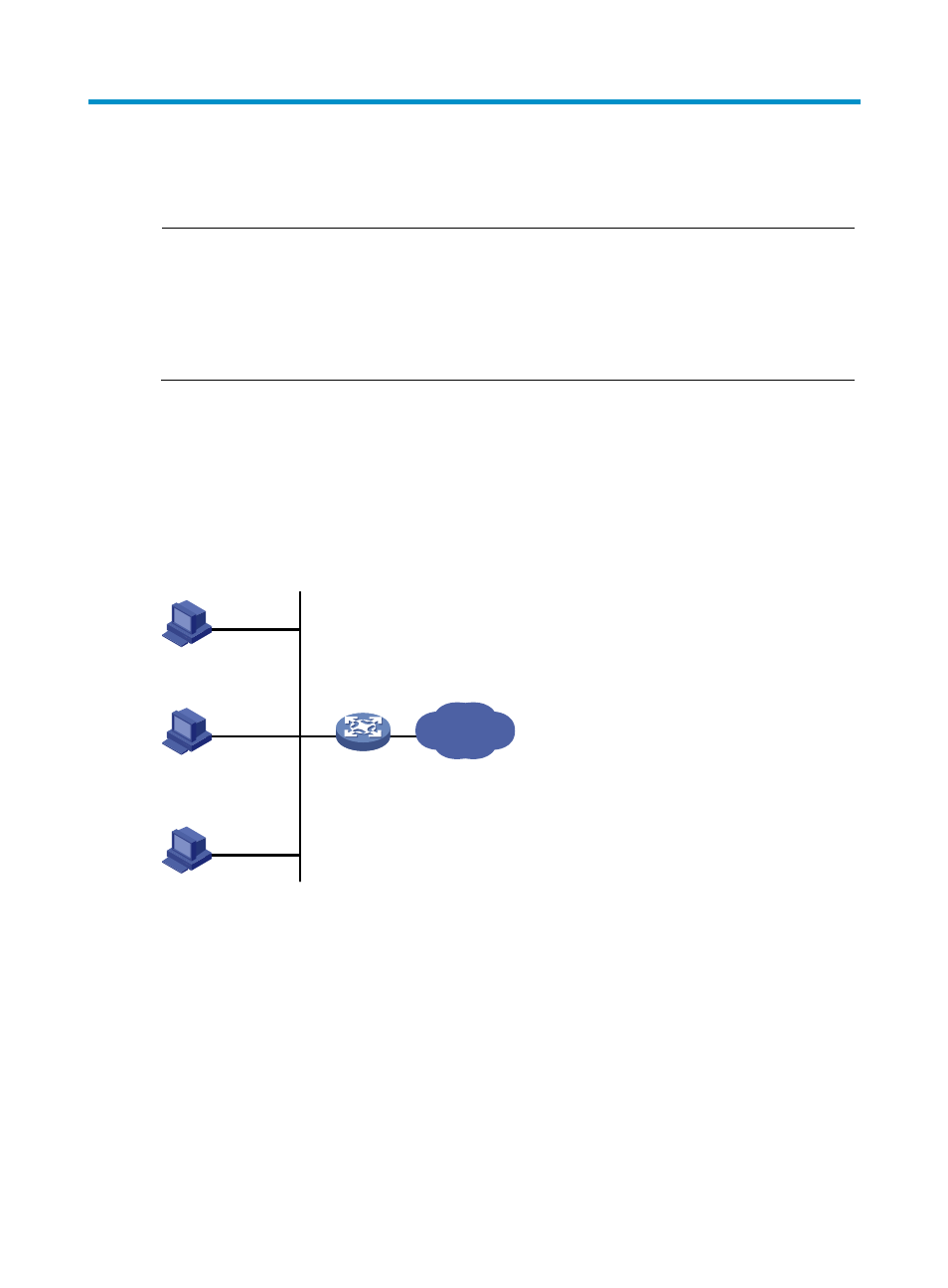
Figure 31 LAN networking
Gateway
Network
Host A
Host B
Host C
Configuring a default route for network hosts facilitates your configuration, but also requires high
performance stability of the device that acts as the gateway. Using more egress gateways is a common
way to improve system reliability, but introduces the problem of routing among the egresses.
Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP) is designed to address this problem. VRRP adds a group of
routers that can act as network gateways to a VRRP group, which forms a virtual router. Routers in the
VRRP group elect a master through the VRRP election mechanism to act as a gateway, and hosts on a
LAN only need to configure the virtual router as their default network gateway.
VRRP is an error-tolerant protocol, which improves the network reliability and simplifies configurations on
hosts. On a multicast and broadcast LAN such as Ethernet, VRRP provides highly reliable default links
without configuration changes (such as dynamic routing protocols, route discovery protocols) when a
router fails, and prevent network interruption due to a single link failure.
- H3C S5800 Series Switches H3C S5820X Series Switches H3C WX3000E Series Wireless Switches H3C SecPath F1000-E H3C SecPath F5000-A5 Firewall H3C SecPath F1000-A-EI H3C SecPath F1000-E-SI H3C SecPath F1000-S-AI H3C SecPath F5000-S Firewall H3C SecPath F5000-C Firewall H3C SecPath F100-C-SI H3C SecPath F1000-C-SI H3C SecPath F100-A-SI H3C SecBlade FW Cards H3C SecBlade FW Enhanced Cards H3C SecPath U200-A U200-M U200-S H3C SecPath U200-CA U200-CM U200-CS