2 key features – Datatek IPv6 Transformer User Manual User Manual
Page 17
S E C T I O N 2
O V E R V I E W
17
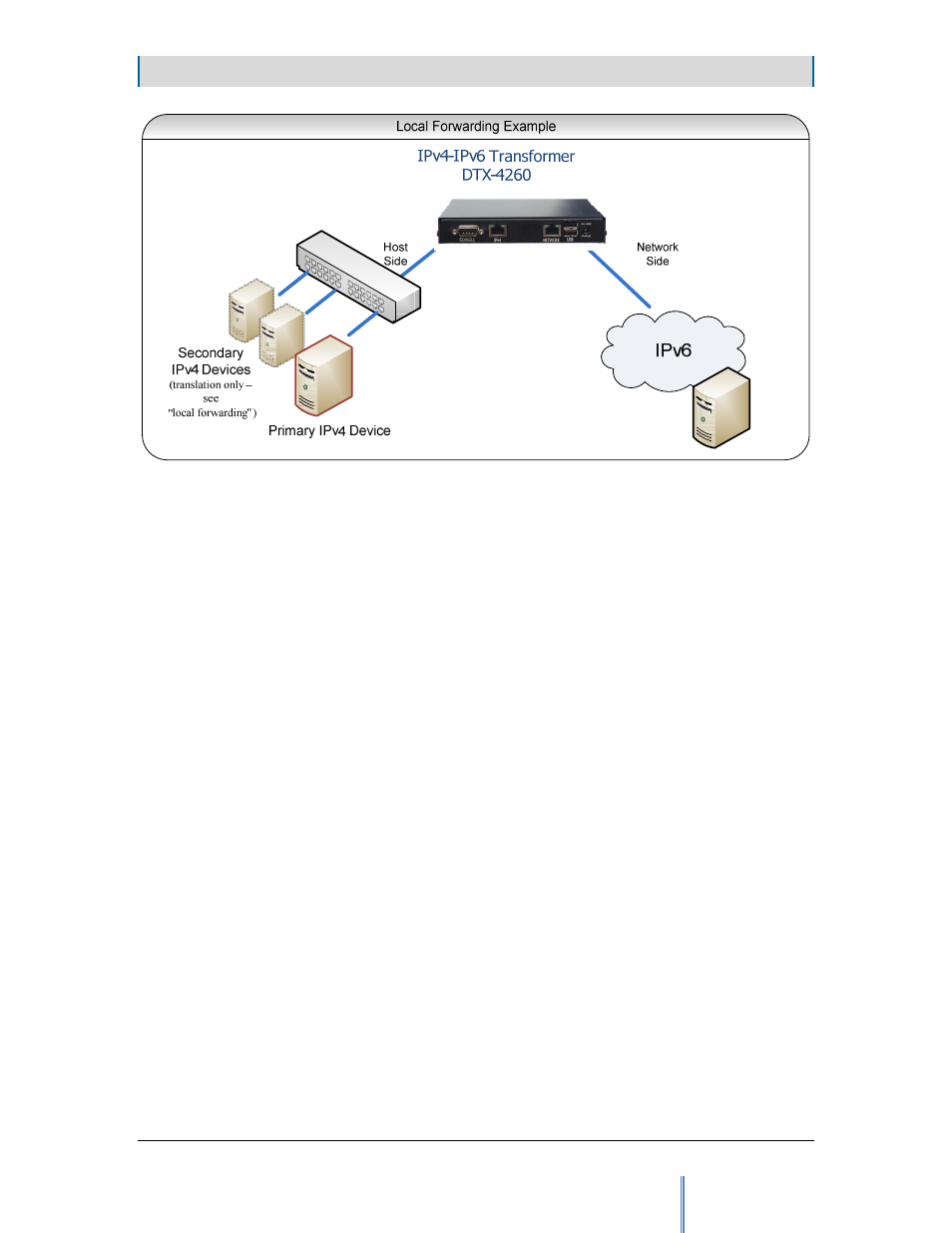
Figure 4. Local Forwarding
2.2 Key Features
Autoconfiguration
The Transformer supports the Stateless Address Autoconfiguration (SLAAC) protocol described
in RFC2462, and an extension to SLAAC for supporting temporary addresses as described in
RFC3041 in configuring the network-side IPv6 address interface.
The Stateless Address Autoconfiguration (SLAAC) process employs the Neighbor Discovery
Protocol (NDP) which includes Router Solicitations/Advertisements and Neighbor
Solicitation/Advertisements. The NDP messages are used to verify that the link local address is
unique on the link. The Router messages are used to discover the network prefix of the
Transformer’s IPv6 link. The prefix is combined with the interface identifier of the link local
address to create a global IPv6 interface address. This address is then configured as the
Transformer’s IPv6/Network interface’s IPv6 address. A proxy IPv6 address is also
autoconfigured for the IPv4 legacy device by using the host-side interface’s MAC address as the
interface identifier for the proxy IPv6 address. The proxy IPv6 address is then bound to the IPv4
address of the legacy device.
The SLAAC process independently supports both the Transformer as an endpoint and the host
as a proxy endpoint.
When temporary addresses are enabled on the Transformer, the interface identifier is a
randomized value that is regenerated periodically and combined with the network prefix that was